Abstract
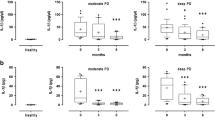
Periostin, an extracellular matrix protein functioning as an important structural mediator and adhesion molecule, has been shown to be an important regulator of connective tissue integrity. This study aimed to evaluate the levels of periostin in chronic periodontitis (CP) and aggressive periodontitis (AgP) compared to non-periodontitis (NP). Individuals were submitted to gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) and saliva sampling. Periodontal examination consisted of plaque index (PI), gingival index (GI), probing depth (PD), bleeding on probing (BOP), and clinical attachment level (CAL) measurements. Assays for periostin were performed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Periodontitis patients presented more severe clinical indices compared to the NP group (p < 0.001). The mean GCF level of periostin was lowest in the AgP group as compared to the other groups and was lower in the CP group as compared to the NP group (p < 0.001). Increased levels of periostin were observed in the saliva of patients with AgP as compared to the CP and NP groups (p < 0.05). There was a negative relationship between GCF periostin levels and clinical parameters (p < 0.01), whereas a positive correlation was observed between salivary periostin levels and full-mouth GI and CAL scores (p < 0.01). To our knowledge, this is the first report investigating periostin levels in GCF and saliva in aggressive periodontitis. The results suggest that subjects with CP and AgP exhibit a different periostin profile. Periostin in GCF may have a protective role against periodontal disease. Furthermore, salivary periostin concentrations may have a promising diagnostic potential for the aggressive forms of periodontal disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kulkarni, C., and D.F. Kinane. 2014. Host response in aggressive periodontitis. Periodontology 2000(65): 79–91.
Califano, J.V. 2003. Position paper: periodontal diseases of children and adolescents. Journal of Periodontology 74: 1696–1704.
Vieira, A.R., and J.M. Albandar. 2014. Role of genetic factors in the pathogenesis of aggressive periodontitis. Periodontology 2000(65): 92–106.
Loe, H., and L.J. Brown. 1991. Early onset periodontitis in the United States of America. Journal of Periodontology 62: 608–616.
Susin, C., A.N. Haas, and J.M. Albandar. 2014. Epidemiology and demographics of aggressive periodontitis. Periodontology 2000(65): 27–45.
Kantarci, A., K. Oyaizu, and T.E. Van Dyke. 2003. Neutrophil-mediated tissue injury in periodontal disease pathogenesis: findings from localized aggressive periodontitis. Journal of Periodontology 74: 66–75.
Kononen, E., and H.P. Muller. 2014. Microbiology of aggressive periodontitis. Periodontology 2000(65): 46–78.
Sgolastra, F., A. Petrucci, R. Gatto, and A. Monaco. 2012. Effectiveness of systemic amoxicillin/metronidazole as an adjunctive therapy to full-mouth scaling and root planing in the treatment of aggressive periodontitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Periodontology 83: 731–743.
Merle, B., and P. Garnero. 2012. The multiple facets of periostin in bone metabolism. Osteoporosis International 23: 1199–1212.
Horiuchi, K., N. Amizuka, S. Takeshita, H. Takamatsu, M. Katsuura, H. Ozawa, Y. Toyama, L.F. Bonewald, and A. Kudo. 1999. Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin, with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament and increased expression by transforming growth factor beta. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 14: 1239–1249.
Oshima, A., H. Tanabe, T. Yan, G.N. Lowe, C.A. Glackin, and A. Kudo. 2002. A novel mechanism for the regulation of osteoblast differentiation: transcription of periostin, a member of the fasciclin I family, is regulated by the bHLH transcription factor, twist. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 86: 792–804.
Yamada, S., T. Tauchi, T. Awata, K. Maeda, T. Kajikawa, M. Yanagita, and S. Murakami. 2014. Characterization of a novel periodontal ligament-specific periostin isoform. Journal of Dental Research 93: 891–897.
Romanos, G.E., K.P. Asnani, D. Hingorani, and V.L. Deshmukh. 2014. PERIOSTIN: role in formation and maintenance of dental tissues. Journal of Cellular Physiology 229: 1–5.
Kruzynska-Frejtag, A., J. Wang, M. Maeda, R. Rogers, E. Krug, S. Hoffman, R.R. Markwald, and S.J. Conway. 2004. Periostin is expressed within the developing teeth at the sites of epithelial-mesenchymal interaction. Developmental Dynamics 229: 857–868.
Ling, L., Y. Cheng, L. Ding, and X. Yang. 2014. Association of serum periostin with cardiac function and short-term prognosis in acute myocardial infarction patients. PloS One 9: e88755.
Bolton, K., D. Segal, J. McMillan, A. Sanigorski, G. Collier, and K. Walder. 2009. Identification of secreted proteins associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes in Psammomys obesus. International Journal of Obesity (Lond) 33: 1153–1165.
Malanchi, I., A. Santamaria-Martinez, E. Susanto, H. Peng, H.A. Lehr, J.F. Delaloye, and J. Huelsken. 2012. Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization. Nature 481: 85–89.
Kotobuki, Y., L. Yang, S. Serada, A. Tanemura, F. Yang, S. Nomura, A. Kudo, K. Izuhara, H. Murota, M. Fujimoto, et al. 2014. Periostin accelerates human malignant melanoma progression by modifying the melanoma microenvironment. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research 27: 630–639.
Ma, D., R. Zhang, Y. Sun, H.F. Rios, N. Haruyama, X. Han, A.B. Kulkarni, C. Qin, and J.Q. Feng. 2011. A novel role of periostin in postnatal tooth formation and mineralization. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 286: 4302–4309.
Kim, S.S., L. Jackson-Boeters, M.R. Darling, M.J. Rieder, and D.W. Hamilton. 2013. Nifedipine induces periostin expression in gingival fibroblasts through TGF-beta. Journal of Dental Research 92: 1022–1028.
Arancibia, R., A. Oyarzun, D. Silva, N. Tobar, J. Martinez, and P.C. Smith. 2013. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits transforming growth factor-beta-stimulated myofibroblastic differentiation and extracellular matrix production in human gingival fibroblasts. Journal of Periodontology 84: 683–693.
Kurtis, B., G. Tuter, M. Serdar, P. Akdemir, C. Uygur, E. Firatli, and B. Bal. 2005. Gingival crevicular fluid levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients with chronic and aggressive periodontitis. Journal of Periodontology 76: 1849–1855.
Padial-Molina, M., S.L. Volk, A.D. Taut, W.V. Giannobile, and H.F. Rios. 2012. Periostin is down-regulated during periodontal inflammation. Journal of Dental Research 91: 1078–1084.
Padial-Molina, M., S.L. Volk, J.C. Rodriguez, J.T. Marchesan, P. Galindo-Moreno, and H.F. Rios. 2013. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharides decrease periostin in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Journal of Periodontology 84: 694–703.
Balli, U., Z.P. Keles, B. Avci, S. Guler, B.O. Cetinkaya, and G.C. Keles. 2014. Assessment of periostin levels in serum and gingival crevicular fluid of patients with periodontal disease. Journal of Periodontal Research. doi:10.1111/jre.12254.
Ustun, K., K. Erciyas, B. Kisacik, U. Sezer, Y. Pehlivan, S. Oztuzcu, H. Gundogar, and A.M. Onat. 2013. Host modulation in rheumatoid arthritis patients with TNF blockers significantly decreases biochemical parameters in periodontitis. Inflammation 36: 1171–1177.
Cairo, F., M. Nieri, S. Cincinelli, J. Mervelt, and U. Pagliaro. 2011. The interproximal clinical attachment level to classify gingival recessions and predict root coverage outcomes: an explorative and reliability study. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38: 661–666.
Armitage, G.C. 1999. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Annals of Periodontology 4: 1–6.
Bial, J.J., and J.T. Mellonig. 1987. Radiographic evaluation of juvenile periodontitis (periodontosis). Journal of Periodontology 58: 321–326.
Adonogianaki, E., J. Mooney, and D.F. Kinane. 1992. The ability of gingival crevicular fluid acute phase proteins to distinguish healthy, gingivitis and periodontitis sites. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 19: 98–102.
Salazar, M.G., N. Jehmlich, A. Murr, V.M. Dhople, B. Holtfreter, E. Hammer, U. Volker, and T. Kocher. 2013. Identification of periodontitis associated changes in the proteome of whole human saliva by mass spectrometric analysis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 40: 825–832.
Kaufman, E., and I.B. Lamster. 2000. Analysis of saliva for periodontal diagnosis—a review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 27: 453–465.
Edgar, W.M. 1992. Saliva: its secretion, composition and functions. British Dental Journal 172: 305–312.
Rivera-Hidalgo, F. 1986. Smoking and periodontal disease. A review of the literature. Journal of Periodontology 57: 617–624.
Obeid, P., and P. Bercy. 2000. Effects of smoking on periodontal health: a review. Advances in Therapy 17: 230–237.
Giannopoulou, C., I. Cappuyns, and A. Mombelli. 2003. Effect of smoking on gingival crevicular fluid cytokine profile during experimental gingivitis. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 30: 996–1002.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to Bülent Özkan, Department of Biostatistics, School of Medicine, Izmir Katip Celebi University, Izmir, Turkey, for his support in statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Izmir Katip Çelebi University and performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aral, C.A., Köseoğlu, S., Sağlam, M. et al. Gingival Crevicular Fluid and Salivary Periostin Levels in Non-Smoker Subjects With Chronic and Aggressive Periodontitis. Inflammation 39, 986–993 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0328-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0328-0