Abstract
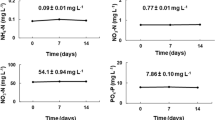
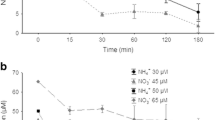
The bioremediation capacities of Palmaria palmata and Ulva lactuca for removing dissolved nutrients in a cold-seawater fully recirculated ecosystemic representation of an estuarine aquatic habitat were evaluated. The seaweeds were cultured in the laboratory based on environmental conditions observed in a large-scale aquarium representing the marine ecosystem of the Gulf of Saint-Lawrence (Québec, Canada), i.e., salinity of 24 PSU, 5 and 10 °C, and under three combinations of high nitrate (NO3 −) and phosphate (PO4 3−) concentrations (2865:195, 3570:242, and 4284: 291 μM). Neither nutrient levels nor temperature significantly changed nitrate and phosphate uptake rates (0.65 ± 0.15 and 1.76 ± 0.59 mg N gDW−1 day−1 and 0.14 ± 0.11 and 0.32 ± 0.21 mg P gDW−1 day−1 for P. palmata and U. lactuca, respectively). Growth rate of P. palmata was independent of temperature and nutrient concentrations with a mean of 0.64 ± 0.18% FW day−1. Ulva lactuca expressed its highest growth rate (2.81 ± 0.72% FW day−1) at 10 °C and intermediate nutrient concentration. C/N ratio was < 10 for both species before and after the experiment, indicating tissue nutrient enrichment possibly limiting nutrient uptake and growth. Under cold temperatures and high dissolved nutrient concentrations, U. lactuca is the leading candidate for bioremediation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansemir A, Blume M, Schröder S, Lindequist U (2006) Screening of cultivated seaweeds for antibacterial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria. Aquaculture 252
Björnsäter BR, Wheeler PA (1990) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus supply on growth and tissue composition of Ulva fenestrata and Enteromorpha intestinalis (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). J Phycol 26:603–611
Boisvert C, Beaulieu L, Bonnet C, Pelletier E (2015) Assessment of the antioxidant and antibacterial activities of three species of edible seaweeds. J Food Biochem 39:377–387
Bracken MES, Stachowick JJ (2006) Seaweed diversity enhances nitrogen uptake via complementary use of nitrate and ammonium. Ecol 87:2397–2403
Bruhn A, Dahl J, Nielsen HB, Nikolaisen L, Rasmussen MB, Markager S, Olesen B, Arias C, Jensen PD (2011) Bioenergy potential of Ulva lactuca: biomass yield, methane production and combustion. Bioresour Technol 102:2595–2604
Cahill PL, Hurd CL, Lokman M (2010) Keeping the water clean—seaweed biofiltration outperforms traditional bacterial biofilms in recirculating aquaculture. Aquaculture 306:153–159
Caines S, Manríquez-Hernández JA, Duston J, Corey P, Garbary DJ (2014) Intermittent aeration affects the bioremediation potential of two red algae cultured in finfish effluent. J Appl Phycol 26:2173–2181
Carmona R, Kraemer GP, Yarish C (2006) Exploring Northeast American and Asian species of Porphyra for use in an integrated finfish-algal aquaculture system. Aquaculture 252:54–65
Chapin FS, Schulze E, Mooney HA (1990) The ecology and economics of storage in plants. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 21:423–447
Chopin T, Buschmann AH, Halling C, Troell M, Kautsky N, Neori A, Kraemer GP, Zertuche-Gonzalez J, Charles Y, Neefus C (2001) Integrating seaweeds into marine aquaculture systems : a key toward sustainability. J Phycol 37:975–986
Chaumont JP (1978) Variations de la teneur en composés azotés du Rhodymenia palmata Grev. Bot Mar 21:23–30
Chung IK, Kang YH, Yarish C, Kraemer GP, Lee JA (2002) Application of seaweed cultivation to the bioremediation of nutrient-rich effluent. Algae 17:187–194
Copertino MDS, Tormena T, Seeliger U (2009) Biofiltering efficiency, uptake and assimilation rates of Ulva clathrata (Roth) J. Agardh (Chlorophyceae) cultivated in shrimp aquaculture waste water. J Appl Phycol 21:31–45
Corey P, Kim JK, Garbary DJ, Prithiviraj B, Duston J (2012) Bioremediation potential of Chondrus crispus (Basin Head) and Palmaria palmata: effect of temperature and high nitrate on nutrient removal. J Appl Phycol 24:441–448
Corey P, Kim JK, Duston J, Garbary DJ, Prithiviraj B (2013) Bioremediation potential of Palmaria palmata and Chondrus crispus (Basin Head): effect of nitrate and ammonium ratio as nitrogen source on nutrient removal. J Appl Phycol 25:1349–1358
Corey P, Kim JK, Duston J, Garbary DJ (2014) Growth and nutrient uptake by Palmaria palmata integrated with Atlantic halibut in a land-based aquaculture system. Algae 29:35–45
Craigie JS, Shacklock PF (1989) Culture of Irish moss. In: Boghen AD (ed) Cold water aquaculture in Atlantic Canada. Can. Inst. Res. Reg. Dev., University of Moncton, Moncton, pp 243–270.
Demetropoulos C, Langdon C (2004a) Pacific dulse (Palmaria mollis) as a food and biofilter in recirculated, land-based abalone culture systems. Aquac Eng 32:57–75
Demetropoulos CL, Langdon CJ (2004b) Enhanced production of Pacific dulse (Palmaria mollis) for co-culture with abalone in a land-based system: nitrogen, phosphorus, and trace metal nutrition. Aquaculture 235:433–455
Dupla M, Comeau Y, Parent S, Villemur R, Jolicoeur M (2006) Design optimization of a self-cleaning moving-bed bioreactor for seawater denitrification. Water Res 40:249–258
Fujita RM (1985) The role of nitrogen status in regulating ammonium transient uptake and nitrogen storage by macroalgae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 92:283–301
Garcia-Bueno N, Decottignies P, Turpin V, Dumay J, Paillard C, Stiger-Pouvreau V, Kervarec N, Pouchus Y-F, Marin-Atucha AA, Fleurence J (2014) Seasonal antibacterial activity of two red seaweeds, Palmaria palmata and Grateloupia turuturu, on European abalone pathogen Vibrio harveyi. Aquat Living Resour 27:83–89
Gordillo FJL, Dring MJ, Savidge G (2002) Nitrate and phosphate uptake characteristics of three species of brown algae cultured at low salinity. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 234:111–118
Grguric G, Wetmore SS, Fournier RW (2000) Biological denitrification in a closed seawater system. Chemosphere 40:549–555
Grote B (2016) Bioremediation of aquaculture wastewater: evaluating the prospects of the red alga Palmaria palmata (Rhodophyta) for nitrogen uptake. J Appl Phycol 28:3075–3082
Hanisak MD (1990) The use of Gracilaria tikvahiae (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) as a model system to understand the nitrogen nutrition of cultured seaweeds. Hydrobiologia 204:79–87
Harrison PJ, Hurd CL (2001) Nutrient physiology of seaweeds: application of concepts to aquaculture. Cah Biol Mar 42:71–82
He J, Chen JP (2014) A comprehensive review on biosorption of heavy metals by algal biomass: materials, performances, chemistry, and modeling simulation tools. Bioresour Technol 160:67–78
Hernandez I, Martinez-Aragon JF, Tovar A, Terez-Llorens JL, Vergara JJ (2002) Biofiltering efficiency in removal of dissolved nutrients by the three species of estuarine macroalgae with sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) waste waters 2. Ammonium. J Appl Phycol 14:375–384
Hofmann LC, Nettleton JC, Neefus CD, Mathieson C (2010) Cryptic diversity of Ulva (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) in the Great Bay Estuarine System (Atlantic USA): introduced and indigenous distromatic species. Eur J Phycol 45:230–239
Kang YH, Park SR, Chung IK (2011) Biofiltration efficiency and biochemical composition of three seaweed species cultivated in a fish-seaweed integrated culture. Algae 26:97–108
Kim JK, Kraemer GP, Neefus CD, Chung IK, Yarish C (2007) Effects of temperature and ammonium on growth, pigment production and nitrogen uptake by four species of Porphyra (Bangiales, Rhodophyta) native to the New England coast. J Appl Phycol 19:431–440
Kincheloe JW, Wedemeyer GA, Koch DL (1979) Tolerance of developing salmonid eggs and fry to nitrate exposure. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 23:575–578
Korzen L, Abelson A, Israel A (2016) Growth, protein and carbohydrate contents in Ulva rigida and Gracilaria bursa-pastoris integrated with an offshore fish farm. J Appl Phycol 28:1835–1845
Labelle MA, Juteau P, Jolicoeur M, Villemur R, Parent S, Comeau Y (2005) Seawater denitrification in a closed mesocosm by a submerged moving bed biofilm reactor. Water Res 39:3409–3417
Lapointe BE, Ryther JH (1979) The effects of nitrogen and seawater flow rate on the growth and biochemical composition of Gracilaria foliifera var. angustissima in mass outdoor cultures. Bot Mar 22:529–537
Lobban CS, Harrison PJ (1997) Seaweed ecology and physiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lourenço SO, Barbarino E, De-Paula JC, Pereira LOS, Lanfer Marquez UM (2002) Amino acid composition, protein content and calculation of nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for 19 tropical seaweeds. Phycol Res 50:233–241
Lu IF, Sung MS, Lee TM (2006) Salinity stress and hydrogen peroxide regulation of antioxidant defense system in Ulva fasciata. Mar Biol 150:1–15
Lundberg P, Weich RG, Jensén P, Vogel HJ (1989) Phosphorus-31 and nitrogen-14 NMR studies of the uptake of phosphorus and nitrogen compounds in the marine macroalgae Ulva lactuca. Plant Physiol 89:1380–1387
Macchiavello J, Bulboa C (2014) Nutrient uptake efficiency of Gracilaria chilensis and Ulva lactuca in an IMTA system with the red abalone Haliotis rufescens. Lat Am J Aquat Res 42:523–533
Mahon R, Stephen KB, Zwanenburg KCT, Atkinson DB, Buja KR, Claflin L, Howell GD, Monaco ME, O’Boyle RN, Sinclair M (1998) Assemblages and biogeography of demersal fishes of the east coast of North America. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:1704–1738
Mann RA, Bavor HJ (1993) Phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands using gravel and industrial waste substrata. Water Sci Technol 27:107–113
Manríquez-Hernández JA, Duston J, Garbary DJ (2016) Effect of irradiance on bioremediation capacity of the red algae Chondrus crispus and Palmaria palmata. Aquac Int 24:39–55
Martineau C, Villeneuve C, Mauffrey F, Villemur R (2014) Complete genome sequence of Hyphomicrobium nitrativorans strain NL23, a denitrifying bacterium isolated from biofilm of a methanol- fed denitrification system treating seawater at the Montreal Biodome. Genome Announc 2:1–2
Martínez B, Rico JM (2004) Inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus uptake kinetics in Palmaria palmata (Rhodophyta). J Phycol 44:642–650
Mata L, Magnusson M, Paul NA, de Nys R (2016) The intensive land-based production of the green seaweeds Derbesia tenuissima and Ulva ohnoi : biomass and bioproducts. J Appl Phycol 28:365–375
Morgan KC, Simpson FJ (1981) The cultivation of Palmaria palmata. Effect of light intensity and nitrate supply on growth and chemical composition. Bot Mar 24:273–277
Morris AL, Hamlin HJ, Francis-Floyd R, Sheppard BJ, Guillette LJ (2011) Nitrate-induced goiter in captive whitespotted bamboo sharks Chiloscyllium plagiosum. J Aquat Anim Health 23:92–99
Naldi M, Viaroli P (2002) Nitrate uptake and storage in the seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh in relation to nitrate availability and thallus nitrate content in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Po River Delta, Italy). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 269:65–83
Navarro-Angulo L, Robledo D (1999) Effects of nitrogen source, N:P ratio and N-pulse concentration and frequency on the growth of Gracilaria cornea (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) in culture. Hydrobiologia 399:315–320
Neori A, Ragg NLC, Shpigle M (1998) The integrated culture of seaweed, abalone, fish and clams in modular intensive land-based systems: II. Performance and nitrogen partitioning within an abalon (Haliotis tuberculata) and macroalgae culture system. Aquac Eng 17:215–239
Pang S, Shan T (2008) Temperature and light tolerance of representative brown, green and red algae in tumble culture revealed by chlorophyll fluorescence measurements. Acta Oceanol Sinica 27:137–146
Parent S, Morin A (2000) N budget as water quality management tool in closed aquatic mesocosms. Water Res 34:1846–1856
Pedersen M, Borum J (1997) Nutrient control of estuarine macroalgae : growth strategy and the balance between nitrogen requirements and uptake. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 161:155–163
Pedersen A, Kraemer G, Yarish C (2004) The effects of temperature and nutrient concentrations on nitrate and phosphate uptake in different species of Porphyra from Long Island Sound (USA). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 312:235–252
Pérez-Mayorga DM, Ladah LB, Zertuche-González JA, Leichter JJ, Filonov AE, Lavín MF (2011) Nitrogen uptake and growth by the opportunistic macroalga Ulva lactuca (Linnaeus) during the internal tide. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 406:108–115
Pettett P (2009) Preliminary investigation into the induction of reproduction in Ulva spp. In: Southeast Queensland for mass cultivation purposes. Master Thesis, University of the Sunshine Coast, p 71
Pierce RH, Weeks JM, Prappas JM (1993) Nitrate toxicity to five species of marine fish. J World Aquacult Soc 24:105–107
Reef R, Pandolfi JM, Lovelock CE (2012) The effect of nutrient enrichment on the growth, nucleic acid concentrations, and elemental stoichiometry of coral reef macroalgae. Ecol Evol 2:1985–1995
Runcie JW, Ritchie RJ, Larkum AWD (2004) Uptake kinetics and assimilation of phosphorus by Catenella nipae and Ulva lactuca can be used to indicate ambient phosphate availability. J Appl Phycol 16:181–194
Ryther JH, Goldman JC, Gifford JE, Huguenin JE, Wing AS, Clarner JP, Williams LD, Lapointe BE (1975) Physical models of integrated waste recycling—marine polyculture systems. Aquaculture 5:163–177
Sode S, Bruhn A, Balsby TJS, Larsen MM, Gotfredsen A, Rasmussen MB (2013) Bioremediation of reject water from anaerobically digested waste water sludge with macroalgae (Ulva lactuca, Chlorophyta). Bioresour Technol 146:426–435
Spotte S (1979) Seawater aquariums. Wiley, New York
Steffensen DA (1976) The effect of nutrient enrichment and temperature on the growth and culture of Ulva lactuca. Aquat Bot 2:337–351
Taylor R, Fletcher RL, Raven JA (2001) Preliminary studies on the growth of selected ‘green tide’ algae in laboratory culture : effects of irradiance, temperature, salinity and nutrients on growth rate. Bot Mar 44:327–336
Townsend S (2009) Incorporating sustainable practices for zoos and aquariums: a triple bottom line approach. Int Zoo Yearb 43:53–63
Tremblay-Gratton A, Boussin JC, Bennachi A, Tamigneaux É, Vandenberg GW, Le François NR (2017) Implementation of sulfur-based denitrification in a large-scale fully recirculated cold-sw aquarium: a sustainability practice. J Zoo Aquar Res 5:104–108
Tsagkamilis P, Danielidis D, Dring MJ, Katsaros C (2010) Removal of phosphate by the green seaweed Ulva lactuca in a small-scale sewage treatment plant (Ios Island, Aegean Sea, Greece). J Appl Phycol 22:331–339
Tsai SJ, Chen JC (2002) Acute toxicity of nitrate on Penaeus monodon juveniles at different salinity levels. Aquaculture 213:163–170
Vidal S, Rocha C, Galvão H (2002) A comparison of organic and inorganic carbon controls over biological denitrification in aquaria. Chemosphere 48:445–451
Wang C, Lei A, Zhou K, Hu Z, Hao W, Yang J (2014) Growth and nitrogen uptake characteristics reveal outbreak mechanism of the opportunistic macroalga Gracilaria tenuistipitata. PLoS One https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108980
Winberg P, Skropeta D, Ullrich A (2011) Seaweed cultivation pilot trials - towards culture systems and marketable products. Rural Industries Research & Development Corporation Technical Report, Canberra
Ye N, Zhang X, Mao Y, Liang C, Xu D, Zou J, Zhuang Z, Wang Q (2011) Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: taking the world’s largest example. Ecol Res 26:477–485
Ye C, Zhang M (2013) Allelopathic effect of macroalgae Gracilaria tenuistipitata (Rhodophyta) on the photosynthetic apparatus of red-tide causing microalgae Prorocentrum micans. IERI PRO 5:209–215
Yeats PA (1990) Reactivity and transport of nutrients and metals in the St. Lawrence estuary. In: el-Sabh MI, Silverberg N. (eds) Coastal and Estuarine studies, vol 39. Springer, New York, pp 153–169
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the research and training organization MITACS (Mathematics of Information Technology and Complex Systems), SABM (Société des Amis du Biodôme de Montréal), FAP (Fonds d’amorçage de partenariat), and NSERC (National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada). The authors would like to thank the technical support from ÉPAQ (École des Pêches et de l’Aquaculture du Québec), the Université Laval, and the Biodôme de Montréal staff members.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tremblay-Gratton, A., Boussin, JC., Tamigneaux, É. et al. Bioremediation efficiency of Palmaria palmata and Ulva lactuca for use in a fully recirculated cold-seawater naturalistic exhibit: effect of high NO3 and PO4 concentrations and temperature on growth and nutrient uptake. J Appl Phycol 30, 1295–1304 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1333-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1333-x