Abstract
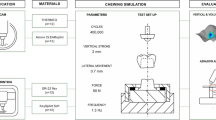
The purpose of this study was to assess the two-body wear of cobalt–chromium (CoCr) samples fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM) in contrast to cast samples and enamel. The following materials were chosen for comparison with SLM-CoCr: a CoCr alloy for use in the lost-wax technique, four gold alloys with different hardness, titanium (grade 1), and human enamel. Seven specimens of diameter 12 mm and thickness 1 mm were produced from each material and polished with emery paper. Al2O3 ceramic balls served as antagonists in the biaxial chewing simulator. Multiple chewing cycles were applied with a static load of 50 N. Wear was analysed laser-optically by the use of cast replicas. Statistical analyses were performed with Kruskal–Wallis test and subsequent post hoc Mann–Whitney U tests at a significance level of 0.05. SLM-CoCr showed less wear than any of the other materials. The difference was statistically significant between SLM-CoCr (vertical loss −54.4 ± 6.9 µm after 300,000 cycles) and cast CoCr (vertical loss −117.2 ± 18.6 µm after 300,000 cycles). Greatest vertical wear was observed for titanium. SLM-CoCr exhibits a great resistance to wear and might represent an alternative for the manufacture of prosthetic restorations even in occlusal loading areas.
Clinical relevance Clinical investigations on wear of SLM-CoCr are needed to assess its in vivo behaviour.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yip, K.H., Smales, R.J., Kaidonis, J.A.: Differential wear of teeth and restorative materials: clinical implications. Int. J. Prosthodont. 17, 350–356 (2004)
Lambrechts, P., Debels, E., Van Landuyt, K., Peumans, M., Van Meerbeek, B.: How to simulate wear? Overview of existing methods. Dent. Mater. 22, 693–701 (2006)
International Organization for Standardization, ISO/TS 14569-2: Dental materials—Guidance on testing of wear—Part 2: Wear by two- and/or three body contact, ICS: 11.060.10, Stage: 90.93 (2014-09-10), 32 pp. (2001)
Beier, U.S., Kapferer, I., Dumfahrt, H.: Clinical long-term evaluation and failure characteristics of 1,335 all-ceramic restorations. Int. J. Prosthodont. 25, 70–78 (2012)
Reitemeier, B., Hansel, K., Kastner, C., Weber, A., Walter, M.H.: A prospective 10-year study of metal ceramic single crowns and fixed dental prosthesis retainers in private practice settings. J. Prosthet. Dent. 109, 149–155 (2013)
Kinsel, R.P., Lin, D.: Retrospective analysis of porcelain failures of metal ceramic crowns and fixed partial dentures supported by 729 implants in 152 patients: patient-specific and implant-specific predictors of ceramic failure. J. Prosthet. Dent. 101, 388–394 (2009)
Faria, A.C., Rodrigues, R.C., Claro, A.P., da Gloria Chiarello de Mattos, M., Ribeiro, R.F.: Wear resistance of experimental titanium alloys for dental applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 4, 1873–1879 (2011)
Quante, K., Ludwig, K., Kern, M.: Marginal and internal fit of metal-ceramic crowns fabricated with a new laser melting technology. Dent. Mater. 24, 1311–1315 (2008)
Castillo-Oyagüe, R., Lynch, C.D., Turrion, A.S., Lopez-Lozano, J.F., Torres-Lagares, D., Suarez-Garcia, M.J.: Misfit and microleakage of implant-supported crown copings obtained by laser sintering and casting techniques, luted with glass-ionomer, resin cements and acrylic/urethane-based agents. J. Dent. 41, 90–96 (2013)
Xu, D., Xiang, N., Wei, B.: The marginal fit of selective laser melting-fabricated metal crowns: an in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 112, 1437–1440 (2014)
Akova, T., Ucar, Y., Tukay, A., Balkaya, M.C., Brantley, W.A.: Comparison of the bond strength of laser-sintered and cast base metal dental alloys to porcelain. Dent. Mater. 24, 1400–1404 (2008)
Wu, L., Zhu, H., Gai, X., Wang, Y.: Evaluation of the mechanical properties and porcelain bond strength of cobalt–chromium dental alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Prosthet. Dent. 111, 51–55 (2014)
Xiang, N., Xin, X.Z., Chen, J., Wei, B.: Metal-ceramic bond strength of Co–Cr alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Dent. 40, 453–457 (2012)
Kilicarslan, M.A., Ozkan, P.: Evaluation of retention of cemented laser-sintered crowns on unmodified straight narrow implant abutments. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 28, 381–387 (2013)
Al Jabbari, Y.S., Koutsoukis, T., Barmpagadaki, X., Zinelis, S.: Metallurgical and interfacial characterization of PFM Co–Cr dental alloys fabricated via casting, milling or selective laser melting. Dent. Mater. 30, e79–e88 (2014)
Takaichi, A., Suyalatu, Nakamoto, T., Joko, N., Nomura, N., Tsutsumi, Y., Migita, S., Doi, H., Kurosu, S., Chiba, A., Wakabayashi, N., Igarashi, Y., Hanawa, T.: Microstructures and mechanical properties of Co–29Cr–6Mo alloy fabricated by selective laser melting process for dental applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 21, 67–76 (2013)
Xin, X.Z., Chen, J., Xiang, N., Wei, B.: Surface properties and corrosion behavior of Co–Cr alloy fabricated with selective laser melting technique. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 67, 983–990 (2013)
Acevedo-Davila, J.L., Lopez, H.F., Cepeda-Rodriguez, F., Rodriguez-Reyes, M., Garcia-Vazquez, F., Hernandez-Garcia, H.M.: Microstructural effects on the wear behavior of a biomedical as-cast Co–27Cr–5Mo–0.25C alloy exposed to pulsed laser melting. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 102, 2008–2016 (2014)
Mehl, A., Gloger, W., Kunzelmann, K.H., Hickel, R.: A new optical 3-D device for the detection of wear. J. Dent. Res. 76, 1799–1807 (1997)
Mair, L.H., Stolarski, T.A., Vowles, R.W., Lloyd, C.H.: Wear: mechanisms, manifestations and measurement. Report of a workshop. J. Dent. 24, 141–148 (1996)
Ohkubo, C., Shimura, I., Aoki, T., Hanatani, S., Hosoi, T., Hattori, M., Oda, Y., Okabe, T.: Wear resistance of experimental Ti–Cu alloys. Biomaterials 24, 3377–3381 (2003)
Chen, G.Z., Fray, D.J., Farthing, T.W.: Cathodic deoxygenation of the alpha case on titanium and alloys in molten calcium chloride. Metall. Mater. Trans. 32, 1041–1052 (2001)
Park, S., Quinn, J.B., Romberg, E., Arola, D.: On the brittleness of enamel and selected dental materials. Dent. Mater. 24, 1477–1485 (2008)
Weatherell, J.A., Robinson, C., Hallsworth, A.S.: Variations in the chemical composition of human enamel. J. Dent. Res. 53, 180–192 (1974)
Hahnel, S., Schultz, S., Trempler, C., Ach, B., Handel, G., Rosentritt, M.: Two-body wear of dental restorative materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 4, 237–244 (2011)
De Boever, J.A., McCall Jr, W.D., Holden, S., Ash Jr, M.M.: Functional occlusal forces: an investigation by telemetry. J. Prosthet. Dent. 40, 326–333 (1978)
Heintze, S.D., Zellweger, D., Zappini, G.: The relationship between physical parameters and wear of dental composites. Wear 263, 1138–1146 (2007)
Stober, T., Lutz, T., Gilde, H., Rammelsberg, P.: Wear of resin denture teeth by two-body contact. Dent. Mater. 22, 243–249 (2006)
Collins, J.A.: Failure of Materials in Mechanical Design: Analysis, Prediction, Prevention, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken (1993)
Lawson, N.C., Janyavula, S., Syklawer, S., McLaren, E.A., Burgess, J.O.: Wear of enamel opposing zirconia and lithium disilicate after adjustment, polishing and glazing. J. Dent. 42, 1586–1591 (2014)
Stober, T., Bermejo, J.L., Rammelsberg, P., Schmitter, M.: Enamel wear caused by monolithic zirconia crowns after 6 months of clinical use. J. Oral Rehabil. 41, 314–322 (2014)
Mundhe, K., Jain, V., Pruthi, G., Shah, N.: Clinical study to evaluate the wear of natural enamel antagonist to zirconia and metal ceramic crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 114, 358–363 (2015)
Chong, B.J., Thangavel, A.K., Rolton, S.B., Guazzato, M., Klineberg, I.J.: Clinical and laboratory surface finishing procedures for zirconia on opposing human enamel wear: a laboratory study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 50, 93–103 (2015)
Stober, T., Dreyhaupt, J., Lehnung, U., Rammelsberg, P.: Occlusal wear of metal-free ceramic-filled polymer crowns after 2 years in service. Int. J. Prosthodont. 21, 161–165 (2008)
Demarco, F.F., Correa, M.B., Cenci, M.S., Moraes, R.R., Opdam, N.J.: Longevity of posterior composite restorations: not only a matter of materials. Dent. Mater. 28, 87–101 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Herbert Gilde for initiating and realizing parts of the investigation. The authors would like to thank Clemens Schmitt, for helping with the laser scanning and performing the SEM images, and Ian Davies, for proofreading the manuscript. This research was made possible by Degudent GmbH by providing the SLM samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwindling, F.S., Seubert, M., Rues, S. et al. Two-Body Wear of CoCr Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting Compared with Different Dental Alloys. Tribol Lett 60, 25 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0601-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0601-7