Abstract
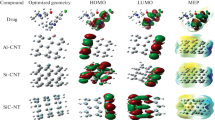
The noncovalent functionalizations of isoniazid (INH) and pyrazinamide (PZA) antitubercular drugs adsorbed onto perfect and N-doped (6,6) and (10,0) single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have been studied using density functional theory (DFT). The binding energies (B.Es), electronic properties, and nature of interaction for the two nanotube model systems have been compared for both periodic and cluster models. The variations in energy values with distance at the DFT/LDA and DFT/GGA levels of calculation can help in correlating the weak noncovalent functionalization governed by the Lennard-Jones type of interactions. The two molecules exhibit a similar pattern of adsorption onto the nanotube sidewall for periodic and cluster models; however, the B.E. values are comparatively higher for the periodic model counterparts. The negative B.E. values suggest the thermodynamic favorability toward the adsorption and presence of N dopant atom facilitates in better drug binding with the tube sidewall. The frontier orbital analysis and global reactivity descriptors before and after functionalization of INH and PZA onto the SWCNTs corresponding to cluster models are compared and the results analyzed. At a theoretical level of understanding through this study we focus that N ad atom doping onto SWCNTs facilitate in enhancing the reactivity of pristine nanotubes toward drug binding thereby modulating its electronic properties and influencing the adsorption.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saha S, Dinadayalane TC, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2012) Open and capped (5,5) armchair SWCNTs: a comparative study of DFT-based reactivity descriptors. Chem Phys Lett 541:85–91
Dinadayalane TC, Leszczynski J (2010) Remarkable diversity of carbon–carbon bonds: structures and properties of fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, and graphene. Struct Chem 21:1155–1169
de Heer WA, Chaelain A, Ugarte D (1995) A carbon nanotube field-emission electron source. Science 270:1179–1180
Terrones M, Ajayan PM, Banhart F, Blase X, Carroll DL, Charlier JC, Czerw R, Foley B, Grobert N, Kamalakaran R, Kohler-Redlich P, Ruhle M, Seeger T, Terrones H (2002) N-doping and coalescence of carbon nanotubes: synthesis and electronic properties. Appl Phys A 74:355–361
Cho JH, Yang SJ, Lee K, Park CR (2011) Si-doping effect on the enhanced hydrogen storage of single walled carbon nanotubes and graphene. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36:12286–12295
Ayala P, Arenal R, Rümmeli M, Rubio A, Pichler T (2010) The doping of carbon nanotubes with nitrogen and their potential applications. Carbon 48:575–586
Saha S, Dinadayalane TC, Murray JS, Leszczynska D, Leszczynski J (2012) Surface reactivity for chlorination on chlorinated (5,5) armchair SWCNT: a computational approach. J Phys Chem C 116:22399–22410
Esrafili MD (2013) Influence of oxygen/sulfur-termination on electronic structure and surface electrostatic potential of (6,0) carbon nanotube: a DFT study. Struct Chem. doi:10.1007/s11224-012-0191-z
Charlier JC, Terrones M, Baxendale M, Meunier V, Zacharia T, Rupesinghe NL, Hsu WK, Grobert N, Terrones H, Amaratunga GAJ (2002) Enhanced electron field emission in B-doped carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett 2:1191–1195
Terrones M, Ajayan PM, Banhart F, Blase X, Carroll DL, Charlier JC, Czerw R, Foley B, Grobert N, Kamalakaran R, Kohler-Redlich P, Rühle M, Seeger T, Terrones H (2002) N-doping and coalescence of carbon nanotubes: synthesis and electronic properties. Appl Phys A 74:355–361
Cruz-Silva E, Barnett ZM, Sumpter BG, Meunier V (2011) Structural, magnetic, and transport properties of substitutionally doped graphene nanoribbons from first principles. Phys Rev B 83:155445
Glerup M, Steinmetz J, Samaille D, Stephan O, Enouz S, Loiseau S, Roth S, Bernier P (2004) Synthesis of N-doped SWNT using the arc-discharge procedure. Chem Phys Lett 387:193–197
Glerup M, Castignolles M, Holzinger M, Hug G, Loiseau A, Bernier P (2003) Synthesis of highly nitrogen-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Commun 20:2542–2543
Castignolles M (2004) Thesis, Université Montpellier II, France
Lee CJ, Lyu SC, Kim HW, Lee JH, Cho KI (2002) Synthesis of bamboo-shaped carbon–nitrogen nanotubes using C2H2–NH3–Fe(CO)5 system. Chem Phys Lett 359:115–120
Jiang K, Schadler LS, Siegel RW, Zhang X, Zhang H, Terrones M (2004) Protein immobilization on carbon nanotubes via a two-step process of diimide-activated amidation. J Mater Chem 14:37–39
Holzinger M, Steinmetz J, Roth S, Glerup M, Graupner R (2005) Purification and functionalisation of nitrogen-doped single-walled carbon nanotubes. AIP Conf Proc 786:211–214
Cui T, Lv R, Huang Z-H, Zhu H, Zhang J, Li Z, Jia Y, Kang F, Wang K, Wu D (2011) Synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon thin films and their applications in solar cells. Carbon 49:5022–5028
Lv R, Cui T, Jun M-S, Zhang Q, Cao A, Su DS, Zhang Z, Yoon S-H, Miyawaki J, Mochida I, Kang F (2011) Open-ended, N-doped carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid nanostructures as high-performance catalyst support. Adv Funct Mater 21:999–1006
Wang Y, Shao YY, Matson DW, Li JH, Lin YH (2010) Nitrogen-doped graphene and its application in electrochemical biosensing. ACS Nano 4:1790–1798
Elias AL et al (2007) Viability studies of pure carbon- and nitrogen-doped nanotubes with Entamoeba histolytica: from amoebicidal to biocompatible structures. Small 3:1723–1729
Carrero-Sanchez JC, Elías AL, Mancilla R, Arrellín G, Terrones H, Laclette JP, Terrones M (2006) Biocompatibility and toxicological studies of carbon nanotubes doped with nitrogen. Nano Lett 6:1609–1616
Singh R, Pantarotto D, Lacerda L, Pastorin G, Klumpp C, Prato M, Bianco A, Kostarelos K (2006) Tissue biodistribution and blood clearance rates of intravenously administered carbon nanotube radiotracers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3357–3362
Muller J, Huaux F, Moreau N, Misson P, Heilier J-F, Delos M, Arras M, Fonseca A, Nagy JB, Lison D (2005) Respiratory toxicity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:221
Yi J-Y, Bernholc J (1993) Atomic structure and doping of microtubules. Phys Rev B 47:1708–1711
Nevidomskyy AH, Czani G, Payne MC (2003) Chemically active substitutional nitrogen impurity in carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev Lett 91:105502-1–105502-4
Saikia N, Deka RC (2012) First principles study on the boron–nitrogen domains segregated within (5,5) and (8,0) single-wall carbon nanotubes: formation energy, electronic structure and reactivity. Comput Theor Chem 996:11–20
Cole ST, Eisenach KD, McMurray DN, Jacobs WR Jr (eds) (2005) Tuberculosis and the tubercle bacillus. ASM Press, Washington
World Health Organization (2011) Global tuberculosis control. World Health Organization, Geneva. ISBN: 978 92 4 156438 0
Scroeder EK, de Souza ON, Santos DS, Blanchard JS, Basso LA (2002) Drugs that inhibit mycolic acid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 3:197–225
Du X, Wang W, Kim R, Yakota H, Nguyen H, Kim SH (2001) Crystal structure and mechanism of catalysis of a pyrazinamidase from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Biochemistry 40:14166–14172
Lemaitre N, Callebaut I, Frenois F, Jarlier V, Sougakoff W (2001) Study of the structure-activity relationships for the pyrazinamidase (PncA) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem J 353:453–458
Vavríková E, Polanc S, Cevar MK, Smrlj JK, Horváti K, Bosze S, Stola ríková J, Imramovský A, Vin sová J (2011) New series of isoniazid hydrazones linked with electron-withdrawing substituents. Eur J Med Chem 46:5902–5909
Maher D, Chaulet P, Spinaci S, Harries A (1997) Treatment of tuberculosis: guidelines for national programmes. World Health Organization, Geneva
Gallo M, Favila A, Glossman-Mitnik D (2007) DFT studies of functionalized carbon nanotubes and fullerenes as nanovectors for drug delivery of antitubercular compounds. Chem Phys Lett 447:105–109
Delley B (1990) An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J Chem Phys 92:508–517
Parr RG, Yang W (1995) Density-functional theory of the electronic structure of molecules. Annu Rev Phys Chem 46:701–728
Geerlings P, De Proft F, Langenaeker W (2003) Conceptual density functional theory. Chem Rev 103:1793–1873
Roy RK, Saha S (2010) Studies of regioselectivity of large molecular systems using DFT-based reactivity descriptors. Annu Rep Prog Chem Sect C 116:118–162
Parr RG, Yang W (1989) Density functional theory of atoms and molecules. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Pauling L (1960) The nature of chemical bond. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Pearson RG (1963) Hard and soft acids and bases. J Am Chem Soc 85:3533–3543
Pearson RG (1997) Chemical hardness: applications from molecules to solids. Wiley, Weinheim
Mulliken RS (1934) Electronic structures of molecules. XI. Electroaffinity, molecular orbitals and dipole moments. J Chem Phys 2:782–793
Chis V, Pirnau A, Jurca T, Vasilescu M, Simon S, Cozar O, David L (2005) Experimental and DFT study of pyrazinamide. Chem Phys 316:153–163
Saikia N, Deka RC (2012) Density functional study on the adsorption of the drug isoniazid onto pristine and B-doped single wall carbon nanotubes. J Mol Model 19(1):215–226. doi:10.1007/s00894-012-1534-9
Saikia N, Rajkhowa S, Deka RC Structure and electronic properties of perfect and Si doped single-wall carbon nanotubes interacting with isoniazid—a density functional and molecular docking study (communicated)
Lin Z, Wang YB (2003) Supramolecular interactions between fullerenes and porphyrins. J Am Chem Soc 125:6072–6073
Improta R, Barone V, Kudin KN, Scusceria GE (2001) Structure and conformational behavior of biopolymers by density functional calculations employing periodic boundary conditions. I. The case of polyglycine, polyalanine, and poly-alpha-aminoisobutyric acid in vacuo. J Am Chem Soc 123:3311–3322
de Leon A, Jalbout AF, Basuik VA (2008) SWNT–amino acid interactions: a theoretical study. Chem Phys Lett 457:185–190
Sun W, Bu Y, Wang Y (2008) Interaction between glycine/glycine radicals and intrinsic/boron-doped (8,0) single-walled carbon nanotubes: a density functional theory study. J Phys Chem B 112:15442–15449
Cao F, Ren W, Ji Y-M, Zhao C (2009) The structural and electronic properties of amine-functionalized boron nitride nanotubes via ammonia plasmas: a density functional theory study. Nanotechnology 20:145703
Wu X, An W, Zeng XC (2006) Chemical functionalization of boron-nitride nanotubes with NH3 and amino functional groups. J Am Chem Soc 128:12001–12006
Shtogun YV, Woods LM, Dovbeshko GI (2007) Adsorption of adenine and thymine and their radicals on single-wall carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 111:18174–18181
Girifalco LA, Hodak M (2002) van der Waals binding energies in graphitic structures. Phys Rev B 65:125404-1–125404-5
Henwood D, David Carey J (2007) Ab initio investigation of molecular hydrogen physisorption on graphene and carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev B 75:245413
Acknowledgments
Nabanita Saikia thanks The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, for the Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) and The Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India for funding the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saikia, N., Deka, R.C. Adsorption of isoniazid and pyrazinamide drug molecules onto nitrogen-doped single-wall carbon nanotubes: an ab initio study. Struct Chem 25, 593–605 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-013-0327-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-013-0327-9