Abstract
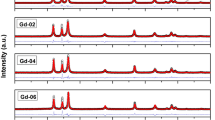
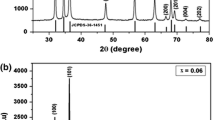
Zn1−xCoxO nanoparticles were prepared by sol–gel method. The microstructure and dopant position were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS). The XRD patterns did not show any signal of impurity in the Zn1−xCoxO nanoparticles with Co concentration from x = 0.01 to 0.08. Neither did the HRTEM image for the highest concentration sample with x = 0.08. The nanoparticles have also been investigated by the EXAFS measurements at Co k-edge. The radical distribution functions, the fitting result of bond length and coordination numbers, indicated there was an impurity in the highest Co concentration sample with x = 0.08. Although most of the Co atoms were substituted for Zn sites in ZnO with x = 0.08, a few of Co atoms formed a microstructure similar to Co3O4, which was not found in the XRD and HRTEM. The room temperature ferromagnetic behaviour was found for x = 0.01 sample by superconducting quantum interference device .





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dietl T, Ohno H, Cibert J et al (2000) Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287:1019–1022
Sato K, Katayama YH (2002) First principles design for semiconductor spintronics. Semicond Sci Technol 17:367–376
Krishnamurthy S, Mcguinness C, Dorneles LS et al (2006) Soft X-ray spectroscopic investigation of ferromagnetic Co-doped ZnO. J Appl Phys 99:08M111-1-3
Ueda K, Tabata H, Kawai T (2001) Magnetic and electric properties of transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Appl Phys Lett 79:988–990
Venkatesan M, Fitzgerald CB, Lunney JG et al (2004) Anisotropic ferromagnetism in substituted zinc oxide. Phys Rev Lett 93:177206–177209
Rode K, Anane A, Mattana R et al (2003) Magnetic semiconductors based on cobalt substituted ZnO. J Appl Phys 93:7676–7678
Okabayashi J, Ono K, Mizuguchi M et al (2004) X-ray absorption spectroscopy of transition-metal doped diluted magnetic semiconductors Zn1−x M x O. J Appl Phys 95:3573–3575
Bhatti KP, Chaudhary S, Pandya DK et al (2007) High temperature investigation of the magnetization behavior in cobalt substituted ZnO. J Appl Phys 101:033902-1-4
Dinia A, Schmerber G, Mény C et al (2005) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Zn1−xCoxO magnetic semiconductors prepared by sputtering. J Appl Phys 97:123908-1-5
Park JH, Kim MG, Jang HM et al (2004) Co-metal clustering as the origin of ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO thin films. J Appl Phys Lett 84:1338–1340
Kim JH, Kim H, Kim D et al (2002) Magnetic properties of epitaxially grown semiconducting Zn1−x Co x O thin films by pulsed laser deposition. J Appl Phys 92:6066–6069
Wi SC, Kang JS, Kim JH et al (2004) Electronic structure of Zn1ÀxCoxO using photoemission and x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett 84:4233–4235
Yan GQ, Xuan HC (2011) Extrinsic origin of room-temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO annealed in Zn vapor. Appl Phys Lett 99:082501-1-2
Liu T, Xu HR, Chin WS et al (2010) Local structural evolution of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles upon calcination studied by in situ quick-scan XAFS. J Phys Chem C 112:3489–3495
Kumar S, Kim YJ, Koo BH et al (2009) Ferromagnetism in Chemically- synthesized Co-doped ZnO. J Korean Phys Soc 55:1060–1064
Vaslilu F, Diamandescu L, Macovei D et al (2009) EXAFS investigation of iron local environment in metal-doped titania photocatalysts prepared by hydrothermal and high-energy ball milling routes. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 20:211–214
Liu XC, Shi EW, Chen ZZ et al (2007) Effect of donor doping on the magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO films. J Cryst Growth 307:14–18
Kunisu M, Oba F, Ikeno H et al (2005) Local environment of Mn dopant in ZnO by near-edge x-ray absorption fine structure analysis. Appl Phys Lett 86:121902-1-3
Zaharko O, Meneghini C, Cervellino A et al (2001) Local structure of Co and Ni in decagonal AlNiCo investigated by polarized EXAFS. Euro Phys J B 19:207–215
Srivastava AK, Gakhar R, Dua P, et al (2010) Structural determination of Zn–O dumbbells in facetted nano-particles. Microscopy: Sci Technol Application Edu 1820–1823
Peng Y, Xu AW, Deng B et al (2006) Polymer-controlled crystallization of zinc oxide hexagonal nanorings and disks. J Phys Chem B 110:2988–2993
Mokili B, Charreire Y, Cortes R et al (1996) Extended X-ray absorption fine structure studies of zinc hydroxo-sulphide thin films chemically deposited from aqueous solution. Thin Solid Films 288:21–28
Fouchet A, Prellier W, Padhan P et al (2004) Structural and magnetic properties of a series of low-doped Zn1−x Co x O thin films deposited from Zn and Co metal targets on (0001) Al2O3 substrates. J Appl Phys 95:7187–7189
Acknowledgments
The research work was supported by the NUAA Fundamental Research Funds (No. NS2013061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Chen, Z., Boafo, F. et al. Dopant position of Co atom in Zn1−xCoxO nanoparticles studied by extended X-ray absorption fine structure. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 66, 163–167 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-2981-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-2981-1