Abstract
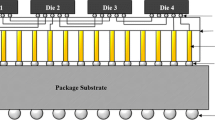
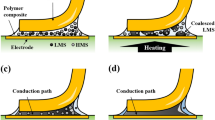
A novel three-dimensional (3D) multi-layer through-hole filling process using solderable polymer composites (SPCs) was developed to overcome several limitations of the conventional 3D package technique. To investigate the multi-layer through-hole filling properties of SPCs, SPCs with functionalized polymer composite and low-melting-point-alloy (LMPA) fillers were formulated, and a multi-layer through-hole filling test was conducted under atmospheric pressure and decompression reflow conditions. The results indicated that the multi-layer through-hole filling assemblies under the atmospheric pressure reflow condition have weak through-hole filling and interlayer interconnection properties because of the weak elimination of residual polymer composite and voids within the through-hole. Meanwhile, the multi-layer through-hole filling assemblies reflowed under the decompression condition showed improved through-hole filling properties because of the favorable elimination of polymer composite and voids within the through-hole and the excellent wetting behavior of molten fillers. The corresponding electrodes between the stacked boards were electrically interconnected by the proper selective wetting behavior of molten LMPA, and the spaces between stacked boards were underfilled by the cured polymer composite.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Lai, S.W. Li, J.Y. Shih, K.N. Chen, Microelectron. Eng. 88, 3282–3286 (2011)
Y.C. Chan, P.L. Tu, K.C. Hung, Microelectron. Reliab. 41, 1867–1875 (2001)
P. Yang, X. Qin, Microelectron. J. 40, 1235–1243 (2009)
D.H. Kim, K. Athikulwongse, S.K. Lim, Proceedings of IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design-Digest of Technical Papers (2009), pp. 674–680
M.D. Diop, M. Radji, W. Andre, Y. Blaquiere, A.A. Hamoui, R. Izquierdo, Proceedings of 19th IEEE Conference on Electrical Performance of Electronic Packaging and Systems (EPEPS) (2010), pp. 245–248
S. Spiesshoefer, L. Schaper, Proceedings of 53rd International Conference on Electronic Components and Technology (2003), pp. 631–633
R. Beica, C. Sharbono, T. Ritzdorf, Proceedings of 58th International Conference on Electronic Components and Technology (2008), pp. 577–583
M. Motoyoshi, Proc. IEEE 97, 43–48 (2009)
D.M. Jang, C. Ryu, K.Y. Lee, B.H. Cho, Performance of 57th International Conference on Electronic Components and Technology (2007), pp. 847–852
J.P. Gambino, S.A. Adderly, J.U. Knickerbocker, Microelectron. Eng. 135, 73–106 (2015)
L. Hofmann, R. Ecke, S.E. Schulz, T. Gessner, Microelectron. Eng. 88, 705–708 (2011)
S. Yamamoto, K. Itoi, T. Suemasu, T. Takizawa, Performance of 16th IEEE Annual International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (2003), pp. 642–645
Y.K. Ko, H.T. Fujii, Y.S. Sato, C.W. Lee, S. Yoo, Proceedings of 61st IEEE International Conference on Electronic Components and Technology (2011), pp. 2091–2095
S.K. Kang, S.L. Buchwalter, N.C. LaBianca, J. Gelorme, S. Purushothaman, K. Papathomas, M. Poliks, I.E.E.E. Trans, Compon. Packag. Technol. 24, 431–435 (2001)
R.N. Das, F.D. Egitto, V.R. Markovich, Circuit World 34, 3–12 (2008)
J.W. Baek, K.S. Jang, Y.S. Eoma, J.T. Moon, J.M. Kim, J.D. Nam, Microelectron. Eng. 87, 1968–1972 (2010)
J.B. Jullien, H. Fremont, J.Y. Deletage, Microelectron. Reliab. 53, 1597–1601 (2013)
A.S. Cebrian, R. Basler, F. Klunker, M. Zogg, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 48, 51–58 (2014)
A.A. Gallo, R. Munamarty, IEEE Trans. Reliab. 44, 362–367 (1995)
J.E. Galloway, B.M. Miles, I.E.E.E. Trans, Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. A 20, 274–279 (1997)
Z. Li, X. Shu, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56, 624–628 (2013)
A.S. Cebrian, M. Zogg, P. Ermanni, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 40, 112–119 (2013)
N.P. Cheremisinoff, Handbook of Industrial Toxicology and Hazardous Materials (CRC Press, New York, 1999), p. 444
A. Lewis, Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Lead Free Electronics and Assemblies (2004), pp. 1–10
K. Banerji, F.D. Alves, R.F. Darveaux, US Patent 5203076 (1993), pp. 4–5
X.R. Guo, W.B. Young, Microelectron. Reliab. 55, 613–622 (2015)
M.K. Schwiebert, W.H. Leong, I.E.E.E. Trans, Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. C 19, 133–137 (1996)
J.D. Kish, C. Leng, J. Kelley, J. Hiltner, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, Atmos. Environ. 79, 561–565 (2013)
M. Takahashi, T. Kawamura, Y. Yamamoto, H. Ohnari, S. Himuro, H. Shakutsui, J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 2171–2173 (2003)
S.D. Beattie, J.R. Dahn, J. Electrochem. Soc. 150, A894–A898 (2003)
N. Saunders, A.P. Miodownik, Bull. Alloys Phase Diagr. 11, 278–287 (1990)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and future Planning (2014007164) and Human Resources Program in Energy Technology of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) granted financial resource from the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea (No. 20134030200350).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.I., Yim, BS., Shin, D. et al. Three-dimensional multi-layer through-hole filling properties of solderable polymer composites with low-melting-point alloy fillers. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 6223–6231 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4553-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4553-y