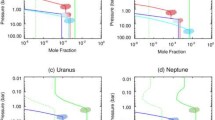
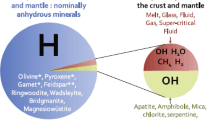
Abstract
Water content and the internal evolution of terrestrial planets and icy bodies are closely linked. The distribution of water in planetary systems is controlled by the temperature structure in the protoplanetary disk and dynamics and migration of planetesimals and planetary embryos. This results in the formation of planetesimals and planetary embryos with a great variety of compositions, water contents and degrees of oxidation. The internal evolution and especially the formation time of planetesimals relative to the timescale of radiogenic heating by short-lived 26Al decay may govern the amount of hydrous silicates and leftover rock–ice mixtures available in the late stages of their evolution. In turn, water content may affect the early internal evolution of the planetesimals and in particular metal-silicate separation processes. Moreover, water content may contribute to an increase of oxygen fugacity and thus affect the concentrations of siderophile elements within the silicate reservoirs of Solar System objects. Finally, the water content strongly influences the differentiation rate of the icy moons, controls their internal evolution and governs the alteration processes occurring in their deep interiors.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.D. Anderson, R.A. Jacobson, T.P. McElrath, W.B. Moore, G. Schubert, P.C. Thomas, Shape, mean radius, gravity field, and interior structure of Callisto. Icarus 153, 157–161 (2001)
J.D. Anderson, E.L. Lau, W.L. Sjogren, G. Schubert, W.B. Moore, Gravitational constraints on the internal structure of Ganymede. Nature 384, 541–543 (1996)
P.J. Armitage, Astrophysics of Planet Formation (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2010), 294 p.
Y. Asahara, T. Kubo, T. Kondo, Phase relations of a carbonaceous chondrite at lower mantle conditions. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 143–144, 421–432 (2004)
X-N. Bai, J.M. Stone, Wind-driven accretion in protoplanetary disks. I. Supression of the magnetorotational instability and launching of the magnetocentrifugal wind. Astrophys. J. 769, 21 (2013)
R.M. Baland et al., Titan’s internal structure inferred from its gravity field, shape, and rotation state. Icarus 237, 29–41 (2014)
A.C. Barr, R.M. Canup, Constraints on gas giant satellite formation from the interior states of partially differentiated satellites. Icarus 198, 163–177 (2008)
A.C. Barr, R.M. Canup, Origin of the Ganymede–Callisto dichotomy by impacts during the Late Heavy Bombardment. Nat. Geosci. 3, 164–167 (2010)
A.C. Barr, G.C. Collins, Tectonic activity on Pluto after the Charon-forming impact. Icarus 246, 146–155 (2015)
C. Béghin, O. Randriamboarison, M. Hamelin, E. Karkoschka, C. Sotin, R.C. Whitten, J.-J. Berthelier, R. Grard, F. Simões, Analytic theory of Titan’s Schumann resonance: constraints on ionospheric conductivity and buried water ocean. Icarus 218(2), 1028–1042 (2012)
P.A. Bland et al., Why aqueous alteration in asteroids was isochemical: high porosity does not equal permeability. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 287, 559–568 (2009)
R. Brett, P.M. Bell, Melting relations in the Fe-rich portion of the system Fe–FeS at 30 kb pressure. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 6, 479–482 (1969)
D. Breuer et al., Iron snow, crystal floats, and inner-core growth: modes of core solidification and implications for dynamos in terrestrial planets and moons. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2, 39 (2015)
A.S. Buono, D. Walker, The Fe-rich liquidus in the Fe–FeS system from 1 bar to 10 GPa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 75, 2072–2087 (2011)
O. Cadek, G. Tobie, T. Van Hoolst, M. Massé, G. Choblet, A. Lefèvre, G. Mitri, R-M. Baland, M. Behounkova, O. Bourgeois, A. Trinh, Enceladus’s internal ocean and ice shell constrained from Cassini gravity, shape, and libration data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43(11), 5653–5660 (2016)
J.C. Castillo-Rogez, J.I. Lunine, Evolution of Titan’s rocky core constrained by Cassini observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L20205 (2010)
J.C. Castillo-Rogez, E. Young, Origin and evolution of volatile-rich asteroids, in Early Differentiation and Consequences for Planets, ed. by L.T. Elkins-Tanton, B. Weiss. Cambridge Planetary Science (2017)
F. Cerantola, N. Walte, D.C. Rubie, Deformation of a crystalline olivine aggregate containing two immiscible liquids: implications for early core-mantle differentiation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 417, 67–77 (2015)
J.E. Chambers, Late-stage planetary accretion including hit-and-run collisions and fragmentation. Icarus 224, 43–56 (2013)
E. Chiang, A.N. Youdin, Forming planetesimals in solar and extrasolar nebula. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 38, 493–522 (2010)
G. Choblet, G. Tobie, C. Sotin, K. Kalousova, O. Grasset, Heat and melt transport in the high-pressure ice mantle of large icy moons. Icarus 285, 252–262 (2017)
L. Chudinovskikh, R. Boehler, Eutectic melting in the system Fe–S to 44 GPa. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 257(1), 97–103 (2007)
A.L. Cochran et al., The composition of comets. Space Sci. Rev. 197(1–4), 9–46 (2015)
A. Coradini, C. Federico, O. Forni, G. Magni, Origin and thermal evolution of icy satellites. Surv. Geophys. 16, 533–591 (1995)
A. Costa, L. Caricchi, N. Bagdassarov, A model for the rheology of particle-bearing suspensions and partially molten rocks. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10, 3010 (2009)
N.B. Cowan, D.S. Abbot, Water cycling between ocean and mantle: super-Earths need not be waterworlds. Astrophys. J. 781(1), 27 (2014).
F.J. Crary, F. Bagenal, Remanent ferromagnetism and the interior structure of Ganymede. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 25757–25773 (1998)
J.W. Crowley, M. Gérault, R.J. O’Connell, On the relative influence of heat and water transport on planetary dynamics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 310, 380–388 (2011)
J.N. Cuzzi, K.J. Zahnle, Material enhancement in protoplanetary nebulae by particle drift through evaporation fronts. Astrophys. J. 614, 490–496 (2004)
T.W. Dahl, D.J. Stevenson, Turbulent mixing of metal and silicate during planet accretion and interpretation of the Hf–W chronometer. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 295, 177–186 (2010)
N. Dauphas, The isotopic nature of the Earth’s accreting material through time. Nature 541, 521–524 (2017)
M.C. de Sanctis et al., Ammoniated phyllosilicates with a likely outer solar system origin on Ceres. Nature 528, 241–244 (2015)
J. de Vries, F. Nimmo, H.J. Melosh, S.A. Jacobson, A. Morbidelli, D.C. Rubie, Impact-induced melting during accretion of the Earth. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 3, 7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-016-0083-8
R. Deguen, M. Landeau, P. Olson, Turbulent metal–silicate mixing, fragmentation, and equilibration in magma oceans. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 391, 274–287 (2014)
T. Encrenaz, Water in the solar system. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 46, 57–87 (2008)
Y. Fei, C.M. Bertka, L.W. Finger, High-pressure iron-sulfur compound, Fe3S2, and melting relations in the Fe–FeS system. Science 275, 1621–1623 (1997)
Y. Fei, J. Li, C.M. Bertka, C.T. Prewitt, Structure type and bulk modulus of Fe3S, a new iron–sulfur compound. Am. Mineral. 85, 1830–1833 (2000)
F.M. Flasar, F. Birch, Energetics of core formation: a correction. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 6101–6103 (1973)
A.J. Friedson, D.J. Stevenson, Viscosity of rock–ice mixtures and applications to the evolution of icy satellites. Icarus 56, 1–14 (1983)
D.J. Frost, C. Liebske, F. Langenhorst, C.A. McCammon, R.G. Trønnes, D.C. Rubie, Experimental evidence for the existence of iron-rich metal in the Earth’s lower mantle. Nature 428, 409–412 (2004)
R.R. Fu, L.T. Elkins-Tanton, The fate of magmas in planetsimals and the retention of primitive chondritic crusts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 390, 128–137 (2014)
R.R. Fu, E. Young, R.C. Greenwood, L.T. Elkins-Tanton, Silicate melting and volatile loss during differentiation in planetesimals, in Early Differentiation and Consequences for Planets, ed. by L.T. Elkins-Tanton, B. Weiss. Cambridge Planetary Science (2017)
P. Gao, D.J. Stevenson, Nonhydrostatic effects and the determination of icy satellites’ moment of inertia. Icarus 226, 1185–1191 (2013)
T.V. Gerya, D.A. Yuen, Robust characteristics method for modelling multiphase visco-elasto-plastic thermo-mechanical problems. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 163, 83–105 (2007)
G.J. Golabek, B. Bourdon, T.V. Gerya, Numerical models of the thermomechanical evolution of planetesimals: application to the acapulcoite-lodranite parent body. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 49, 1083–1099 (2014)
G.J. Golabek, T.V. Gerya, B.J.P. Kaus, R. Ziethe, P.J. Tackley, Rheological controls on the terrestrial core formation mechanism. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10, Q11007 (2009)
O. Grasset et al., Jupiter ICy moons Explorer (JUICE): an ESA mission to orbit Ganymede and to characterise the Jupiter system. Planet. Space Sci. 78, 1–21 (2013)
O. Grasset, C. Sotin, The cooling rate of a liquid shell in Titan’s interior. Icarus 123, 101–112 (1996)
O. Grasset, C. Sotin, F. Deschamps, On the internal structure and dynamics of Titan. Planet. Space Sci. 48, 617–636 (2000)
L. Grossman, A.V. Fedkin, S.B. Simon, Formation of the first oxidized iron in the solar system. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 47, 2160–2169 (2012)
W.M. Grundy et al., Surface compositions across Pluto and Charon. Science 351(6279), aad9189 (2016)
N.P. Hammond, A.C. Barr, E.M. Parmentier, Recent tectonic activity on Pluto driven by phase changes in the ice shell. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43(13), 6775–6782 (2016)
L. Hartmann, in Discs, Planetesimals, and Planets, ed. by F. Garzon, C. Eiroa, D. de Winter, T.J. Mahoney. ASP Conf. Ser., vol. 219 (Astron. Soc. Pac, San Francisco, 2000), p. 95
T.I. Hasegawa, E. Herbst, C.M. Leung, Models of gas–grain chemistry in dense interstellar clouds with complex organic molecules. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 82, 167 (1992)
S.A. Hauck, J.M. Aurnou, A.J. Dombard, Sulfur’s impact on core evolution and magnetic field generation on Ganymede. J. Geophys. Res. 111(E9), E09008 (2006)
V.J. Hillgren, C.K. Gessmann, J. Li, An experimental perspective on the light element in Earth’s core, in Origin of the Earth and Moon, ed. by R.M. Canup, K. Righter (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2000), pp. 245–264
M.M. Hirschmann, Water, melting, and the deep Earth H2O cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 34, 629–653 (2006)
G. Hirth, D.L. Kohlstedt, Water in the oceanic upper mantle: implications for rheology, melt extraction and the evolution of the lithosphere. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 144, 93–108 (1996)
A. Holzheid, Sulphide melt distribution in partially molten silicate aggregates: implications to core formation scenarios in terrestrial planets. Eur. J. Mineral. 25, 267–277 (2013)
A. Holzheid, M.D. Schmitz, T.L. Grove, Textural equilibria of iron sulphide liquids in partly molten silicate aggregates and their relevance to core formation scenarios. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 13555–13567 (2000)
A.W. Howard et al., Planet occurrence within 0.25 AU of solar-type stars from Kepler. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 201(2), 15 (2012)
H.H. Hsieh, D. Jewitt, A population of comets in the main asteroid belt. Science 312, 561–563 (2006)
H.-W. Hsu, F. Postberg, Y. Sekine et al., Ongoing hydrothermal activities within Enceladus. Nature 519, 207–210 (2015)
H. Hussmann et al., Subsurface oceans and deep interiors of medium-sized outer planet satellites and large trans-neptunian objects. Icarus 185, 258–273 (2006)
H. Hussmann, C. Sotin, J.I. Lunine, Interiors and evolution of icy satellites, in Physics of Terrestrial Planets and Moons Treatise on Geophysics, vol. 10, 2nd edn. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2015), pp. 605–635
L. Iess et al., Gravity field, shape, and moment of inertia of Titan. Science 327, 1367–1369 (2010)
L. Iess et al., The tides of Titan. Science 337, 457 (2012)
L. Iess et al., The gravity field and interior structure of Enceladus. Science 344, 78–80 (2014)
S.A. Jacobson, A. Morbidelli, S.N. Raymond, D.P. O’Brien, K.J. Walsh, D.C. Rubie, Highly siderophile elements in the Earth’s mantle as a clock for the Moon-forming impact. Nature 508, 84–87 (2014)
D. Jewitt, B. Yang, N. Haghighipour, Main-belt Comet P/2008 R1 (Garradd). Astron. J. 137, 4313–4321 (2009)
A. Johansen, M.-M. Mac Low, P. Lacerda, M. Bizzarro, Growth of asteroids, planetary embryos, and Kuiper belt objects by chondrule accretion. Sci. Adv. 1, 1500109 (2015)
S. Kamada, H. Terasaki, E. Ohtani, T. Sakai, T. Kikegawa, Y. Ohishi, N. Hirao, N. Sata, T. Kondo, Phase relationships of the Fe–FeS system in conditions up to the Earth’s outer core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 294(1), 94–100 (2010)
S. Karato, V.R. Murthy, Core formation and chemical equilibrium in the Earth—I. Physical considerations. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 100, 61–79 (1997)
J.S. Kargel, Ammonia±water volcanism on icy satellites: phase relations at 1 atmosphere. Icarus 100, 556–574 (1992)
R.F. Katz, M. Spiegelman, C.H. Langmuir, A new parameterization of hydrous mantle melting. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 4 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GC000433
Y. Ke, V.S. Solomatov, Coupled core-mantle thermal evolution of early Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 114, E07004 (2009)
J.D. Kendall, H.J. Melosh, Differentiated planetesimal impacts into a terrestrial magma ocean: fate of the iron core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 448, 24–33 (2016)
J.F. Kerridge, T.E. Bunch, in Asteroids, ed. by T. Gehrels (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1979), pp. 745–764
K.K. Khurana, M.G. Kivelson, D.J. Stevenson, G. Schubert, C.T. Russell, R.J. Walker, S. Joy, C. Polanskey, Induced magnetic fields as evidence for subsurface oceans in Europa and Callisto. Nature 395, 777–780 (1998)
R.L. Kirk, D.J. Stevenson, Thermal evolution of a differentiated Ganymede and implications for surface features. Icarus 69, 91–134 (1987)
M.G. Kivelson et al., Ganymede’s magnetosphere: magnetometer overview. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 19,963–19,972 (1998)
M.G. Kivelson, K.K. Khurana, C.T. Russell, M. Volwerk, R.J. Walker, C. Zimmer, Galileo magnetometer measurements: a stronger case for a subsurface ocean at Europa. Science 289, 1340–1343 (2000)
M. Kivelson, K. Khurana, C. Russell, R. Walker, J. Warnecke, F. Coroniti, C. Polanskey, D. Southwood, G. Schubert, Discovery of Ganymede’s magnetic field by the Galileo spacecraft. Nature 384(6609), 537–541 (1996)
J. Korenaga, Scaling of plate-tectonic convection with pseudoplastic rheology. J. Geophys. Res. 115, B11405 (2010)
K.J. Kossacki, J. Leliwa-Kopystynski, Medium-sized icy satellites: thermal and structural evolution during accretion. Planet. Space Sci. 41, 729–741 (1993)
A.N. Krot et al., Progressive alteration in CV3 chondrites: more evidence for asteroidal alteration. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 33, 1065–1085 (1998)
A.N. Krot, B. Fegley, K. Lodders, Meteoritical and astrophysical constraints on the oxidation state of the solar nebula, in Protostars and Planets IV, ed. by V. Mannings, A.P. Boss, S.S. Russell (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2000), pp. 1019–1054
M. Küppers et al., Localized sources of water vapour on the dwarf planet (1) Ceres. Nature 505, 525–527 (2014)
M. Landeau, P. Olson, R. Deguen, B.H. Hirsh, Core merging and stratification following giant impact. Nat. Geosci. 9, 786–789 (2016)
J.S. Lewis, Satellites of the outer planets: their physical and chemical nature. Icarus 15, 174–185 (1971)
J. Li, Y. Fei, H. Mao, K. Hirose, S. Shieh, Sulfur in the Earth’s inner core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 193(3), 509–514 (2001)
T. Lichtenberg, G.J. Golabek, T.V. Gerya, M.R. Meyer, The effects of short-lived radionuclides and porosity on the early thermo-mechanical evolution of planetesimals. Icarus 274, 350–365 (2016)
C. Liebske, B. Schmickler, H. Terasai, B.T. Poe, A. Suzuki, K. Funakoshi, R. Ando, D.C. Rubie, Viscosity of peridotite liquid up to 13 GPa: implications for magma ocean viscosities. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 240, 589–604 (2005)
U. Malamud, D. Prialnik, Modeling Kuiper belt objects Charon, Orcus and Salacia by means of a new equation of state for porous icy bodies. Icarus 246, 21–36 (2015)
U. Mann, D.J. Frost, D.C. Rubie, Evidence for high-pressure core-mantle differentiation from the metal-silicate partitioning of lithophile and weakly siderophile elements. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 73, 7360–7386 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2009.08.006
G.W. Marcy et al., Masses, radii, and orbits of small Kepler planets: the transition from gaseous to rocky planets. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 210(2), 20 (2014)
T. Matsui, Y. Abe, Evolution of an impact-induced atmosphere and magma ocean on the accreting Earth. Nature 319, 303–305 (1986)
M. Mayor, C. Lovis, N.C. Santos, Doppler spectroscopy as a path to the detection of Earth-like planets. Nature 513, 328–335 (2014)
W.B. McKinnon, Core evolution in the icy Galilean satellites, and the prospects for dynamo-generated magnetic fields. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 28, 1076 (1996)
W.B. McKinnon, Note: mystery of Callisto: is it undifferentiated? Icarus 130, 540–543 (1997)
W.G. Minarik, F.J. Ryerson, E.B. Watson, Textural entrapment of core-forming melts. Science 272, 530–533 (1996)
G. Mitri et al., Shape, topography, gravity anomalies and tidal deformation of Titan. Icarus 236, 169–177 (2014)
J. Monteux, N. Coltice, F. Dubuffet, Y. Ricard, Thermo-mechanical adjustment after impacts during planetary growth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L24201 (2007)
J. Monteux, G. Tobie, G. Choblet, M. Le Feuvre, Can large icy moons accrete undifferentiated? Icarus 237, 377–387 (2014)
J.M. Moore et al., The geology of Pluto and Charon through the eyes of New Horizons. Science 351, 6279 (2016)
G. Morard, D. Andrault, N. Guignot, C. Sanloup, M. Mezouar, S. Petitgirard et al., In situ determination of Fe–Fe3S phase diagram and liquid structural properties up to 65 GPa. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 272, 620–662 (2008)
A. Morbidelli, B. Bitsch, A. Crida, M. Gounelle, T. Guillot, S. Jacobson, A. Johansen, M. Lambrechts, E. Lega, Fossilized condensation lines in the Solar System protoplanetary disk. Icarus 267, 368–376 (2016)
I. Mosqueira, P.R. Estrada, Formation of the regular satellites of giant planets in an extended gaseous nebula. I: subnebula model and accretion of satellites. Icarus 163, 198–231 (2003)
O. Mousis, A. Drouard, P. Vernazza, J.I. Lunine, M. Monnereau, R. Maggiolo, K. Altwegg, H. Balsiger, J.-J. Berthelier, G. Cessateur, J. De Keyser, S.A. Fuselier, S. Gasc, A. Korth, T. Le Deun, U. Mall, B. Marty, H. Rème, M. Rubin, C.-Y. Tzou, J.H. Waite, P. Wurz, Impact of radiogenic heating on the formation conditions of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Astrophys. J. Lett. 839, L4 (2017)
S. Mueller, W.B. McKinnon, Three-layered models of Ganymede and Callisto—compositions, structures, and aspects of evolution. Icarus 76, 437–464 (1988)
K. Nagel, D. Breuer, T. Spohn, A model for the interior structure, evolution, and differentiation of Callisto. Icarus 169, 402–412 (2004)
T. Nakamura, Yamato 793321 CM chondrite: dehydrated regolith material of a hydrous asteroid. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 242, 26–38 (2006)
A. Nakato, T. Nakamura, F. Kitajima, T. Noguchi, Evaluation of dehydration mechanism during heating of hydrous asteroids based on mineralogical and chemical analysis of naturally and experimentally heated CM chondrites. Earth Planets Space 60, 855–864 (2008)
H.B. Niemann et al., Composition of Titan’s lower atmosphere and simple surface volatiles as measured by the Cassini–Huygens probe gas chromatograph mass spectrometer experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 115, E12006 (2010)
F. Nimmo, D. O’Brien, T. Kleine, Tungsten isotopic evolution during late-stage accretion: constraints on Earth–Moon equilibration. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 292, 363–370 (2010)
D.P. O’Brien, K.J. Walsh, A. Morbidelli, S.N. Raymond, A.M. Mandell, Water delivery and giant impacts in the ‘Grand Tack’ scenario. Icarus 239, 74–84 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2014.05.009
E. Ohtani, N. Hirao, T. Kondo, M. Ito, T. Kikegawa, Iron–water reaction at high pressure and temperature, and hydrogen transport into the core. Phys. Chem. Miner. 32, 77–82 (2005)
T. Okuchi, Hydrogen partitioning into molten iron at high pressure: implications for Earth’s core. Science 278, 1781–1784 (1997)
H.St.C. O’Neill, D.C. Rubie, D. Canil, C.A. Geiger, C.R. Ross II., F. Seifert, A.B. Woodland, Ferric iron in the upper mantle and in transition zone assemblages: implications for relative oxygen fugacities in the mantle, in Evolution of the Earth and Planets, ed. by E. Takahashi, R. Jeanloz, D.C. Rubie. Geophysical Monograph, vol. 74, IUGG 14 (1993), pp. 73–88
P. O’Rourke, D.J. Stevenson, Stability of ice/rock mixtures with application to a partially differentiated Titan. Icarus 227, 67–77 (2014)
R.T. Pappalardo, G.C. Collins, J.W. Head III., P. Helfenstein, T.B. McCord, J.M. Moore, L.M. Prockter, P.M. Schenk, J.R. Spencer, Geology of Ganymede, in Jupiter: The Planet, Satellites and Magnetosphere, ed. by F. Bagenal, T.E. Dowling, W.B. McKinnon. Cambridge Planetary Science (2004), pp. 363–396
C.C. Porco et al., Cassini observes the active South Pole of Enceladus. Science 311, 1393–1401 (2006)
F. Postberg et al., Sodium salts in E-ring ice grains from an ocean below the surface of Enceladus. Nature 459, 1098–1101 (2009)
F. Postberg, J. Schmidt, J. Hillier, S. Kempf, R. Srama, A salt-water reservoir as the source of a compositionally stratified plume on Enceladus. Nature 474, 620–622 (2011)
D. Prialnik, G. Sarid, E.D. Rosenberg, R. Merk, Thermal and chemical evolution of comet nuclei and Kuiper belt objects. Space Sci. Rev. 138, 147–164 (2008)
S.N. Raymond, A. Izidoro, Origin of water in the inner Solar System: planetesimals scattered inward during Jupiter and Saturn’s rapid gas accretion. Icarus (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2017.06.030
S.N. Raymond, D.P. O’Brien, A. Morbidelli, N.A. Kaib, Building the terrestrial planets: constrained accretion in the inner Solar System. Icarus 203, 644–662 (2009)
S.N. Raymond, T. Quinn, J.I. Lunine, Making other earths: dynamical simulations of terrestrial planet formation and water delivery. Icarus 168, 1–17 (2004)
Y. Ricard, O. Šrámek, F. Dubuffet, A multi-phase model of runaway core-mantle segregation in planetary embryos. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 284, 144–150 (2009)
G. Robuchon, F. Nimmo, Thermal evolution of Pluto and implications for surface tectonics and a subsurface ocean. Icarus 216(2), 426–439 (2011)
L. Roth et al., Transient water vapor at Europa’s South pole. Science 343, 171 (2014)
D.C. Rubie, D.J. Frost, U. Mann, Y. Asahara, K. Tsuno, F. Nimmo, P. Kegler, A. Holzheid, H. Palme, Heterogeneous accretion, composition and core-mantle differentiation of the Earth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 301, 31–42 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.11.030
D.C. Rubie, S.A. Jacobson, A. Morbidelli, D.P. O’Brien, E.D. Young, J. de Vries, F. Nimmo, H. Palme, D.J. Frost, Accretion and differentiation of the terrestrial planets with implications for the compositions of early-formed Solar System bodies and accretion of water. Icarus 248, 89–108 (2015a)
D.C. Rubie, V. Laurenz, S.A. Jacobson, A. Morbidelli, H. Palme, A.K. Vogel, D.J. Frost, Highly siderophile elements were stripped from Earth’s mantle by iron sulfide segregation. Science 353, 1141–1144 (2016)
D.C. Rubie, H.J. Melosh, J.E. Reid, C. Liebske, K. Righter, Mechanisms of metal-silicate equilibration in the terrestrial magma ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 205, 239–255 (2003)
D.C. Rubie, F. Nimmo, H.J. Melosh, Formation of the Earth’s core, in Treatise on Geophysics, ed. by D. Stevenson. Evolution of the Earth, vol. 9, 2nd edn. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2015b), pp. 43–79
J. Rudge, T. Kleine, B. Bourdon, Broad bounds on Earth’s accretion and core formation constrained by geochemical models. Nat. Geosci. 3, 439–443 (2010)
T. Rushmer, N. Petford, Microsegregation rates of liquid Fe–Ni–S metal in natural silicate-metal systems: a combined experimental and numerical study. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 12 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GC003413
H. Samuel, A re-evaluation of metal diapir breakup and equilibration in terrestrial magma oceans. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 313, 105–114 (2012)
H. Samuel, P.J. Tackley, M. Evonuk, Heat partitioning in terrestrial planets during core formation by negative diapirism. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 290, 13–19 (2010)
J. Saur et al., The search for a subsurface ocean in Ganymede with Hubble Space Telescope observations of its auroral ovals. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120 (2015)
L. Schaefer, D. Sasselov, The persistence of oceans on Earth-like planets: insights from the deep-water cycle. Astrophys. J. 801(1), 40 (2015)
A. Scheinberg, R.R. Fu, L.T. Elkins-Tanton, B.P. Weiss, Asteroid differentiation: melting and large-scale structure, in Asteroids IV, ed. by P. Michel, F.E. DeMeo, W.F. Bottke (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2015), pp. 533–552
M. Schönbächler, R.W. Carlson, M.F. Horan, T.D. Mock, E.H. Hauri, Heterogeneous accretion and the moderately volatile element budget of Earth. Science 328, 884–887 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1186239
G. Schubert, H. Hussmann, V. Lainey, D.L. Matson, W.B. McKinnon, F. Sohl, C. Sotin, G. Tobie, D. Turrini, T. Van Hoolst, Evolution of icy satellites. Space Sci. Rev. 153(1), 447–484 (2010)
G. Schubert, T. Spohn, R.T. Reynolds, Thermal histories, compositions and internal structures of the moons of the solar system, in Satellites, ed. by J.A. Burns, M.S. Matthews (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1986), pp. 224–292
G. Schubert, D.J. Stevenson, K. Ellsworth, Internal structures of the Galilean satellites. Icarus 47, 46–59 (1981)
H.P. Scott, Q. Williams, F.J. Ryerson, Experimental constraints on the chemical evolution of large icy satellites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 203, 399–412 (2002)
Y. Sekine et al., High-temperature water–rock interactions and hydrothermal environments in the chondrite-like core of Enceladus. Nat. Commun. 6, 8604 (2015)
Y. Sekine, H. Genda, S. Kamata, T. Funatsu, The Charon-forming giant impact as a source of Pluto’s dark equatorial regions. Nat. Astron. 1, 0031 (2017)
N.I. Shakura, R.A. Sunyaev, Black holes in binary systems. Observational appearance. Astron. Astrophys. 24, 337–355 (1973)
Z.D. Sharp, F.M. McCubbin, C.K. Shearer, A hydrogen-based oxidation mechanism relevant to planetary formation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 380, 88–97 (2013)
Y. Shibazaki, E. Ohtani, H. Terasaki, A. Suzuki, K. Funakoshi, Hydrogen partitioning between iron and ringwoodite: implications for water transport into the Martian core. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 287, 463–470 (2009)
J.B. Simon, P.J. Armitage, R. Li, A.N. Youdin, The mass and size distribution of planetesimals formed by the streaming instability. I. The role of self-gravity. Astrophys. J. 822, 55 (2016)
F. Sohl et al., Subsurface water oceans on icy satellites: chemical composition and exchange processes. Space Sci. Rev. 153, 485–510 (2010)
V.S. Solomatov, Magma oceans and primordial mantle differentiation, in Treatise on Geophysics, 2nd edn. (2015), pp. 81–104
C. Sotin, G. Mitri, N. Rappaport, G. Schubert, D. Stevenson, in Titan from Cassini/Huygens, ed. by R.H. Brown, J.P. Lebreton, J.H. Waite (2009a), pp. 61–73
C. Sotin, G. Tobie, J. Wahr, W.B. McKinnon, in Tides and Tidal Heating on Europa, ed. by R. Pappalardo et al., Space Science Series (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2009b), pp. 85–117
S.W. Squyres, R.T. Raynolds, A.L. Summers, F. Shung, Accretional heating of the satelites of Saturn and Uranus. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8779–8794 (1988)
D.J. Stevenson, Fluid dynamics of core formation, in The Origin of the Earth, ed. by H.E. Newsom, J.H. Jones (Oxford University Press, London, 1990), pp. 231–249
R. Tajeddine, N. Rambaux, V. Lainey, S. Charnoz, A. Richard, A. Rivoldini, B. Noyelles, Constraints on Mimas’ interior from Cassini ISS libration measurements. Science 346(6207), 322–324 (2014)
H. Terasaki, D.J. Frost, D.C. Rubie, F. Langenhorst, The effect of oxygen and sulphur on the dihedral angle between Fe–O–S melt and silicate minerals at high pressure: implications for Martian core formation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 232, 379–392 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.01.030
H. Terasaki, D.J. Frost, D.C. Rubie, F. Langenhorst, Percolative core formation in planetesimals. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 273, 132–137 (2008)
P.C. Thomas et al., Enceladus’s measured physical libration requires a global subsurface ocean. Icarus 264, 37–47 (2016)
G. Tobie, J.I. Lunine, J. Monteux, O. Mousis, F. Nimmo, The origin and evolution of Titan, in: Titan: Surface, Atmosphere and Magnetosphere, ed. by I. Mueller-Wodarg, C. Griffith, T. Cravens, E. Lellouch (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2013)
K.A. Todd, H.C. Watson, T. Yu, Y. Wang, The effects of shear deformation on planetesimal core segregation: results from in-situ X-ray micro-tomography. Am. Mineral. 101, 1996–2004 (2016)
T.M. Usselman, Experimental approach to the state of the core. Part I. The liquidus relations of the Fe-rich portion of the Fe–Ni–S system. Am. J. Sci. 275, 278–290 (1975)
S. Vance, J.M. Brown, Thermodynamic properties of aqueous MgSO4 to 800 MPa at temperatures from −20 to \(100\,{}^{\circ}\)C and concentrations to 25 mol kg−1 from sound speeds, with applications to icy world oceans. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 110, 176–189 (2013)
N. von Bargen, H.S. Waff, Permeabilities, interfacial areas and curvatures of partially molten systems: results of numerical computations of equilibrium microstructures. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 9261–9276 (1986)
J.-B. Wacheul, M. Le Bars, J. Monteux, J.M. Aurnou, Laboratory experiments on the breakup of liquid metal diapirs. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 403, 236–245 (2014)
J. Wade, B.J. Wood, Core formation and the oxidation state of the Earth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 236, 78–95 (2005)
K.J. Walsh, A. Morbidelli, S.N. Raymond, D.P. O’Brien, A.M. Mandell, A low mass for Mars from Jupiter’s early gas-driven migration. Nature 475, 206–209 (2011)
M.J. Walter, E. Cottrell, Assessing uncertainty in geochemical models for core formation in Earth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 365, 165–176 (2013)
K. Willacy, H.H. Klahr, T.J. Millar, Th. Henning, Gas and grain chemistry in a protoplanetary disk. Astron. Astrophys. 338, 995–1005 (1998)
B.J. Wood, M.J. Walter, J. Wade, Accretion of the Earth and segregation of its core. Nature 441, 825–833 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04763
T. Yoshino, M.J. Walter, T. Katsura, Core formation in planetesimals triggered by permeable flow. Nature 422, 154–157 (2003)
E.D. Young, The hydrology of carbonaceous chondrite parent bodies and the evolution of planet progenitors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 359, 2095–2110 (2001)
E.D. Young, R.D. Ash, P. England, D. Rumble III, Fluid flow in chondrite parent bodies: deciphering the compositions of planetesimals. Science 286, 1331–1335 (1999)
E. Young, K. Zhang, G. Schubert, Conditions for pore water convection within carbonaceous chondrite parent bodies—implications for planetesimal size and heat production. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 213, 249–259 (2003)
K. Zhang, K.M. Pontoppidan, C. Salyk, G.A. Blake, Evidence for a snow line beyond the transitional radius in the TW Hya protoplanetary disk. Astrophys. J. 766, 82 (2013)
M.E. Zolensky, W.L. Bourcier, J.L. Gooding, Aqueous alteration on the hydrous asteroids: results of EQ3/6 computer simulations. Icarus 78, 411–425 (1989)
M.Y. Zolotov, J.S. Kargel, On the composition of Europa’s icy shell, ocean and underlying rocks, in Europa, ed. by R. Pappalardo, W.B. McKinnon, K. Khurana (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2009), pp. 431–457
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Elkins-Tanton, A. Morbidelli and two anonymous reviewers for detailed and thoughtful comments that helped to improve the manuscript. D.C.R. was supported by the European Research Council Advanced Grant “ACCRETE” (contract number 290568) and additional support was provided by the German Science Foundation (DFG) Priority Programme SPP1833 “Building a Habitable Earth” (Ru 1323/10-1). J.M. was funded by the Auvergne Fellowship program. This is Laboratory of Excellence ClerVolc contribution no. 283. G.J.G. thanks Taras Gerya for providing the code I2MART. G.T. acknowledges support from the project ANR OASIS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Delivery of Water to Protoplanets, Planets and Satellites
Edited by Michel Blanc, Allessandro Morbidelli, Yann Alibert, Lindy Elkins-Tanton, Paul Estrada, Keiko Hamano, Helmut Lammer, Sean Raymond and Maria Schönbächler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteux, J., Golabek, G.J., Rubie, D.C. et al. Water and the Interior Structure of Terrestrial Planets and Icy Bodies. Space Sci Rev 214, 39 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-018-0473-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-018-0473-x