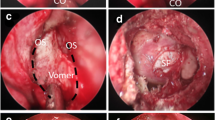
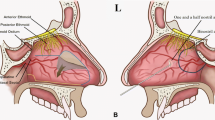
Abstract
Purpose
To report the results of a consecutive series of patients who underwent an endoscopic endonasal approach (EEA) for resection of a pituitary adenoma and compare them to previous series of microscopic and endoscopic approaches.
Methods
A retrospective review of clinical and radiographic outcomes of a consecutive series of patients operated at our center between 2002 and 2011 was performed.
Results
555 patients underwent an EEA for removal of a pituitary adenoma. The mean follow up was 3.1 years (range 3 months to 9.5 years); 36 were lost to follow up. Ninety-one (17.5 %) harbored recurrent adenomas. An expanded approach to reach the supra-, para- and infra-sellar spaces was employed in 290 patients (55.9 %). Reconstruction with a nasal septal flap was used in 238 cases (65.6 %). The rate of gross total resection was 65.3 % in the 359 patients with non-functioning adenomas. The remission rates with EEA alone were 82.5 % in the 57 ACTH-secreting adenomas, 65.3 % in the 49 GH-secreting adenomas and 54.7 % in the 53 prolactinomas. Of the 237 patients presenting with visual loss, 190 (80.2 %) improved or normalized, 41 (17.3 %) remained unchanged and 4 (1.7 %) experienced transient visual deterioration due to postoperative apoplexy. In addition, no patient without preexisting visual loss suffered new visual decline. The overall post-operative CSF leak rate was 5 % and this decreased to 2.9 % after the introduction of reconstruction with the naso-septal flap. Two patients (0.3 %) had an ICA injury.
Conclusions
The EEA is a safe and effective way to surgically approach pituitary adenomas, particularly in recurrent tumors, those with supra-sellar extension or cavernous sinus invasion. The remission and complication rates are comparable or favorable compared with those reported in previous series of microscopic and endoscopic approaches.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guiot G, Rougerie J, Fourestier M et al (1963) Explorations endoscopiques intracraniennes. Presse Med 71:1225–1228
Jho HD, Carrau RL (1997) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: experience with 50 patients. J Neurosurg 87(1):44–51
Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A, Gardner P, Carrau RL (2005) Expanded endonasal approach: the rostrocaudal axis. Part I. Crista galli to the sella turcica. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E3
Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A, Gardner P, Carrau RL (2005) Expanded endonasal approach: the rostrocaudal axis. Part II. Posterior clinoids to the foramen magnum. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E4
Kassam AB, Gardner P, Snyderman C, Mintz A, Carrau R (2005) Expanded endonasal approach: fully endoscopic, completely trans- nasal approach to the middle third of the clivus, petrous bone, middle cranial fossa, and infratemporal fossa. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E6
Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Colao A, de Divitiis E (2002) Surgical complications associated with the endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas. J Neurosurg 97(2):293–298
Frank G, Pasquini E, Farneti G, Mazzatenta D, Sciarretta V, Grasso V, Faustini Faustini M (2006) The endoscopic versus the traditional approach in pituitary surgery. Neuroendocrinology 83:240–248
Dehdashti AR, Ganna A, Karabatsou K, Gentili F (2008) Pure endoscopic endonasal approach for pituitary adenomas: early surgical results in 200 patients and comparison with previous microsurgical series. Neurosurgery 62(5):1006–1015 (discussion 1015-7)
Gondim JA, Schops M, de Almeida JP, de Albuquerque LA, Gomes E, Ferraz T, Barroso FA (2010) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: surgical results of 228 pituitary adenomas treated in a pituitary center. Pituitary 13(1):68–77 (Epub 2009 Aug 21)
Hofstetter CP, Shin BJ, Mubita L, Huang C, Anand VK, Boockvar JA, Schwartz TH (2011) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery for functional pituitary adenomas. Neurosurg Focus 30(4):E10
Alahmadi H, Dehdashti AR, Gentili F (2012) Endoscopic endonasal surgery in recurrent and residual pituitary adenomas after microscopic resection. World Neurosurg 77(3–4):540–547
Powell M (2009) Microscopic and endoscopic pituitary surgery. Acta Neurochir 151:723–728
Giustina A, Chanson P, Bronstein MD, Klibanski A, Lamberts S, Casanueva FF, Trainer P, Ghigo E, Ho K, Melmed S (2010) Acromegaly consensus group. A consensus on criteria for cure of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:3141–3148
Knosp E, Steiner E, Kitz K, Matula C (1993) Pituitary adenomas with invasion of the cavernous sinus space: a magnetic resonance imaging classification compared with surgical findings. Neurosurgery 33(4):610–617
Hadad G, Bassagasteguy L, Carrau RL, Mataza JC, Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A (2006) A novel reconstructive technique after endoscopic expanded endonasal approaches: vascular pedicle nasoseptal flap. Laryngoscope 116(10):1882–1886
Ebersold MJ, Quast LM, Laws ER Jr, Scheithauer B, Randall RV (1986) Long-term results in transsphenoidal removal of nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. J Neurosurg 64:713–719
Zada G, Kelly DF, Cohan P, Wang C, Swerdloff R (2003) Endonasal transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas and other sellar lesions: an assessment of efficacy, safety and patients impressions. J Neurosurg 98:350–358
Mortini P, Losa M, Barzaghi R, Boari N, Giovanelli M (2005) Results of transsphenoidal surgery in a large series of patients with pituitary adenoma. Neurosurgery 56(6):1222–1233
Yap LB, Turner HE, Adams CB, Wass JA (2002) Undetectable postoperative cortisol does not always predict long-term remission in Cushing’s disease: a single centre audit. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56:25–31
Hammer GD, Tyrrell JB, Lamborn KR, Applebury CB, Hannegan ET, Bell S, Rahl R, Lu A, Wilson CB (2004) Transsphenoidal microsurgery for Cushing’s disease: initial outcome and long-term results. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:6348–6357
Freda PU, Wardlaw SL, Post KD (1998) Long-term endocrinological follow-up evaluation in 115 patients who underwent transsphenoidal surgery for acromegaly. J Neurosurg 89:353–358
Kreutzer J, Vance ML, Lopes MB, Laws ER Jr (2001) Surgical management of GH-secreting pituitary adenomas: an outcome study using modern remission criteria. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4072–4077
Nomikos P, Buchfelder M, Fahlbusch R (2005) The outcome of surgery in 668 patients with acromegaly using current criteria of biochemical ‘cure’. Eur J Endocrinol 152:379–387
Tyrrel JB, Lamborn KR, Hannegan LT, Applebury CB, Wilson CB (1999) Transsphenoidal microsurgical therapy of prolactinomas: initial outcomes and long-term results. Neurosurgery 44(2):254–261; discussion 261–263
Ciric I, Ragin A, Baumgartner C, Pierce DB (1997) Complications of transsphenoidal surgery: results of a national survey, review of the literature and personal experience. Neurosurgery 40:225–237
Semple PL, Laws ER Jr (1999) Complications in a contemporary series of patients who underwent transsphenoidal surgery for Cushing’s disease. J Neurosurg 91:175–179
de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P, Cavallo M (2003) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to the sellar region. In: de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P (eds) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. Springer, Wien, pp 91–130
Shin SS, Tormenti MJ, Paluzzi A, Rothfus WE, Chang YF, Zainah H, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Snyderman CH, Challinor SM, Gardner PA (2012) Endoscopic endonasal approach for growth hormone secreting pituitary adenomas: outcomes in 53 patients using 2010 consensus criteria for remission. Pituitary. (Epub ahead of print)
Rivera-Serrano CM, Snyderman CH, Gardner P, Prevedello D, Wheless S, Kassam AB, Carrau RL, Germanwala A, Zanation A (2011) Nasoseptal “rescue” flap: a novel modification of the nasoseptal flap technique for pituitary surgery. Laryngoscope 121(5):990–993. doi:10.1002/lary.21419
Chee GH, Mathias DB, James RA, Kendall-Taylor P (2001) Transsphenoidal pituitary surgery in Cushing’s disease: can we predict outcome? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 54(5):617–626
Scanlon MF, Peters JR, Thomas JP, Richards SH, Morton WH, Howell S, Williams ED, Hourihan M, Hall R (1985) Management of selected patients with hyperprolactinaemia by partial hypophysectomy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 291(6508):1547–1550
Pereira AM, van Aken MO, van Dulken H, Schutte PJ, Biermasz NR, Smit JW, Roelfsema F, Romijn JA (2003) Long-term predictive value of postsurgical cortisol concentrations for cure and risk of recurrence in Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(12):5858–5864
Beauregard C, Truong U, Hardy J, Serri O (2003) Long-term outcome and mortality after transsphenoidal adenomectomy for acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 58(1):86–91
Cho DY, Liau WR (2002) Comparison of endonasal endoscopic surgery and sublabial microsurgery for prolactinomas. Surg Neurol 58(6):371–375; discussion 375–376
Hofmann BM, Fahlbusch R (2006) Treatment of Cushing’s disease: a retrospective clinical study of the latest 100 cases. Front Horm Res 34:158–184
Maira G, Anile C, De Marinis L, Barbarino A (1990) Prolactin-secreting adenomas--surgical results. Can J Neurol Sci 17(1):67–70
Ciric I, Ragin A, Baumgartner C, Pierce D (1997) Complications of transsphenoidal surgery: results of a national survey, review of the literature, and personal experience. Neurosurgery 40(2):225–236; discussion 236–237
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paluzzi, A., Fernandez-Miranda, J.C., Tonya Stefko, S. et al. Endoscopic endonasal approach for pituitary adenomas: a series of 555 patients. Pituitary 17, 307–319 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-013-0502-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-013-0502-4