Abstract
Context
The problem of how ecological mechanisms create and interact with patterns across different scales is fundamental not only for understanding ecological processes, but also for interpretations of ecological dynamics and the strategies that organisms adopt to cope with variability and cross-scale influences.
Objectives
Our objective was to determine the consistency of the role of individual habitat patches in pattern-process relationships (focusing on the potential for dispersal within a network of patches in a fragmented landscape) across a range of scales.
Methods
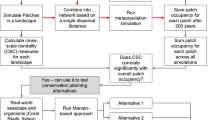
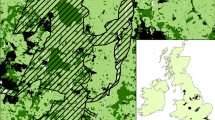
Network analysis was used to assess and compare the potential connectivity and spatial distribution of highland fynbos habitat in and between protected areas of the Western Cape of South Africa. Connectivity of fynbos patches was measured using ten maximum threshold distances, ranging from five to 50 km, based on the known average dispersal distances of fynbos endemic bird species.
Results
Network connectivity increased predictably with scale. More interestingly, however, the relative contributions of individual protected areas to network connectivity showed strong scale dependence.
Conclusions
Conservation approaches that rely on single-scale analyses of connectivity and context (e.g., based on data for a single species with a given dispersal distance) are inadequate to identify key land parcels. Landscape planning, and specifically the assessment of the value of individual areas for dispersal, must therefore be undertaken with a multi-scale approach. Developing a better understanding of scaling dependencies in fragmenting landscapes is of high importance for both ecological theory and conservation planning.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baggio R, Scott N, Cooper C (2010) Network acience: a review focused on tourism
Bakun A, Broad K (2003) Environmental ‘loopholes’ and fish population dynamics: comparative pattern recognition with focus on El Nino effects in the Pacific. Fish Oceanogr 12(4/5):458–473
Ball I, Possingham H (2000) MARXAN (V1.8.2): marine reserve design using spatially explicit annealing, a manual. The Ecology Centre, University of Queensland, Brisbane
Bettsetter C (2002) On the minimum node degree and connectivity of a wireless multihop network. In: Proceedings of ACM international symposium. Mobile Ad Hoc Netw. and Como (MobiHoc)
BirdLife International (2010) Endemic Bird Area factsheet: Cape fynbos. Downloaded from 450 http://www.birdlife.org. Accessed 20 Aug 2014
Bodin Ö, Tengö M, Norman A, Lundberg J, Elmqvist T (2006) The value of small size: loss of forest patches and ecological thresholds in southern Madagascar. Ecol Appl 16(2):440–451
Borgatti SP, Mehra A, Brass DJ, Labianca G (2009) Network analysis in the social sciences. Science 323:892–895
Boyd C, Brooks TM, Butchart SHM, Edgar GJ, da Fonseca GAB, Hawkins F, Hoffmann M, Sechrest W, Stuart SN, van Dijk PP (2008) Spatial scale and the conservation of threatened species. Conserv Lett 1(1):37–43
Brooks CP (2003) A scalar analysis of landscape connectivity. Oikos 102(2):433–439
Brown JD, Berghaus RD, Costa TP, Poulson R, Carter DL, Lebarbenchon C, Stallknecht DE (2012) Intestinal excretion of a wild bird-origin H3N8 low pathogenic avian influenza virus in Mallards (Anas Platyrhynchos). J Wildl Dis 48(4): 991-998.
Cadenasso ML, Pickett STA (2001) Effect of edge structure on the flux of species into forest interiors. Conserv Biol 15(1):91–97
Cadenasso ML, Pickett STA, Weathers KC, Bell SS, Benning TL, Cerreiro MM, Dawson TE (2003) An interdisciplinary and synthetic approach to ecological boundaries. BioScience 53:717–722
Cowling RM, Hilton-Taylor C (1994) Patterns of plant diversity and endemism in Southern Africa: an overview. In: Huntley BJ (ed) Botanical Diversity in Southern Africa. National Botanical Institute, Pretoria, pp 31–52
Csardi G, Nepusz T (2006) The igraph software package for complex network research. Int J Complex Syst 1695(5):1–9
Cumming GS (2011) Spatial resilience: integrating landscape ecology, resilience, and sustainability. Landscape Ecol 26(7):899–909
Cumming GS, Bodin O, Ernstson H, Elmqvist T (2010) Network analysis in conservation biogeography: challenges and opportunities. Divers Distrib 16:414–425
Debinski DM, Holt RD (2000) A survey and overview of habitat fragmentation experiments. Conserv Biol 14(2):342–355
Driscoll DD, Banks SC, Barton PS, Lindenmayer DB, Smith AL (2013) Conceptual domain of the matrix in fragmented landscapes. Trends Ecol Evol 28(10):605–613
Dunk JR, Zielinski WJ, Priesler HK (2004) Predicting the occurrence of rare mollusks in northern California forests. Ecol Appl 14:713–729
Erdös P, Rényi R (1959) On random graphs. Publ Math Debr 6:290–297
ESRI (2012) ArcGIS desktop: release 10. Environmental Systems Research Institute, Redlands
Franklin JF, Lindenmayer DB (2009) Importance of matrix habitats in maintaining biological diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(2):349–350
Fruchterman TM, Reingold EM (1991) Graph drawing by force-directed placement. Softw Pract Exp 21(11):1129–1164
Gaidet N, El Mamy ABO, Cappelle J, Caron A, Cumming GS, Grosbois V, Gil P, Hammouni S, de Almeida RS, Fereidouni SR, Cattoli G, Abolnik C, Mundava J, Fofana B, Ndlovu M, Diawara Y, Hurtado R, Newman SH, Dodman T, Balanca G (2012) Investigating avian influenza infection hotspots in old-world shorebirds. PLoS One 7(9):e46049
Geselbracht L, Torres R, Cumming GS, Dorfman D, Beck M, Shaw D (2009) Identification of a spatially efficient portfolio of priority conservation sites in marine and estuarine areas of Florida. Aquat Conserv-Mar Freshw Ecosyst 19(4):408–420
Gibson CC, Ostrom E, Ahn T-K (2000) The concept of scale and the human dimensions of global change: a survey. Ecol Econ 32(2):217–239
Gonzalez A (2000) Community relaxation in fragmented landscapes: the relation between species richness, area and age. Ecol Lett 3(5):441–448
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ, Ryan P (2005) Roberts Birds of Southern Africa, VIIth edn. The Trustees of the John Voelcker Bird Book Fund, Cape Town
Huntley B, Barnard P (2012) Potential impacts of climatic change on southern African birds of fynbos and grassland biodiversity hotspots. Divers Distrib 18(8):769–781
Janssen MA, Orjan B, Anderies JM, Elmqvist T, Ernstson H, McAllister RRJ, Per O, Ryan P (2006) Toward a network perspective of the study of resilience in social-ecological systems. Ecol Soc 11(1):15
Keitt TH, Urban DL, Milne BT (1997) Detecting critical scales in fragmented landscapes. Conserv Ecol 1(1):4
Kim H, Anderson R (2013) An experimental evaluation of robustness of networks. Syst J IEEE 7(2):179–188
Kuussaari M, Bommarco R, Heikkinen RK et al (2009) Extinction debt: a challenge for biodiversity conservation. Trends Ecol Evol 24(10):564–571
Lee ATK, Barnard P (2012) Endemic fynbos avifauna: comparative range declines a cause for concern. Ornithol Observ 3:19–28
Levin SA (1992) The problem of pattern and scale in ecology: the Robert H. MacArthur award lecture. Ecology 73(6):1943–1967
Levin SA (2000) Multiple scales and the maintenance of biodiversity. Ecosystems 3(6):498–506
Lindenmayer DB, Fischer J (2006) Habitat fragmentation and landscape change. Island Pres, Washington
Mateo Sánchez MC, Cushman SA, Saura S (2013) Scale dependence in habitat selection: the case of the endangered brown bear (Ursus arctos) in the Cantabrian Range (NW Spain). Int J Geogr Inf Sci 28(8):1531–1546
Matisziw TC, Murray AT (2008) Connectivity change in habitat networks. Landscape Ecol 24(1):89–100
Matisziw TC, Alam M, Trauth KM, Inniss EC, Semlitsch RD, McIntosh S, Horton J (2015) A vector approach for modeling landscape corridors and habitat connectivity. Environ Model Assess 20(1):1–16
Minor ES, Urban DL (2007) Graph theory as a proxy for spatially explicit population models in conservation planning. Ecol Appl 17(6):1771–1782
Mitchell BA (2005) Editorial. -Parks 15:6
Moore C, Cumming GS, Slingsby J, Grewar J (2014) Tracking socioeconomic vulnerability using network analysis: insights from an avian influenza outbreak in an ostrich production network. PLoS One 9(1):e86973
Norberg J, Wilson J, Walker B, Ostrom E (2008) Diversity and Resilience of social-ecological systems. In: Norberg J, Cumming GS (eds) Complexity theory for a sustainable future. Columbia University Press, New York, pp 46–79
Pascual-Hortal L, Saura S (2007) Impact of spatial scale on the identification of critical habitat patches for the maintenance of landscape connectivity. Landscape Urban Plan 83:176–186
Peters DPC, Bestelmeyer BT, Turner MG (2007) Cross-scale interactions and changing pattern-process relationships: consequences for system dynamics. Ecosystems 10(5):790–796
Poiani KA, Richter BD, Anderson MG, Richter HE (2000) Biodiversity conservation at multiple scales: functional sites, landscapes, and networks. Bioscience 50:133–146
Poteete A, Ostrom E (2004) Heterogeneity, group size, and collective action: the role of institutions in forest management. Dev Change 35(3):435–461
Pressey RL, Cabeza M, Watts ME, Cowling RM, Wilson KA (2007) Conservation planning in a changing world. Trends Ecol Evol 22(11):583–592
Prugh LR, Hodges KE, Sinclair ARE, Brashares JS (2008) Effect of habitat area and isolation on fragmented animal populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:20770–20775
Rebelo A (1992) Red Data Book species in the Cape Floristic Region: threats, priorities and target species. Trans R Soc S Afr 48(1):55–86
Reppas AI, Spiliotis KG, Siettos CI (2011) On the effect of path length of small-world networks on epidemic dynamics. Virulence 3:146–153
Saura S, Pascual-Hortal L (2007) A new habitat availability index to integrate connectivity in landscape conservation planning: comparison with existing indices and application to a case study. Landscape and Urban Plan 83(2):91–103
Simberloff D, Farr JA, Cox J, Mehlman DW (1992) Movement corridors—conservation bargains or poor investments. Conserv Biol 6(4):493–504
Stauffer D (1985) Introduction to percolation theory. Taylor and Francis, London
Swindle KA, Ripple WJ, Meslow EC, Schafer D (1999) Old-forest distribution around spotted owl nests in the central Cascade Mountains, Oregon. J Wildl Manag 63(4):1212–1221
Terborgh J, Lopez L, Nunez P et al (2001) Ecological meltdown in predator-free forest fragments. Science 294(5548):1923–1926
Thompson M (1996) A standard land-cover classification scheme for remote-sensing applications in South Africa. S Afr J Sci 92:34–42
Tigas LA, Van Vuren DH, Sauvajot RM (2002) Behavioral responses of bobcats and coyotes to habitat fragmentation and corridors in an urban environment. Biol Conserv 108(3):299–306
TNC (2003) The five-s framework for site conservation: a practitioner’s handbook for site conservation planning and measuring conservation success. The Nature Conservancy, Washington, DC
Turner MG, Gardner RH, O’Neill RV (2001) Landscape ecology in theory and practice: pattern and process. Springer, Berlin
Uezu A, Beyer DD, Metzger JP (2008) Can agroforest woodlots work as stepping stones for birds in the Atlantic forest region? Biodivers Conserv 17(8):1907–1922
Urban DL, Minor ES, Treml EA, Schick RS (2009) Graph models of habitat mosaics. Ecol Lett 12(3):260–273
van Dijk JGB, Hoye BJ, Verhagen JH, Nolet BA, Fouchier RAM, Klaassen M (2014) Juveniles and migrants as drivers for seasonal epizootics of avian influenza virus. J Anim Ecol 83:266–275
Walters S (2007) Modeling scale-dependent landscape pattern, dispersal, and connectivity from the perspective of the organism. Landscape Ecol 22(6):867–881
Wasserman S, Faust K (1994) Social network analysis—methods and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Watts DJaSHS (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393:440–442
Weisstein EW (2015) Fast Fourier Transform, from MathWorld–A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/FastFourierTransform.html
With KA, Crist TO (1995) Critical thresholds in species responses to landscape structure. Ecology 76(8):2446–2459
Wu J (1999) Hierarchy and scaling: extrapolating information along a scaling ladder. Can J Remote Sens 25:367–380
Wu J (2004a) Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: scaling relations. Landscape Ecol 19:125–138
Wu J (2004b) Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: scaling relations. Landscape Ecol 19(2):125–138
Wu J, Loucks OL (1995) From balance of nature to hierarchical patch dynamics: a paradigm shift in ecology. Q Rev Biol 70:439–466
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the DST/NRF Centre of Excellence at the Percy FitzPatrick Institute of African Ornithology, a CPRR Grant to GSC from the National Research Foundation of South Africa, and a James S. McDonnell Foundation complexity scholar award to GSC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maciejewski, K., Cumming, G.S. Multi-scale network analysis shows scale-dependency of significance of individual protected areas for connectivity. Landscape Ecol 31, 761–774 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0285-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0285-2