Abstract
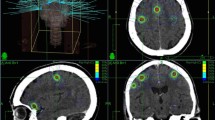
We prospectively analyzed the safety and outcome of frameless image-guided robotic stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for treatment of brain metastases in patients that would have otherwise been treated with frame-based techniques. During a three-year period, 333 patients with 783 brain metastases of various histologies underwent 391 outpatient SRS procedures. Fifty-five percent of patients had multiple brain metastases. The median (mean) tumor volume was 1.0 cc (2.7 cc). The mean prescribed tumor dose was 18.5 Gy (±1.3 Gy). Local/distant tumor recurrences were treated by additional SRS for patients with stable systemic disease. Survival and freedom from local tumor recurrence was analyzed with the Kaplan–Meier method. Prognostic factors were obtained from the Cox proportional hazards model. System accuracy tests (end-to-end tests) were performed with a standard head phantom. Overall median survival was 12.2 months after SRS. The actuarial one-year local control rate was 95.2% (95% CI: 92.0–97.2); the distant brain tumor control rate was 67% (95% CI: 61.0–71.2). Most patients died from systemically progressing cancer (69%). A Karnofsky performance score (KPS) > 70 was related to prolonged survival in the univariate and multivariate analysis. Recursive partition analysis (RPA) classes I and II were related to prolonged survival in the univariate analysis. Twenty-one patients (6.3%) developed treatment-related neurotoxic effects; no patient died because of complications of SRS. Forty-five end-to-end tests documented a mean targeting accuracy of 0.48 ± 0.22 mm. Single-session, frameless robotic SRS is feasible, accurate, and safe in selected patients with brain metastases of various primary tumors. There seems to be no difference in patient selection, adverse effects, treatment outcomes, or system accuracy compared with frame-based SRS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic SRS boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 22:1665–1672
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic SRS plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic SRS alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Auchter RM, Lamond JP, Alexander E et al (1996) A multiinstitutional outcome and prognostic factor analysis of SRS for resectable single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 35:27–35
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD et al (1994) Multi-institutional experience with stereotactic SRS for Solitary Brain Metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 28:797–802
Hasegawa T, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Germanwala A, Lunsford LD (2003) Brain metastases treated with SRS alone: an alternative to whole brain radiotherapy? Neurosurgery 52:1318–1326
Joseph J, Adler JR, Hancock SL (1996) Linear accelerator-based stereotaxic SRS for brain metastases: the influence of number of lesions on survival. J Clin Oncol 14:1085–1092
Muacevic A, Wowra B, Siefert A, Tonn JC, Steiger HJ, Kreth FW (2008) Microsurgery plus whole brain irradiation versus Gamma Knife surgery alone for treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized controlled multicentre phase III trial. J Neurooncol 87:299–307
Pirzkall A, Debus J, Lohr F et al (1998) SRS alone or in combination with whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 16:3563–3569
Sneed PK, Lamborn KR, Forstner JM et al (1999) SRS for brain metastases: is whole brain radiotherapy necessary? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:549–558
Sturm V, Kober B, Hoever KH et al (1987) Stereotactic percutaneous single dose irradiation of brain metastasis with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 13:279–282
Wowra B, Siebels M, Muacevic A, Kreth FW, Mack A, Hofstetter Al (2002) Repeated gamma knife surgery for multiple brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma. J Neurosurg 97:785–793
Chang SD, Main W, Martin DP, Gibbs IC, Heilbrun MP (2003) An analysis of the accuracy of the CyberKnife: a robotic frameless stereotactic radiosurgical system. Neurosurgery 52:140–146
Fu D, Kuduvalli G (2008) A fast, accurate, and automatic 2D-3D image registration for image-guided cranial radiosurgery. Med Phys 35:2180–2194
Kamath R, Ryken TC, Meeks SL, Pennington EC, Ritchie J, Buatti JM (2005) Initial clinical experience with frameless radiosurgery for patients with intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61:1467–1472
Nishizaki T, Saito K, Jimi Y et al (2006) The role of cyberknife radiosurgery/radiotherapy for brain metastases of multiple or large-size tumors. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 49:203–209
Breneman JC, Steinmetz R, Smith A, Lamba M, Warnick RE (2009) Frameless image-guided intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery: clinical outcomes for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:702–706
Furuse M, Aoki T, Takagi T, Takahashi JA, Ishikawa M (2008) Frameless stereotactic radiosurgery with a bite-plate: our experience with brain metastases. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 51:333–335
Shimamoto S, Inoue T, Shiomi H et al (2002) CyberKnife stereotactic irradiation for metastatic brain tumors. Radiat Med 20:299–304
Muacevic A, Kreth FW, Horstmann GA et al (1999) Surgery and radiotherapy compared with gamma knife SRS in the treatment of solitary cerebral metastases of small diameter. J Neurosurg 91:35–43
Trotti A, Byhardt R, Stetz J et al (2000) Common Toxicity Criteria version 2.0: an improved reference for grading the acute effects of cancer treatment: impact on radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:13–47
Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (2009) RTOG/EORTC late radiationmorbidity scoring schema. http://www.rtog.org/members/toxicity/late.html. Accessed 9 Jan 2009
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW et al (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastasis to the brain. N Engl J Med 322:494–500
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:475–481
Cox DR, Oakes D (1984) Analysis of survival data. Chapman and Hall, New York
Antypas C, Pantelis E (2008) Performance evaluation of a CyberKnife G4 image-guided robotic stereotactic radiosurgery system. Phys Med Biol 53:4697–4718
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M et al (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Mintz A, Perry J, Spithoff K, Chambers A, Laperriere N (2007) Management of single brain metastasis: a practice guideline. Curr Oncol 14:131–143
Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H, Noordijk EM et al (1993) Treatment of single brain metastasis: radiotherapy alone or combined with neurosurgery? Ann Neurol 33:583–590
Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:898–903
Jawahar A, Matthew RE, Minagar A et al (2004) Gamma knife surgery in the management of brain metastases from lung carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of survival, local tumor control, and freedom from new brain metastasis. J Neurosurg 100:842–847
Chen JC, Petrovich Z, Giannotta SL, Yu C, Apuzzo ML (2000) Radiosurgical salvage therapy for patients presenting with recurrence of metastatic disease to the brain. Neurosurgery 46:860–866
Fuller BG, Kaplan ID, Adler J, Cox RS, Bagshaw MA (1992) Stereotactic SRS for brain metastasis: the importance of adjuvant whole brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23:413–418
Hart MG, Grant R, Walker M, Dickinson H (2005) Surgical resection and whole brain radiation therapy versus whole brain radiation therapy alone for single brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 25:CD003292
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF et al (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA 280:1485–1489
Sneed PK, Suh JH, Goetsch SJ et al (2002) A multi-institutional review of SRS alone vs. SRS with whole brain radiotherapy as the initial management of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:519–526
Patchell RA, Regine WF (2003) The rationale for adjuvant whole brain radiation therapy with SRS in the treatment of single brain metastases. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2:111–116
Mehta MP, Tsao MN, Whelan TJ et al (2005) The American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based review of the role of SRS for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:37–46
Aoyama H, Tago M, Kato N et al (2007) Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic SRS or SRS alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:1388–1395
Regine WF, Huhn JL, Patchell RA et al (2002) Risk of symptomatic brain tumor recurrence and neurologic deficit after SRS alone in patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: results and implications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 52:333–338
Murphy MJ, Balter J, Balter S et al (2007) The management of imaging dose during image-guided radiotherapy: report of the AAPM Task Group 75. Med Phys 34:4041–4063
Mack A, Czempiel H, Kreiner HJ, Dürr G, Wowra B (2002) Quality assurance in stereotactic space. A system test for verifying the accuracy of aim in radiosurgery. Med Phys 29:561–568
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dave Schaal and Pam Commike of Accuray for language editing and Stefanie Himmerich, Tanja Helminger and Daniela Ellmann for helping with data management of the electronic database system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muacevic, A., Kufeld, M., Wowra, B. et al. Feasibility, safety, and outcome of frameless image-guided robotic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 97, 267–274 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0023-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0023-1