Abstract
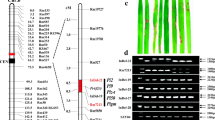
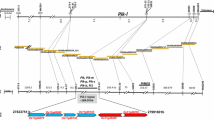
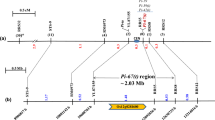
Pi-z is a disease resistance gene that has been effectively used to combat a broad-spectrum of races of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Although DNA markers have been reported for selection of the Pi2(t) and Pi-z resistance genes at the Pi-z locus, markers that are more tightly linked to the Pi-z locus would benefit rapid and effective cultivar development. Analysis of the publicly available genome sequence of Nipponbare near the Pi-z locus revealed numerous SSRs that could be converted into markers. Three SSRs on rice PAC AP005659 were found to be very tightly linked to the Pi-z locus, with one marker, AP5659-3, co-segregating with the Pi-z resistance reaction. The Pi-z factor conferring resistance to two races of blast was mapped to a 57 kb region on the physical map of Nipponbare in a location where the Pi2(t) gene was physically mapped. Two SSR marker haplotypes were unique for cultivars carrying the Pi-z gene, which indicates these markers are useful for selection of resistance genes at the Pi-z locus in rice germplasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSR:
-
simple sequence repeat
- BAC/PAC:
-
bacterial/P1-derived artificial chromosome
References
C.A. Conaway-Bormans M.A. Marchetti C.W. Johnson A.M. McClung W.D. Park (2003) ArticleTitleMolecular markers linked to the blast resistance gene Pi-z in rice for use in marker-assisted selection Theor. Appl. Genet. 107 1014–1020 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00122-003-1338-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvVCgtLg%3D Occurrence Handle12955204
K. Hayashi N. Hashimoto M. Daigen I. Ashikawa (2004) ArticleTitleDevelopment of PCR-based SNP markers for rice blast resistance genes at the Piz locus Theor. Appl. Genet. 108 1212–1220 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjtlOqsrs%3D Occurrence Handle14740086
S. Hittalmani M.R. Foolad T. Mew R.L. Rodriguez N. Huang (1995) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a PCR-based marker to identify rice blast resistance genePi-2(t)in a segregating population Theor. Appl. Genet. 91 9–14 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00220852 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsFKrsbo%3D
T. Inukai R.J. Nelson R.S. Ziegler S. Sarkarung D.J. Mackill J.M. Bonman I. Takamure T. Kinoshita (1994) ArticleTitleAllelism of blast resistance genes in near-isogenic lines of rice Phytopathology 84 1278–1283
S. Kiyosawa (1967) ArticleTitleThe inheritance of resistance of the Zenith type varieties of rice to the blast fungus Jap. J. Breed. 17 99–107
G. Liu G. Lu L. Zeng G.-L. Wang (2002) ArticleTitleTwo broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pi9(t) Pi2(t)are physically linked on rice chromosome 6 Mol. Genet. Genom. 267 472–480 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XntVShtLk%3D
K.F. Manly R.H. Cudmore SuffixJr. J.M. Meer (2001) ArticleTitleMap Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping Mamm. Genome 12 930–932 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00335-001-1016-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXosFGgtbo%3D Occurrence Handle11707780
M.A. Marchetti X. Lai C.N. Bollich (1987) ArticleTitleInheritance of resistance to Pyricularia oryzae in rice cultivars grown in the United States Phytopathology 77 799–804
A.M. McClung (2002) Techniques for development of new cultivars C.W. Smith R.H. Dilday (Eds) Rice: Origin, History, Technology and Production John Wiley & Sons Hoboken, NJ 177–202
S. Rozen H.J. Skaletsky (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers S. Krawetz S. Misener (Eds) Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols: Methods in Molecular Biology Humana Press TotowaNJ 365–386
S. Temnykh G. DeClerck A. Lukashova L. Lipovich S. Cartinhour S. McCouch (2001) ArticleTitleComputational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential Genome Res. 11 1441–1452 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gr.184001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlvVGgu70%3D Occurrence Handle11483586
Z.H. Yu D.J. Mackill J.M. Bonman S.D. Tanksley (1991) ArticleTitleTagging genes for blast resistance in rice via linkage to RFLP markers Theor. Appl. Genet. 81 471–476 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00219436
D. Ware P. Jaiswal J. Ni X. Pan K. Chang K. Clark L. Teytelman S. Schmidt W. Zhao S. Cartinhour S. McCouch L. Stein (2002) ArticleTitleGramene: a resource for comparative grass genomics Nucleic Acids Res. 30 103–105 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/30.1.103 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xht12kt7g%3D Occurrence Handle11752266
B. Zhou S. Qu G. Liu M. Dolan H. Sakai M. Bellizzi B. Han G.-L. Wang (2004) Functional and evolutional analysis of the Pi2 blast resistance gene cluster Proc. Plant & Animal Genome Conf. XII San DiegoCA 399
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fjellstrom, R., McClung, A.M. & Shank, A.R. SSR Markers Closely Linked to the Pi-z Locus are Useful for Selection of Blast Resistance in a Broad Array of Rice Germplasm. Mol Breeding 17, 149–157 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-005-4735-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-005-4735-4