Abstract
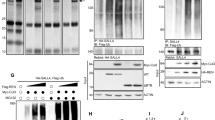
Eph receptors and ephrin ligands are master regulators of oncogenic signaling required for proliferation, migration, and metastasis. Yet, Eph/ephrin expression and activity in medulloblastoma (MB), the most common malignant brain tumor of childhood, remains poorly defined. We hypothesized that Eph/ephrins are differentially expressed by sonic hedgehog (SHH) and non-SHH MB and that specific members contribute to the aggressive phenotype. Affymetrix gene expression profiling of 29 childhood MB, separated into SHH (N = 11) and non-SHH (N = 18), was performed followed by protein validation of selected Eph/ephrins in another 60 MB and two MB cell lines (DAOY, D556). Functional assays were performed using MB cells overexpressing or deleted for selected ephrins. We found EPHB4 and EFNA4 almost exclusively expressed by SHH MB, whereas EPHA2, EPHA8, EFNA1 and EFNA3 are predominantly expressed by non-SHH MB. The remaining family members, except EFNB1, are ubiquitously expressed by over 70–90 % MB, irrespective of subgroup. EFNB1 is the only member differentially expressed by 28 % of SHH and non-SHH MB. Corresponding protein expression for EphB/ephrinB1 and B2 was validated in MB. Only ephrinB2 was also detected in fetal cerebellum, indicating that EphB/ephrinB1 expression is MB-specific. EphrinB1 immunopositivity localizes to tumor cells within MB with the highest proliferative index. EphrinB1 overexpression promotes EphB activation, alters F-actin distribution and morphology, decreases adhesion, and significantly promotes proliferation. Either silencing or overexpression of ephrinB1 impairs migration. These results indicate that EphrinB1 is uniquely dysregulated in MB and promotes oncogenic responses in MB cells, implicating ephrinB1 as a potential target.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crawford JR, MacDonald TJ, Packer RJ (2007) Medulloblastoma in childhood: new biological advances. Lancet Neurol 6:1073–1085
Palmer A, Zimmer M, Erdmann KS, Eulenburg V, Porthin A et al (2002) EphrinB phosphorylation and reverse signaling: regulation by Src kinases and PTP-BL phosphatase. Mol Cell 9:725–737
Gu C, Park S (2001) The EphA8 receptor regulates integrin activity through p110gamma phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in a tyrosine kinase activity-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol 21:4579–4597
Miao H, Strebhardt K, Pasquale EB, Shen TL, Guan JL (2004) Inhibition of integrin-mediated cell adhesion but not directional cell migration requires catalytic activity of EphB3 receptor tyrosine kinase. Role of Rho family small GTPases. J Biol Chem 280:923–932
Pasquale EB (2008) Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell 133:38–52
Paquale EB (2005) Eph receptor signalling casts a wide net on cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:462–475
Kemp HA, Cooke JE, Moens CB (2009) EphA4 and EfnB2a maintain rhombomere coherence by independently regulating intercalation of progenitor cells in the zebrafish neural keel. Devel Biol 327:313–326
Batlle E, Bacani J, Begthel H, Jonkheer S, Gregorieff A et al (2005) EphB receptor activity suppresses colorectal cancer progression. Nature 435:1126–1130
Sentürk A, Pfennig S, Weiss A, Burk K, Acker-Palmer A (2011) Ephrin Bs are essential components of the Reelin pathway to regulate neuronal migration. Nature 472:356–360
Kullander K, Klein R (2002) Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:475–486
Akay T, Acharya HJ, Fouad K, Pearson KG (2006) Behavioral and electromyographic characterization of mice lacking Eph A4 receptors. J Neurophysiol 96:642–651
Dottori M, Hartley L, Galea M, Paxinos G, Polizzotto M et al (1998) EphA4(Sek1) receptor tyrosine kinase is required for the development of the corticospinal tract. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:13248–13253
Miko I, Henkemeyer M, Cramer K (2008) Auditory brainstem responses are impaired in EphA4 and ephrin-B2 deficient mice. Hear Res 235:39–46
Dong Y, Wang J, Sheng Z, Li G, Ma H et al (2009) Downregulation of EphA1 in colorectal carcinomas correlates with invasion and metastasis. Mod Pathol 22:151–160
Jubb AM, Zhong F, Bheddah S, Grabsch HI, Frantz GD et al (2005) EphB2 is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:5181–5187
Campbell TN, Robbins SM (2008) The Eph receptor/ephrin system: an emerging player in the invasion game. Curr Issues Mol Biol 10:61–66
Petty A, Myshkin E, Qin H, Guo H, Miao H et al (2012) A small molecule agonist of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits tumor cell migration in vitro and prostate cancer metastasis in vivo. PLoS One 7:e42120
Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart CG et al (2011) Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29:1408–1414
Kool M, Koster J, Bunt J, Hasselt NE, Lakeman A et al (2008) Integrated genomics identifies five medulloblastoma subtypes with distinct genetic profiles, pathway signatures and clinicpathological features. PLoS One 3:1–14
MacDonald TJ, Brown K, LaFleur B, Peterson K, Lawlor C et al (2001) Expression profiling of medulloblastoma: PDGFRA and the RAS/MAPK pathway as therapeutic targets for metastatic disease. Nat Genet 29:143–152
Sikkema AH, den Dunnen WF, Hulleman E, van Vuurden DG, Garcia-Manero G et al (2012) EphB2 activity plays a pivotal role in pediatric medulloblastoma cell adhesion and invasion. Neuro Oncol 14:1125–1135
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ et al (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics 4:249–264
Cho YJ, Tsherniak A, Tamayo P, Santagata S, Ligon A et al (2011) Integrative genomic analysis of medulloblastoma identifies a molecular subgroup that drives poor clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol 29:1424–1430
Northcott PA, Hielscher T, Dubuc A, Mack S, Shih D et al (2011) Pediatric and adult sonic hedgehog medulloblastomas are clinically and molecularly distinct. Acta Neuropathol 122:231–240
Holen H, Shadidi M, Narvhus K, Kjøsnes O, Tierens A et al (2008) Signaling through ephrin-A ligand leads to activation of Src-family kinases, Akt phosphorylation, and inhibition of antigen receptor-induced apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol 84:1183–1191
Zisch AH, Kalo MS, Chong LD, Pasquale EB (1998) Complex formation between EphB2 and Src requires phosphorylation of tyrosine 611 in the EphB2 juxtamembrane region. Oncogene 16:2657–2670
Nakada M, Hayashi Y, Hamada J (2011) Role of Eph/ephrin tyrosine kinase in malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol 13:1163–1170
Johnson RA, Wright KD, Poppleton H, Mohankumar KM, Finkelstein D et al (2010) Cross-species genomics matches driver mutations and cell compartments to model ependymoma. Nature 466:632–636
Jiang G, Freywald T, Webster J, Kozan D, Geyer R et al (2008) In human leukemia cells ephrin-B-induced invasive activity is supported by Lck and is associated with reassembling of lipid raft signaling complexes. Mol Cancer Res 6:291–305
Tanaka M, Kamata R, Takigahira M, Yanagihara K, Sakai R (2007) Phosphorylation of ephrin-B1 regulates dissemination of gastric scirrhous carcinoma. Am J Pathol 171:68–78
Tanaka M, Sasaki K, Kamata R, Sakai R (2007) The C-terminus of ephrin-B1 regulates metalloproteinase secretion and invasion of cancer cells. J Cell Sci 120:2179–2189
Tanaka M, Kamata R, Sakai R (2005) Phosphorylation of ephrin-B1 via the interaction with claudin following cell–cell contact formation. EMBO J 24:3700–3711
Nakada M, Drake KL, Nakada S, Niska JA, Berens ME (2006) Ephrin-B3 ligand promotes glioma invasion through activation of Rac1. Cancer Res 66:8492–8500
Cortina C, Palomo-Ponce S, Iglesias M, Fernández-Masip JL, Vivancos A et al (2007) EphB-ephrin-B interactions suppress colorectal cancer progression by compartmentalizing tumor cells. Nat Genet 39:1376–1383
Chiu ST, Chang KJ, Ting CH, Shen HC, Li H et al (2009) Over-expression of EphB3 enhances cell–cell contacts and suppresses tumor growth in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 30:1475–1486
Lee HS, Nishanian TG, Mood K, Bong YS, Daar IO (2008) EphrinB1 controls cell–cell junctions through the Par polarity complex. Nat Cell Biol 10:979–986
Bong YS, Lee HS, Carim-Todd L, Mood K, Nishanian TG et al (2007) EphrinB1 signals from the cell surface to the nucleus by recruitment of STAT3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:17305–17310
Acknowledgments
Video microscopy results were obtained using the Integrated Cellular Imaging (ICI) Core Facility, Emory University Winship Cancer Institute. Funding support provided in part by National Institute Health R01CA111835 (TJM), CURE Childhood Cancer (NM), and the Georgia Research Alliance (TJM).
Ethical standards
The experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKinney, N., Yuan, L., Zhang, H. et al. EphrinB1 expression is dysregulated and promotes oncogenic signaling in medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 121, 109–118 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1618-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1618-8