Abstract
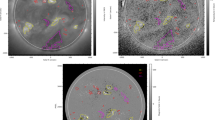
We perform the detailed imaging and spectroscopic analysis of two coronal bright points (CBPs). These CBPs are dominated by bright dots or elongated bright features. Their rapid temporal variations lead to a continuous change in their overall morphology at chromospheric and transition-region (TR) temperatures. A 3D potential magnetic field extrapolation predicts the dominance of magnetic loops in the extent of both CBPs, which are clearly visible at the Si iv 1393.75 Å line formation temperature. Short, low-lying magnetic loops or loop segments are the integral parts of these CBPs at TR temperature. A correlation between the various parameters of Mg ii resonance lines (e.g. intensity, Doppler velocity, velocity gradient) is present in the region of magnetic loops or loop segments. However, a quiet-Sun (QS) region does not show any correlation. Doppler velocities as well as the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of these lines are very prominent in the magnetic loops and loop segments compared to the Doppler velocities and FWHM in the QS region. Higher red-shifts and FWHM at TR temperatures are directly related to the dominance of the energy release process in these regions in the framework of the nanoflare model. A magnetogram from the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) onboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) reveals the existence of two opposite magnetic polarities in the extent of both CBPs, which is a very well established result. We find that one CBP is formed by the convergence of two opposite magnetic polarities, while the other is triggered by the emergence of a new magnetic field prior to the onset of this CBP.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brekke, P., Hassler, D.M., Wilhelm, K.: 1997, Doppler shifts in the quiet-Sun transition region and corona observed with SUMER on SOHO. Solar Phys. 175, 349. DOI .
Brown, D.S., Parnell, C.E., Deluca, E.E., Golub, L., McMullen, R.A.: 2001, The magnetic structure of a coronal X-ray bright point. Solar Phys. 201, 305. DOI .
Bruni, D.: 2006, Proquest Dissertations and Theses 2006. The Univ. of Alabama, Huntsville.
Chandrashekhar, K., Krishna Prasad, S., Banerjee, D., Ravindra, B., Seaton, D.B.: 2013, Dynamics of coronal bright points as seen by Sun Watcher using Active Pixel system detector and image processing (SWAP), Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA), and Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI). Solar Phys. 286, 125. DOI .
Dadashi, N., Teriaca, L., Solanki, S.K.: 2011, The quiet Sun average Doppler shift of coronal lines up to 2 MK. Astron. Astrophys. 534, A90. DOI .
Dadashi, N., Teriaca, L., Tripathi, D., Solanki, S.K., Wiegelmann, T.: 2012, Doppler shift of hot coronal lines in a moss area of an active region. Astron. Astrophys. 548, A115. DOI .
De Pontieu, B., Title, A.M., Lemen, J.R., Kushner, G.D., Akin, D.J., Allard, B., Berger, T., Boerner, P., Cheung, M., Chou, C., et al.: 2014, The Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS). Solar Phys. 289, 2733. DOI .
Doschek, G.A., Landi, E., Warren, H.P., Harra, L.K.: 2010, Bright points and jets in polar coronal holes observed by the Extreme-ultraviolet Imaging Spectrometer on Hinode. Astrophys. J. 710, 1806. DOI .
Dowdy, J.F. Jr.: 1993, Observational evidence for hotter transition region loops within the supergranular network. Astrophys. J. 411, 406. DOI .
Gary, G.A.: 1996, Potential field extrapolation using three components of a solar vector magnetogram with a finite field of view. Solar Phys. 163, 43. DOI .
Golub, L., Krieger, A., Simon, R., Vaiana, G., Timothy, A.F.: 1975a, Temporal and spatial properties of coronal bright points. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 7, 350. ADS .
Golub, L., Kriegher, A.S., Silk, J.K., Timothy, A.F., Vaiana, G.S.: 1975b, Time variations of solar X-ray bright points. In: Kane, S.R. (ed.) Solar Gamma-, X-, and EUV Radiation, IAU Symp. 68, 23. ADS .
Golub, L., Krieger, A.S., Vaiana, G.S.: 1976, Distribution of lifetimes for coronal soft X-ray bright points. Solar Phys. 49, 79. DOI .
Golub, L., Krieger, A.S., Harvey, J.W., Vaiana, G.S.: 1977, Magnetic properties of X-ray bright points. Solar Phys. 53, 111. DOI .
Golub, L.: 1980, X-ray bright points and the solar cycle. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 297, 595. DOI .
Golub, L., Bookbinder, J., Deluca, E., Karovska, M., Warren, H., Schrijver, C.J., Shine, R., Tarbell, T., Title, A., Wolfson, J., Handy, B., Kankelborg, C.: 1999, A new view of the solar corona from the transition region and coronal explorer (TRACE). Phys. Plasmas 6, 2205. DOI .
Habbal, S.R., Withbroe, G.L.: 1981, Spatial and temporal variations of EUV coronal bright points. Solar Phys. 69, 77. DOI .
Habbal, S.R., Withbroe, G.L., Dowdy, J.F. Jr.: 1990, A comparison between bright points in a coronal hole and a quiet-Sun region. Astrophys. J. 352, 333. DOI .
Habbal, S.R.: 1992, Coronal energy distribution and X-ray activity in the small scale magnetic field of the quiet Sun. Ann. Geophys. 10(1 – 2), 34. ADS .
Handy, B.N., Schrijver, C.J.: 2001, On the evolution of the solar photospheric and coronal magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 547, 1100. DOI .
Hansteen, V.: 1993, A new interpretation of the redshift observed in optically thin transition region lines. Astrophys. J. 402, 741. DOI .
Hansteen, V., De Pontieu, B., Carlsson, M., Lemen, J., Title, A., Boerner, P., Hurlburt, N., Tarbell, T.D., Wuelser, J.P., Pereira, T.M.D., De Luca, E.E., Golub, L., McKillop, S., Reeves, K., Saar, S., Testa, P., Tian, H., Kankelborg, C., Jaeggli, S., Kleint, L., Martínez-Sykora, J.: 2014, The unresolved fine structure resolved: IRIS observations of the solar transition region. Science 346(6207), 1255757. DOI .
Harvey, K.L.: 1985, The relationship between coronal bright points as seen in He I Lambda 10830 and the evolution of the photospheric network magnetic fields. Aust. J. Phys. 38, 875. DOI .
Huang, Z., Madjarska, M.S., Doyle, J.G., Lamb, D.A.: 2012, Coronal hole boundaries at small scales. IV. SOT view. Magnetic field properties of small-scale transient brightenings in coronal holes. Astron. Astrophys. 548, A62. DOI .
Huang, Z., Xia, L., Li, B., Madjarska, M.S.: 2015, Cool transition region loops observed by the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. Astrophys. J. 810, 46. DOI .
Kayshap, P., Banerjee, D., Srivastava, A.K.: 2015, Diagnostics of a Coronal Hole and the adjacent Quiet Sun by the Hinode/EUV Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). Solar Phys. 290, 2889. DOI .
Krieger, A.S., Vaiana, G.S., van Speybroeck, L.P.: 1971, The X-Ray Corona and the Photospheric Magnetic Field. In: Solar Magnetic Fields, IAU Symp. 43, 397. ADS .
Leenaarts, J., Pereira, T.M.D., Carlsson, M., Uitenbroek, H., De Pontieu, B.: 2013, The formation of IRIS diagnostics. II. The formation of the Mg II h & k lines in the solar atmosphere. Astrophys. J. 772, 90. DOI .
Lemen, J.R., Title, A.M., Akin, D.J., Boerner, P.F., Chou, C., Drake, J.F., et al.: 2012, The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 17. DOI .
Madjarska, M.S., Doyle, J.G., Teriaca, L., Banerjee, D.: 2003, An EUV bright point as seen by SUMER, CDS, MDI and EIT on-board SoHO. Astron. Astrophys. 398, 775. DOI .
Madjarska, M.S., Huang, Z., Doyle, J.G., Subramanian, S.: 2012, Coronal hole boundaries evolution at small scales. III. EIS and SUMER views. Astron. Astrophys. 545, A67. DOI .
McIntosh, S.W.: 2007, On the mass and energy loading of extreme-UV bright points. Astrophys. J. 670, 1401. DOI .
Moses, D., Cook, J.W., Bartoe, J.-D.F., Brueckner, G.E., Dere, K.P., Webb, D.F., Davis, J.M., Harvey, J.W., Recely, F., Martin, S.F., Zirin, H.: 1994, Solar fine scale structures in the corona, transition region, and lower atmosphere. Astrophys. J. 430, 913. DOI .
Mou, C., Huang, Z., Xia, L., Madjarska, M.S., Li, B., Fu, H., Jiao, F., Hou, Z.: 2016, Magnetic flux supplement to coronal bright points. Astrophys. J. 818, 9. DOI .
Orange, N.B., Oluseyi, H.M., Chesny, D.L., Patel, M., Hesterly, K., Preuss, L., Neira, C., Turner, N.E.: 2014, Comparative analysis of a transition region bright point with a blinker and coronal bright point using multiple EIS emission lines orange. Solar Phys. 289, 1557. DOI .
Peter, H., Judge, P.G.: 1999, On the Doppler shifts of solar ultraviolet emission lines. Astrophys. J. 522, 1148. DOI .
Pereira, T.M.D., Leenaarts, J., De Pontieu, B., Carlsson, M., Uitenbroek, H.: 2013, The formation of IRIS diagnostics. III. Near-ultraviolet spectra and images. Astrophys. J. 778, 143. DOI .
Priest, E.R., Parnell, C.E., Martin, S.F.: 1994, A converging flux model of an X-ray bright point and an associated canceling magnetic feature. Astrophys. J. 427, 459. DOI .
Pérez-Suárez, D., Maclean, R.C., Doyle, J.G., Madjarska, M.S.: 2008, The structure and dynamics of a bright point as seen with Hinode, SoHO and TRACE. Astron. Astrophys. 492, 575. DOI .
Rathore, B., Carlsson, M., Leenaarts, J., De Pontieu, B.: 2015, The formation of IRIS diagnostics. VI. The diagnostic potential of the C II lines at 133.5 nm in the solar atmosphere. Astrophys. J. 811, 81. DOI .
Rudenko, G.V.: 2001, A constructing method for a self-consistent three-dimensional solution of the magnetohydrostatic equations using full-disk magnetogram data. Solar Phys. 198, 5. DOI .
Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Golub, L.: 1979, Rapid changes in the fine structure of a coronal ‘bright point’ and a small coronal ‘active region’. Solar Phys. 63, 119. DOI .
Teriaca, L., Doyle, J.G., Erdélyi, R., Sarro, L.M.: 1999, New insight into transition region dynamics via SUMER observations and numerical modeling. Astron. Astrophys. 352, L99. ADS .
Testa, P., De Pontieu, B., Allred, J., Carlsson, M., Reale, F., Daw, A., et al.: 2014, Evidence of nonthermal particles in coronal loops heated impulsively by nanoflares. Science 346, 1255724. DOI .
Wang, X., McIntosh, S.W., Curdt, W., Tian, H., Peter, H., Xia, L.-D.: 2013, Temperature dependence of ultraviolet line parameters in network and internetwork regions of the quiet sun and coronal holes. Astron. Astrophys. 557, A126. DOI
Webb, D.F.: 1986, Small-scale coronal structure, part 3. NASA CP-2442, 329. ADS .
Webb, D.F., Martin, S.F., Moses, D., Harvey, J.W.: 1993, The correspondence between X-ray bright points and evolving magnetic features in the quiet Sun. Solar Phys. 144, 15. DOI .
Vaiana, G.S., Davis, J.M., Giacconi, R., Krieger, A.S., Silk, J.K., Timothy, A.F., Zombeck, M.: 1973, X-ray observations of characteristic structures and time variations from the solar corona: preliminary results from SKYLAB. Astrophys. J. Lett. 185, L47. DOI .
Young, P.R., O’Dwyer, B., Mason, H.E.: 2012, Velocity measurements for a solar active region Fan loop from Hinode/EIS Observations. Astrophys. J. 744, 14. DOI .
Zhang, J., Kundu, M.R., White, S.M.: 2001, Spatial distribution and temporal evolution of coronal bright points. Solar Phys. 198, 347. DOI .
Zhao, J., Schmieder, B., Li, H., Pariat, E., Zhu, X., Feng, L., et al.: 2017, Observational evidence of magnetic reconnection for brightenings and transition region arcades in IRIS observations. Astrophys. J. 836, 52. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge an anonymous referee for constructive comments that improved the paper substantially. P.K is financially supported by the project from the Polish National Foundation (NCN) Grant no. 2014/15/B/ST9/0010. IRIS is a NASA small explorer mission developed and operated by LMSAL with mission operations executed at NASA Ames Research center and major contributions to downlink communications funded by ESA and the Norwegian Space Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kayshap, P., Dwivedi, B.N. Diagnostics of Coronal Bright Points using IRIS, AIA, and HMI Observations. Sol Phys 292, 108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1132-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-017-1132-1