Abstract
Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) is the commonest cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) worldwide. Renal transplantation (RTx) is the best therapeutic modality for such patients. First-degree relatives of patients with type 2 DM have high risk of diabetes/pre-diabetes. Parents are often too old to be suitable donors, and siblings/children/spouse are either not suitable/acceptable or do not come forward for organ donation. This leaves deceased donation (DD) as only suitable donors. Data scarcity on DDRTx outcome in diabetic nephropathy (DN) prompted us to review our experience. This retrospective single-center 10-year study was undertaken to evaluate patient/graft survival, graft function, rejection episodes, and mortality in these patients.
Materials and methods
Between January 2001 and March 2011, thirty-five DN–ESRD patients underwent DDRTx in our center following cardiac fitness assessment of recipients. All patients received single-dose rabbit-anti-thymocyte globulin for induction and steroids, calcineurin inhibitor, and mycophenolate mofetil/azathioprine for maintenance immunosuppression. Mean recipient age was 49.66 ± 6.76 years, and 25 were men. Mean donor age was 50 ± 16.45 years, 23 were men.
Results
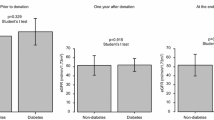
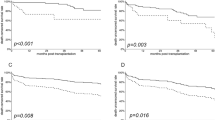
Over a mean follow-up of 2.28 ± 2.59 years, patient and graft survival rates were 68.5% and 88.5%, respectively, with mean SCr of 1.9 ± 0.62 mg/dl. Delayed graft function was observed in 34.3% patients, and 25.7% had biopsy-proven acute rejection; 31.5% patients died, mainly because of infections (22.8%), coronary artery disease (2.86%), and cerebrovascular events (5.7%).
Conclusion
DDRTx in patients with DN has acceptable graft function and patient/graft survival over 10-year follow-up in our center and, therefore, we believe it should be encouraged.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joshi SR, Parikh RM (2007) India-diabetes capital of the world: now heading towards hypertension. J Assoc Physicians India 55:323–324
Modi GK, Jha V (2006) The incidence of end-stage renal disease in India: a population-based study. Kidney Int 70(12):2131–2133 (Epub 2006 Oct 25)
5 year cumulative annual report (2010) CKD registry of India: Indian society of nephrology online resources. Available from: http://www.ckdri.org
Rajapurkar M, Dabhi M (2010) Burden of disease-prevalence and incidence of renal disease in India. Clin Nephrol 74(suppl 1):S9–S12
Friedman EA (2002) Diabetic nephropathy: improving prognosis. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 13(3):281–310
Acharya VN (2011) Diabetic and hypertensive nephropathy in India. J Assoc Physicians India 59:143
Chugh KS (2009) Five decades of Indian nephrology: a personal journey: American. J Kidney Dis 54:753–763 (Epub 2 Sept 2009)
Feroz A, Dabhi M, Gumber M et al (2007) Cadaveric renal transplantation: our experience at the Institute of kidney diseases & research centre, Institute of transplantation sciences, Ahmedabad. Transpl Proc 39:721–722
Ma H, Gong Y, Liu YY, Song J, Tian HM, Chen T et al. (2001) Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes mellitus in the first-degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes in Chengdu (Article in Chinese). Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 42:264–268
Benhamou PY, Marwah T, Balducci F et al (1992) Classification of diabetes in patients with end-stage renal disease: validation of clinical criteria according to fasting plasma C-peptide. Clin Nephrol 38:239–244
American diabetes association expert committee report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus (1997) Diabetes Care 20:1183–1197
Mieghem AV, Fonck C, Coosemans W et al. (2001) Outcome of cadaver kidney transplantation in 23 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nephrol Dial Transpl 16(8):1686–1691
KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease (2007) Am J Kidney Dis 49(2 suppl 2):S12–S154
Biesenbach G, Bodlaj G, Pieringer H, Sedlak M (2011) Clinical versus histological diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy–is renal biopsy required in type 2 diabetic patients with renal disease? QJM. 18 April 2011 (Epub ahead of print) PMID: 21504987
Sharma AM, Weir MR (2011) The role of angiotensin receptor blockers in diabetic nephropathy. Postgrad Med 123(3):109–121
Tervaert TW, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB et al. (2010) Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(4):556
Luan FL, Samaniego M (2010) Transplantation in diabetic kidney failure patients: modalities, outcomes, and clinical management. Semin Dial 23(2):198–205 (Epub 2010 Mar 30)
Reilly JB, Berns JS (2010) Selection and dosing of medications for management of diabetes in patients with advanced kidney disease. Semin Dial 23(2):163–168
Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL et al (1999) Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med 341(23):1725–1730
Locatelli F, Pozzoni P, Del Vecchio L (2004) Renal replacement therapy in patients with diabetes and endstage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(suppl 1):S25–S29
Cosio FG, Hickson LJ, Griffin MD et al (2008) Patient survival and cardiovascular risk after kidney transplantation: the challenge of diabetes. Am J Transpl 8(3):593–599
Witczak BJ, Hartmann A, Jenssen T et al (2006) Routine coronary angiography in diabetic nephropathy patients before transplantation. Am J Transpl 6(10):2403–2408
Ramanathan V, Goral S, Tanriover B et al (2005) Screening asymptomatic diabetic patients for coronary artery disease prior to renal transplantation. Transplantation 79(10):1453–1458
Welsh RC, Cockfield SM, Campbell P, Hervas-Malo M, Gyenes G, Dzavik V (2011) Cardiovascular assessment of diabetic end-stage renal disease patients before renal transplantation. Transplantation 91:213–218
Gang S, Dabhi M, Rajapurkar MM (2007) Ischaemia imaging in type 2 diabetic kidney transplant candidates–is coronary angiography essential? Nephrol Dial Transpl 22:2334–2338 (Epub 5 June 2007)
Friedman EA (1999) Advanced glycation end-products in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transpl 14(suppl 3):1–9
Manske CL, Wang Y, Rector T et al (1992) Coronary revascularisation in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with chronic renal failure. Lancet 340(8826):998–1002
Evans RW, Manninen DL, Garrison LP Jr et al (1985) The quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease. N Engl J Med 312:553–559
Goldfarb-Rumyantzev A, Hurdle JF, Scandling J et al (2005) Duration of end-stage renal disease and kidney transplant outcome. Nephrol Dial Transpl 20(1):167–175
Shoskes DA, Cecka JM (1998) Deleterious effects of delayed graft function in cadaveric renal transplant recipients independent of acute rejection. Transplantation 66(12):1697–1701
Parekh J, Bostrom A, Feng S (2010) Diabetes mellitus: a risk factor for delayed graft function after deceased donor kidney transplantation. Am J Transpl 10(2):298–303
Rao PS, Ojo A (2009) The alphabet soup of kidney transplantation: SCD, DCD, ECD-fundamentals for the practicing nephrologist. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4(11):1827–1831 (Epub 2009 Sep 24)
Jha V, Chugh KS (2002) Post-transplant infections in the tropical countries. Artif Organs 26(9):770–777
Jha V, Chugh S, Chugh KS (2000) Infections in dialysis and transplant patients in tropical countries. Kidney Int 57(suppl 74):S85–S93
Kher V (2002) End-stage renal disease in developing countries. Kidney Int 62(1):350–362
Sakhuja V, Jha V, Varma PP et al (1996) The high incidence of tuberculosis among renal transplant recipients in India. Transplantation 61(2):211–215
Jha V (2010) Post-transplant infections: an ounce of prevention. Indian J Nephrol 20(4):171–178
Shah BR, Hux JE (2003) Quantifying the risk of infectious diseases from people with diabetes. Diabetes Care 26(2):510–513
John GT, Shankar V, Abraham AM, Mukundan U, Thomas PP, Jacob CK (2001) Risk factors for post-transplant tuberculosis. Kidney Int 60(3):1148–1153
Bhowmik D, Dinda AK, Khilnani GC, Mahajan S, Gupta S, Agarwal SK et al (2002) Pulmonary mucormycosis in a diabetic renal transplant patient. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 44(44):275–277
Agrawal V, Gupta RK, Jain M (2005) Invasive fungal infections in renal allograft recipients. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 48(4):448–452
Singh N, Aguado JM, Bonatti H, Forrest G, Gupta KL, Safdar N et al. (2009) Zygomycosis in solid organ transplant recipients: a prospective, matched case-control study to assess risks for disease and outcome. J Infect Dis 200(6):1002–1011
Abraham G, John GT, Shroff S et al (2010) Evolution of renal transplantation in India over the last four decades. NDT Plus 3(2):203–207
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Priya shah, Sengunthar Shobhanarani, and Jyotsna suthar, who contributed to data collection and statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kute, V.B., Godara, S.M., Shah, P.R. et al. Outcome of deceased donor renal transplantation in diabetic nephropathy: a single-center experience from a developing country. Int Urol Nephrol 44, 269–274 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-011-0040-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-011-0040-9