Abstract
Precise prediction of scour near the circular uniform pier may lead to the economic design of piers and avoid disastrous instances. Present study mainly deals with cohesionless sediment with gravel particles. Authors checked the three latest bridge pier scour models in this study. Three new relationships are proposed by authors for computing maximum scour depth, maximum scoured length and maximum effected scoured width in cohesionless sediment at equilibrium scour condition. Maximum scour depth equation is validated by the available literature data, and this relationship is applicable for both gravel as well as the sand bed. Graphically and statistically the new maximum scour depth relationship gives better agreements between observed and computed values of maximum scour depth. Relationships for maximum scoured length and maximum effected scoured width are only applicable for gravel and coarse sand bed and also gives better agreement with computed values.

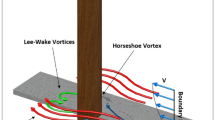
(Reproduced with the permission from Raudkivi and Witte 1990)







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SU, Choi B (2016) Prediction of time-dependent local scour around bridge piers. Water Environ J 30(1–2):14–21
Das S, Midya R, Das R, Mazumdar A (2013) A study of wake vortex in the scour region around a circular pier. Int J Fluid Mech Res 40(1):42–59
Dey S, Bose SK, Sastry GL (1995) Clear water scour at circular piers: a mode. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 121(12):869–876
Diab R, Link O, Zanke U (2010) Geometry of developing and equilibrium scour holes at bridge piers in gravel. Can J Civ Eng 37(4):544–552
Garde RJ, Raju KR (2000) Mechanics of sediment transportation and alluvial stream problems, vol 17. Taylor & Francis, London, p 686
Holnbeck SR (2011) Investigation of pier scour in coarse-bed streams in Montana, 2001 through 2007 (No. Scientific Investigations Report 2011–5107), US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey
Khan M, Azamathulla HM, Tufail M (2012) Gene-expression programming to predict pier scour depth using laboratory data. J Hydroinform 14(3):628–645
Khan M, Azamathulla HM, Tufail M, Ab Ghani A, Neill C, Andres D (2014) Discussion: Bridge pier scour prediction by gene expression programming. Proc Inst Civ Eng 167(6):368
Khosronejad A, Kang S, Sotiropoulos F (2012) Experimental and computational investigation of local scour around bridge piers. Adv Water Resour 37:73–85
Kothyari UC (1989) Scour around bridge piers, Doctoral Thesis, India: University of Roorkee
Kothyari UC, Ranga Raju KG (2001) Scour around spur dikes and bridge abutments. J Hydraul Res (ASCE) 39(4):367–374
Kothyari UC, Garde RJ, Ranga Raju KG (1992a) Temporal variation of scour around circular bridge piers. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 118(8):1091–1106
Kothyari UC, Garde RJ, Ranga Raju KG (1992b) Live bed scour-around cylindrical bridge piers. J Hydraul Res (IAHR) 30(5):701–715
Kothyari UC, Hager WH, Oliveto G (2007) Generalized approach for clear-water scour at bridge foundation elements. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 133(11):1229–1240
Lança RM, Fael CS, Maia RJ, Pêgo JP, Cardoso AH (2013) Clear-water scour at comparatively large cylindrical piers. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 139(11):1117–1125
Lauchlan CS, Melville BW (2001) Riprap protection at bridge piers. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 127:412–418
Lodhi AS (2015) Scour around spur dikes and bridge piers founded in cohesive sediment mixtures. Doctoral Thesis, India: Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee
Lodhi AS, Jain RK, Sharma PK, Karna N (2014) Time evolution of clear water bridge pier scour. In: Proceedings of international civil engineering symposium. VIT University Vellore, India, pp 252–260
Melville BW, Coleman SE (2000) Bridge scour, vol 9. Water Resources Publication, Littleton, p 547
Oliveto G, Hager WH (2002) Temporal evolution of clear-water pier and abutment scour. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 128(9):811–820
Oliveto G, Hager WH (2005) Further results to time-dependent local scour at bridge elements. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 131(2):97–105
Pandey M, Ahmad Z, Sharma PK (2015) Estimation of maximum scour depth near a spur dike. Can J Civ Eng 43(3):270–278
Pandey M, Ahmad Z, Sharma PK (2017a) Scour around impermeable spur dikes: a review. ISH J Hydraul Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2017.1342571
Pandey M, Sharma PK, Ahmad Z, Singh UK, Karna N (2017b) Three-dimensional velocity measurements around bridge piers in gravel bed. Mar Georesour Geotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2017.1362085
Pandey M, Sharma PK, Ahmad Z, Singh UK (2017c) Evaluation of existing equations for temporal scour depth around circular bridge piers. Environ Fluid Mech 17(5):981–995
Qi M, Li J, Chen Q (2016) Comparison of existing equations for local scour at bridge piers: parameter influence and validation. Nat Hazards 82(3):1–17
Raikar RV, Dey S (2005) Clear-water scour at bridge piers in fine and medium gravel beds. Can J Civ Eng 32(4):775–781
Raudkivi AJ, Witte HH (1990) Development of bed features. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 116(9):1063–1079
Richardson EV, Davis SR (2001) Evaluating scour at bridges: Federal Highway Administration Hydraulic Engineering Circular No. 18, FHWA NHI, 01-001
Sheppard DM, Odeh M, Glasser T (2004) Large scale clear-water local pier scour experiments. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 130(10):957–963
Sheppard DM, Melville B, Demir H (2013) Evaluation of existing equations for local scour at bridge piers. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 140(1):14–23
Yanmaz AM (2006) Temporal variation of clear water scour at cylindrical bridge piers. Can J Civ Eng 33(8):1098–1102
Yanmaz AM, Altinbilek HDGA (1991) Study of time-dependent local scour around bridge piers. J Hydraul Eng (ASCE) 117(10):1247–1268
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, M., Sharma, P.K., Ahmad, Z. et al. Maximum scour depth around bridge pier in gravel bed streams. Nat Hazards 91, 819–836 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3157-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3157-z