Abstract
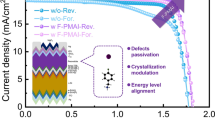
Boosting the contact property of intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H(i)) film is pivotal to achieving high-efficiency silicon heterojunction (SHJ) solar cells. Here, the microstructure of a-Si:H(i) film is modified with hydrogen dilution ratio using hot wire chemical vapor deposition (HWCVD) for the application into rear-emitter SHJ solar cells. A higher hydrogen content associated with high valence band offset was found to decrease the fill factor FF for low dilution, while high interface defect densities related to epitaxial growth are responsible for the deterioration of both FF and open-circuit voltage VOC for high dilution. In particular, the most compact film prepared at a moderate dilution exhibits the most compact structure with most hydrogen located as isolated hydrogen rather than clustered hydrogen. Finally, high efficiency of SHJ solar cells up to 22.5% was yielded using the optimized a-Si:H(i) layer thanks to a significant enhancement of FF, which is attributed to improved passivation quality and rational band alignment at the a-Si:H(i)/c-Si interface. This work clearly interpreted the correlation between SHJ device parameters and a-Si:H(i)/c-Si interface properties, which might guide the design of a-Si:H passivation layers in pursuit of high-efficiency SHJ solar cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Haschke, O. Dupré, M. Boccard, C. Ballif, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 187, 140–153 (2018)
D. Adachi, J.L. Hernandez, K. Yamamoto, Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 233506 (2015)
M.A. Green, Y. Hishikawa, E.D. Dunlop, D.H. Levi, J. Hohl-Ebinger, A.W.Y. Ho‐Baillie, Prog. Photovolt. 26(7), 427–436 (2018)
F. Wang, X. Zhang, L. Wang, Y. Jiang, C. Wei, S. Xu, Y. Zhao, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 20202–20208 (2014)
R. Gogolin, R. Ferré, M.Turcu and N.-P.Harder, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 106, 47–50 (2012)
T. Ruan, M. Qu, J. Wang, Y. He, X. Xu, C. Yu, Y. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 13330–13335 (2019)
A.H.M. Smets, W.M.M. Kessels, M.C.M. van de Sanden, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1547 (2003)
Z.E. Smith, S. Wagner, Phys. Rev. B 32, 5510 (1985)
M.H. Brodsky, J.J. Manuel Cardona, Cuomo, Phys. Rev. B 16, 3556 (1977)
A.H.M. Smets, M.C.M. van de Sanden, Phys. Rev. B 76, 073202 (2007)
A. Richter, M. Hermle, S.W. Glunz, IEEE J. Photovol. 3, 1184–1191 (2013)
H. Matsumur, H. Umemoto, A. Masuda, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 338, 19–26 (2004)
Z. Wu, L. Zhang, R. Chen, W. Liu, Z. Li, F. Meng, Z. Liu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 475, 504–509 (2019)
M.A. Lieberman, J.P. Booth, P. Chabert, J.M. Rax, M.M. Turner, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 11, 283 (2002)
K. Ishibashi, M. Karasawa, G. Xu, N. Yokokawa, I. Manabu, A. Masuda, H. Matsumura, Thin Solid Films 430, 58 (2003)
P.A. Frigeri, O. Nos, J.D. Calvo, P. Carreras, R. Roldan, A. Antony, J.M. Asensi, J. Bertomeu, Phys. Status Solidi C 7, 588–591 (2010)
G.E. Jellison Jr., F.A. Modine, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 371–373 (1996)
Z. Iqbal, S. Veprek, J. Phys. C 15, 377–392 (1982)
S. Sriraman, S. Agarwal, E.S. Aydil, D. Maroudas, Nature 418, 62 (2002)
F. Wang, R. Du, Q. Ren, C. We, Y. Zhao, X. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 1751–1757 (2017)
N. Layadi, P. Roca i Cabarrocas, B. Drévillon, I. Solomon, Phys. Rev. B 52, 5136 (1995)
H. Fujiwara, M. Kondo, A. Matsuda, Phys. Rev. B 63, 115306 (2001)
J. Oh, H.C. Yuan, H.M. Branz, Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 743 (2012)
S. De Wolf, M. Kondo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 042111 (2007)
B. Macco, J. Melskens, N.J. Podraza, K. Arts, C. Pugh, O. Thomas, W.M.M. Kessels, J. Appl. Phys. 122, 035302 (2017)
M. Mews, M. Liebhaber, B. Rech, L. Korte, Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 013902 (2015)
W. Liu, L. Zhang, S. Cong, R. Chen, Z. Wu, F. Meng, Q. Shi, Z. Liu, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 174, 233–239 (2018)
T.F. Schulze, L. Korte, F. Ruske, B. Rech, Phys. Rev. B 83, 165314 (2011)
Z. Shu, U. Das, J. Allen, R. Birkmire, S. Hegedus, Prog. Photovolt. 23, 78–93 (2014)
A. Kanevce, W.K. Metzger, J. Appl. Phys. 105, 094507 (2009)
M.W.M. van Cleef, R.E.I. Schropp, F.A. Rubinelli, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2609 (1998)
M. Leilaeioun, W. Weigand, M. Boccard, Z.J. Yu, K. Fisher, Z.C. Holman, IEEE J. Photovol. 10, 54–62 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by projects of the Strategic Priority Research Program and the Joint Fund of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA17020403, 6141A01141604), the Innovation Development Fund of Shanghai Zhangjiang (ZJ2018-ZD-010), Shanghai Sailing Program (17YF1423000) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (17DZ1201100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zhang, L., Liu, W. et al. Role of hydrogen in modifying a-Si:H/c-Si interface passivation and band alignment for rear-emitter silicon heterojunction solar cells. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 9468–9474 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03486-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03486-5