Abstract
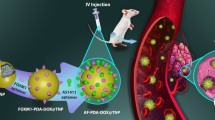
Effective delivery of therapeutic molecules by proper surface-modified nanomaterial can disallow the progression of cancer. We report an effective treatment approach based on targeted delivery of ruthenium pro-drug (Ru) by poly ethylamine (PEI) coated ZnO–SiO2 core–shell nanoparticle for encapsulating large quantity of Ru pro-drug and subsequently grafted with functionalized with cholic acid (CA) as a tumor-specific moiety. An elaborate mechanism of core–shell formation and the size, composition, and morphology were characterized with diverse physiochemical studies such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Further, the anti-tumor activity of CA–Ru–PEI–ZnO–SiO2 nanoparticle was confirmed by in vitro studies. The synthesized CA–Ru–PEI–ZnO–SiO2 has a wide core with thicker outer shell showed excellent biocompatibility and a high potential for loading Ru pro-drug for anti-cancer therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Ginsburg, F. Bray, M.P. Coleman, The global burden of women’s cancers: an unmet grand challenge in global health. Lancet 389, 847 (2016)
J. Shi, P.W. Kantoff, R. Wooster, O.C. Farokhzad, Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17(1), 20 (2017)
S. Gupta, Y. Pathak, M.K. Gupta, S.P. Vyas, Nanoscale drug delivery strategies for therapy of ovarian cancer: conventional vs targeted. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 47(1), 4066–4088 (2019)
D. Howard, J. Garcia-Parra, G.D. Healey, C. Amakiri, L. Margarit, L.W. Francis, D. Gonzalez, R.S. Conlan, Antibody–drug conjugates and other nanomedicines: the frontier of gynaecological cancer treatment. Interface Focus 6(6), 20160054 (2016)
J. Lou, L. Zhang, G. Zheng, Advancing cancer immunotherapies with nanotechnology. Adv. Ther. 2(4), 1800128 (2019)
F. Din, W. Aman, I. Ullah, O.S. Qureshi, O. Mustapha, S. Shafique, A. Zeb, Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 12, 7291 (2017)
S.K. Golombek, J.N. May, B. Theek, L. Appold, N. Drude, F. Kiessling, T. Lammers, Tumor targeting via EPR: Strategies to enhance patient responses. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 130, 17 (2018)
K. Mondal, A. Sharma, Recent advances in the synthesis and application of photocatalytic metal–metal oxide core–shell nanoparticles for environmental remediation and their recycling process. RSC Adv. 6, 83589–83612 (2016)
H. Wang, L. Chen, Y. Feng, H. Chen, Exploiting core–shell synergy for nanosynthesis and mechanistic investigation. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 1636–1646 (2013)
H. Pang, Z. Zhao, J.W. Ding, R.M. Zhu, The synthesis and electrochemical applications of core–shell MOFs and their derivatives. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 15519 (2019)
H. DzudzevicCancar, S. Soylemez, Y. Akpinar, M. Kesik, S. Göker, G. Gunbas, M. Volkan, L. Toppare, A novel acetylcholinesterase biosensor: core–shell magnetic nanoparticles incorporating a conjugated polymer for the detection of organophosphorus pesticides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 8058–8067 (2016)
S. Kayal, R.V. Ramanujan, Anti-cancer drug loaded iron–gold core–shell nanoparticles (Fe@ Au) for magnetic drug targeting. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10(9), 5527–5539 (2010)
D. Mangalaraj, D.N. Devi, Ag/TiO2 (metal/metal oxide) core shell nanoparticles for biological applications, in Recent Trends in Materials Science and Applications, ed. by J. Ebenezar (Springer, Cham, 2017), pp. 9–17
V. Sharma, D. Anderson, A. Dhawan, Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human liver cells (HepG2). Apoptosis 17(8), 852–870 (2012)
X. Zhao, X. Ren, R. Zhu, Z. Luo, B. Ren, Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 180, 56–70 (2016)
Y. Singh, M. Palombo, P.J. Sinko, Recent trends in targeted anticancer pro-drug and conjugate design. Curr. Med. Chem. 15(18), 1802–1826 (2008)
H. Kobayashi, R. Watanabe, P.L. Choyke, Improving conventional enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects; what is the appropriate target? Theranostics 4(1), 81 (2014)
R.M. Mohammad, I. Muqbil, L. Lowe, C. Yedjou, H.Y. Hsu, L.T. Lin, M.D. Siegelin, C. Fimognari, N.B. Kumar, Q.P. Dou, H. Yang, Broad targeting of resistance to apoptosis in cancer, in Seminars in Cancer Biology, vol. 35, ed. by B. Anupam, B. Keith (Academic Press, Cambridge, 2015), pp. S78–S103
W.H. Chen, X.D. Xu, G.F. Luo, H.Z. Jia, Q. Lei, S.X. Cheng, R.X. Zhuo, X.Z. Zhang, Dual-targeting pro-apoptotic peptide for programmed cancer cell death via specific mitochondria damage. Sci. Rep. 3, 3468 (2013)
H. Yang, R.M. Villani, H. Wang, M.J. Simpson, M.S. Roberts, M. Tang, X. Liang, The role of cellular reactive oxygen species in cancer chemotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 37(1), 266 (2018)
S.K. Golombek, J.-N. May, B. Theek, L. Appold, N. Drude, F. Kiessling, T. Lammers, Tumor targeting via EPR: strategies to enhance patient responses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 130, 17 (2018)
J. Kydd, R. Jadia, P. Velpurisiva, A. Gad, S. Paliwal, P. Rai, Targeting strategies for the combination treatment of cancer using drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 9, 46 (2017)
S. Gupta, M.K. Gupta, Possible role of nanocarriers in drug delivery against cervical cancer. Nano Rev. Exp. 8, 1335567 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the College of Clinical Medicine, Yangzhou University, China for availing the needed laboratory and instrument facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W. Cholic Acid-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded With Ruthenium Pro-drug Delivery to Cervical Cancer Therapy. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 311–318 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01710-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01710-7