Abstract
Introduction
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a rare disease with a dismal prognosis compared to its systemic large B-cell lymphoma counterpart. Real world data are limited, when considering a uniform backbone treatment.
Methods
A retrospective study of all adult patients treated sequentially with a high-dose methotrexate (HD MTX)-based regimen in a single tertiary medical center between 2003 and 2019.
Results
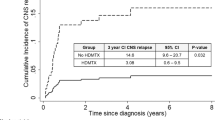
The 2015–2019 period differed from its predecessor in that most patients were treated with an HD MTX-based polychemotherapy regimen as opposed to HD MTX monotherapy (81% vs. 13%, P < .001), rituximab was given as standard of care (100% vs. 56%, P < .01), and most induction-responsive patients received consolidation treatment (70% vs. 18%, P = .01). The median progression-free and overall survival (OS) for the entire cohort (n = 73, mean age 64 years) was 9.9 and 29.8 months, respectively. Patients diagnosed between 2015 and 2019 had superior OS (P = .03) compared to those treated earlier. An interim partial response (PR) state, documented after two cycles of chemotherapy, was associated with increased incidence of progression, with only 33% of those patients achieving end-of-induction complete response. Twenty-three percent of patients developed thrombotic events and 44% developed grade 3–4 infections. HD MTX-based polychemotherapy induction was associated with both increase in thrombotic and infection incidence.
Conclusions
Contemporary HD MTX-based combination therapies suggestively improved the outcomes for PCNSL, but at a cost of increased incidence of toxicity. Patients who achieve an interim PR status are at a high risk for treatment failure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA et al (2016) The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 127:2375–2390
Houillier C, Soussain C, Ghesquieres H et al (2020) Management and outcome of primary CNS lymphoma in the modern era: an LOC network study. Neurology 94:e1027–e1039
Pfreundschuh M, Schubert J, Ziepert M et al (2008) Six versus eight cycles of bi-weekly CHOP-14 with or without rituximab in elderly patients with aggressive CD20 + B-cell lymphomas: a randomised controlled trial (RICOVER-60). Lancet Oncol 9:105–116
Villano JL, Koshy M, Shaikh H et al (2011) Age, gender, and racial differences in incidence and survival in primary CNS lymphoma. Br J Cancer 105:1414–1418
Camilleri-Broet S, Criniere E, Broet P et al (2006) A uniform activated B-cell-like immunophenotype might explain the poor prognosis of primary central nervous system lymphomas: analysis of 83 cases. Blood 107:190–196
Deeken JF, Loscher W (2007) The blood-brain barrier and cancer: transporters, treatment, and Trojan horses. Clin Cancer Res 13:1663–1674
Abrey LE, Yahalom J, DeAngelis LM (2000) Treatment for primary CNS lymphoma: the next step. J Clin Oncol 18:3144–3150
Ferreri AJ, Cwynarski K, Pulczynski E et al (2016) Chemoimmunotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: results of the first randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 (IELSG32) phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol 3:e217–e227
Ferreri AJ, Reni M, Foppoli M et al (2009) High-dose cytarabine plus high-dose methotrexate versus high-dose methotrexate alone in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 374:1512–1520
Rubenstein JL, Hsi ED, Johnson JL et al (2013) Intensive chemotherapy and immunotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma: CALGB 50202 (Alliance 50202). J Clin Oncol 31:3061–3068
Bromberg JEC, Issa S, Bakunina K et al (2019) Rituximab in patients with primary CNS lymphoma (HOVON 105/ALLG NHL 24): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 intergroup study. Lancet Oncol 20:216–228
Schmitt AM, Herbrand AK, Fox CP et al (2019) Rituximab in primary central nervous system lymphoma—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hematol Oncol 37:548–557
Ferreri AJM, Cwynarski K, Pulczynski E et al (2017) Whole-brain radiotherapy or autologous stem-cell transplantation as consolidation strategies after high-dose methotrexate-based chemoimmunotherapy in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: results of the second randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol 4:e510–e523
Ferreri AJ, Blay JY, Reni M et al (2003) Prognostic scoring system for primary CNS lymphomas: the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol 21:266–272
D’Haene N, Catteau X, Maris C et al (2008) Endothelial hyperplasia and endothelial galectin-3 expression are prognostic factors in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Br J Haematol 140:402–410
Abrey LE, Ben-Porat L, Panageas KS et al (2006) Primary central nervous system lymphoma: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model. J Clin Oncol 24:5711–5715
Abrey LE, Batchelor TT, Ferreri AJ et al (2005) Report of an international workshop to standardize baseline evaluation and response criteria for primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23:5034–5043
Kasenda B, Ferreri AJ, Marturano E et al (2015) First-line treatment and outcome of elderly patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL)—a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Ann Oncol 26:1305–1313
Joerger M, Huitema AD, Illerhaus G, Ferreri AJ (2012) Rational administration schedule for high-dose methotrexate in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 53:1867–1875
Abrey LE, DeAngelis LM, Yahalom J (1998) Long-term survival in primary CNS lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 16:859–863
Morris PG, Correa DD, Yahalom J et al (2013) Rituximab, methotrexate, procarbazine, and vincristine followed by consolidation reduced-dose whole-brain radiotherapy and cytarabine in newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma: final results and long-term outcome. J Clin Oncol 31:3971–3979
Houillier C, Taillandier L, Dureau S et al (2019) Radiotherapy or autologous stem-cell transplantation for primary cns lymphoma in patients 60 years of age and younger: results of the Intergroup ANOCEF-GOELAMS Randomized Phase II PRECIS Study. J Clin Oncol 37:823–833
Pels H, Juergens A, Schirgens I et al (2010) Early complete response during chemotherapy predicts favorable outcome in patients with primary CNS lymphoma. Neuro Oncol 12:720–724
Hottinger AF, DeAngelis LM, Yahalom J, Abrey LE (2007) Salvage whole brain radiotherapy for recurrent or refractory primary CNS lymphoma. Neurology 69:1178–1182
Arellano-Rodrigo E, Lopez-Guillermo A, Bessell EM et al (2003) Salvage treatment with etoposide (VP-16), ifosfamide and cytarabine (Ara-C) for patients with recurrent primary central nervous system lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 70:219–224
Mappa S, Marturano E, Licata G et al (2013) Salvage chemoimmunotherapy with rituximab, ifosfamide and etoposide (R-IE regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma relapsed or refractory to high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy. Hematol Oncol 31:143–150
Pentsova E, Deangelis LM, Omuro A (2014) Methotrexate re-challenge for recurrent primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Neurooncol 117:161–165
Choi MK, Kang ES, Kim DW et al (2013) Treatment outcome of relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a single-center experience of autologous stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol 98:346–354
Welch MR, Sauter CS, Matasar MJ et al (2015) Autologous stem cell transplant in recurrent or refractory primary or secondary central nervous system lymphoma using thiotepa, busulfan and cyclophosphamide. Leuk Lymphoma 56:361–367
Goldschmidt N, Linetsky E, Shalom E et al (2003) High incidence of thromboembolism in patients with central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer 98:1239–1242
Hohaus S, Tisi MC, Bartolomei F et al (2018) Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in patients with lymphoma requiring hospitalization. Blood Cancer J 8:54
Funding
The authors received no funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarid, N., Bokstein, F., Blumenthal, D.T. et al. Impact of contemporary regimens on the outcomes and toxicity of primary CNS lymphoma: a single-center retrospective analysis of 73 patients. J Neurooncol 151, 211–220 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03654-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03654-x