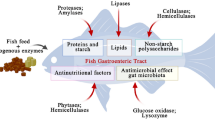
Abstract
The present study investigated the effect of various alternative diet ingredients partially replacing fishmeal (FM) on digestive and metabolic parameters in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) post-smolts (initial body mass 305 ± 69 g) following 12 weeks of feeding. Experimental diets containing 20 % extracted sunflower (ESF), pea protein concentrate (PPC), soy protein concentrate (SPC), feather meal (FeM) and poultry by-product (PBY) were compared to a reference diet containing FM as the main protein source. For the different intestinal compartments trypsin, lipase, bile salts, dry matter and chyme-associated leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) were measured from the content and LAP was measured in the tissue. Selected metabolites were measured in plasma samples. In general, use of plant proteins resulted in low C-LAP activity, low plasma cholesterol and high plasma magnesium. The plasma levels of cholesterol and Mg reflecting were most likely reflections of the composition of the diet, while the LAP activity in chyme may indicate lower epithelial cell turnover. Other responses varied depending on the plant protein source. Results from the animal protein substitution also varied both between diets and compartments; however, both materials increased lipase activity in DI. FeM resulted in a significant increase in both total and specific LAP activities suggesting an attempt to increase the digestive capacity in response to low digestibility of the diet while PBY showed very little difference from the FM-fed control fish. The present trial indicates that 20 % PPC, SPC and PBY can partially replace FM in diets for Atlantic salmon. The qualities of ESF and FeM used in this trial show little promise as FM replacement at 20 % inclusion level.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeverfjord G, Krogdahl A (1996) Development and regression of soybean meal induced enteritis in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. distal intestine: a comparison with the intestines of fasted fish. J Fish Dis 19:375–387
Bakke AM, Glover C, Krogdahl Å (2011) Feeding digestion and absorption of nutrients. In: Grosell M, Farrell A, Brauner CJ (eds) The Multifunctional Gut of Fish. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 57–111
Bakke-McKellep AM, Refstie S (2008) Alternative protein sources and digestive function alternations in teleost fishes. In: Cyrino JEP, Bureau DP, Kapoor BG (eds) Feeding and Digestive Functions of Fishes. Science Publisher, Enfield, pp 445–478
Bakke-McKellep AM, Press CM, Baeverfjord G, Krogdahl Å, Landsverk T (2000) Changes in immune and enzyme histochemical phenotypes of cells in the intestinal mucosa of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. with soybean meal-induced enteritis. J Fish Dis 23:115–127
Bakke-McKellep AM, Penn MH, Salas PM, Refstie S, Sperstad S, Landsverk T, Ringø E, Krogdahl Å (2007) Effects of dietary soybean meal inulin and oxytetracycline on intestinal microbiota and epithelial cell stress apoptosis and proliferation in the teleost Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Brit J Nut 97:699–713
Bakke-McKellep AM, Sanden M, Danieli A, Acierno R, Hemre GI, Maffia M, Krogdahl Å (2008) Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr fed genetically modified soybeans and maize: histological digestive metabolic and immunological investigations. Res Vet Sci 84:395–408
Bieth J, Spiess B, Wermuth CG (1974) The synthesis and analytical use of a highly sensitive and convenient substrate of elastase. Biochem Med 11:350–357
Bogevik AS, Tocher DR, Langmyhr E, Waagbø R, Olsen RE (2009) Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) postsmolts adapt lipid digestion according to elevated dietary wax esters from Calanus finmarchicus. Aquac Nut 15:94–103
Buddington RK, Chen JW, Diamond J (1987) Genetic and phenotypic adaptation of intestinal nutrient transport to diet in fish. J Physiol 393:261–281
Buddington RK, Krogdahl A, Bakke-Mckellep AM (1997) The intestines of carnivorous fish: structure and functions and the relations with diet. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 638:67–80
Bureau DP, Harris AM, Cho CY (1999) Apparent digestibility of rendered animal protein ingredients for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 180:345–358
Chikwati EM, Sahlmann C, Holm H, Penn MH, Krogdahl Å, Bakke AM (2013a) Alterations in digestive enzyme activities during the development of diet-induced enteritis in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. Aquaculture 402–403:28–37
Chikwati EM, Gu J, Penn MH, Bakke AM, Krogdahl Å (2013b) Intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and migration in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L.: effects of temperature and inflammation. Cell Tissue Res 353:123–137
Cho CY, Bureau DP (1997) Reduction of waste output from salmonid aquaculture through feeds and feeding. Progress Fish Cult 59:155–160
Cortés E, Papastamatiou YP, Carlson JK, Ferry-Graham L, Wetherbee BM (2008) An overview of the feeding ecology and physiology of elasmobranch fishes. In: Cyrino JEP, Bureau DP, Kapoor BG (eds) Feeding and digestive functions of fish. Science Publisher, Enfield, pp 393–443
Forster I, Higgs DA, Bell GR, Dosanjh BS, March BE (1988) Effect of diets containing herring oil oxidized to different degrees on growth and immunocompetence of juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Can J Fisheries Aquat Sci 45:2187–2194
Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their affects in fish. Aquaculture 199:197–227
Frøystad MK, Lilleeng E, Sundby A, Krogdahl Å (2006) Cloning and characterization of α-amylase from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 145:479–492
Gatlin DM, Barrows FT, Brown P, Dabrowski K, Gaylord TG, Hardy RW, Herman E, Hu G, Krogdahl Å, Nelson R, Overturf K, Rust M, Sealey W, Skonberg DJ, Souza E, Stone D, Wilson R, Wurtele E (2007) Expanding the utilization of sustainable plant products in aquafeeds: a review. Aquac Res 38:551–579
Gelman A, Hill J (2007) In: Data analysis using regression and multilevel/hierarchical models. Alvarez M, Beck NL, Wu LL (eds.) Cambridge University Press, New York
Gelman A, Kuz’mina V, Drabkin V, Glatman L (2008) Temperature adaptation of digestive enzymes in fish. In: Bureau DP, Kapoor BG, Cyrino JEP (eds) Feeding and digestive functions of fishes. Science Publishers, New Hampshire
Gill N, Higgs DA, Skura BJ, Rowshandeli M, Dosanjh BS, Mann J, Gannam AL (2006) Nutritive value of partially dehulled and extruded sunflower meal for post-smolt Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in sea water. Aquac Res 37:1348–1359
Gjellesvik DR, Lombardo D, Walther BT (1992) Pancreatic bile salt dependent lipase from cod (Gadus morhua): purification and properties. BBA Lipid Lipid Metab 1124:123–134
Gómez-Requeni P, Mingarro M, Calduch-Giner JA, Médale F, Martin SAM, Houlihan DF, Kaushik S, Pérez-Sánchez J (2004) Protein growth performance amino acid utilization and somatotropic axis responsiveness to fish meal replacement by plant protein sources in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 232:493–510
Hardy RW (1996) Alternate protein sources for salmon and trout diets. Anim Feed Sci Tech 59:71–80
Hardy RW (2010) Utilization of plant proteins in fish diets: effects of global demand and supplies of fishmeal. Aquac Res 41:770–776
Hartviksen M, Vecino JLG, Ringø E, Bakke AM, Wadsworth S, Krogdahl Å, Ruohonen K, Kettunen A (2014) Alternative dietary protein sources for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) effect on intestinal microbiota intestinal and liver histology and growth. Aquac Nut DOI: 10.1111/anu.12087
Helland SJ, Grisdale-Helland B, Nerland S (1996) A simple method for the measurement of daily feed intake of groups of fish in tanks. Aquaculture 139:157–163
Kortner TM, Björkhem I, Krasnov A, Timmerhaus G, Krogdahl A (2014) Dietary cholesterol supplementation to a plant-based diet suppresses the complete pathway of cholesterol synthesis and induces bile acid production in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Br J Nutr 111:2089–2103
Koshio S, Ackman RG, Lall SP (1994) Effects of oxidized herring and canola oils in diets on growth survival and flavor of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. J Agric Food Chem 42:1164–1169
Kraugerud OF, Penn M, Storebakken T, Refstie S, Krogdahl Å, Svihus B (2007) Nutrient digestibilities and gut function in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed diets with cellulose and non-starch polysaccharides from soy. Aquaculture 273:96–107
Krogdahl Å, Bakke-McKellep AM (2005) Fasting and refeeding causes rapid changes in the intestinal tissue mass and digestive enzyme capacities of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 141:450–460
Krogdahl Å, Bakke-McKellep AM, Baeverfjord G (2003) Effects of graded levels of standard soybean meal on intestinal structure mucosal enzyme activities and pancreatic response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac Nut 9:361–371
Krogdahl Å, Hemre GI, Mommsen TP (2005) Carbohydrates in fish nutrition: digestion and absorption in postlarval stages. Aquac Nut 11:103–122
Krogdahl Å, Penn MH, Thorsen J, Refstie S, Bakke AM (2010) Important antinutrients in plant feedstuffs for aquaculture: an update on recent findings regarding responses in salmonids. Aquac Res 41:333–344
Kuz’mina V (2008) Classical and modern concepts in fish digestion. In: Cyrino JEP, Bureau DP, Kapoor BG (eds) Feeding and digestive functions of fishes. Science Publisher, Enfield, pp 85–154
Lilleeng E, Froystad MK, Ostby GC, Valen EC, Krogdahl A (2007) Effects of diets containing soybean meal on trypsin mRNA expression and activity in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 147:25–36
Naylor RL, Hardy RW, Bureau DP, Chiu A, Elliott M, Farrell AP, Forster I, Gatlin DM, Goldburg RJ, Hua K, Nichols PD (2009) Feeding aquaculture in an era of finite resources. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:15103–15110
Nicieza AG, Reiriz L, Braña F (1994) Variation in digestive performance between geographically disjunct populations of Atlantic salmon: countergradient in passage time and digestion rate. Oecologia 99:243–251
NRC & Nutrition (2011) Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp. The National Academies Press, USA
Olli JJ, Krogdahl Å, van den Ingh TSGAM, Brattås LE (1994) Nutritive Value of Four Soybean Products in Diets for Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar, L.). Acta Agric Scand Sect A 44:50–60
Penn MH, Bendiksen EA, Campbell P, Krogdahl Å (2011) High level of dietary pea protein concentrate induces enteropathy in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 310:267–273
Pringle GM, Houlihan DF, Callanan KR, Mitchell AI, Ravnard RS, Houghton GH (1992) Digestive enzyme levels and histopathology of pancreas disease in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Comp Biochem Physiol A: Mol Integr Physiol 102:759–768
R Development Core Team (2012) R a language and environment for statistical computing. In R foundation of statistical computing. Vienna, Austria
Ray AK, Ghosh K, Ringø E (2012) Enzyme-producing bacteria isolated from fish gut: a review. Aquac Nut 18:465–492
Refstie S, Landsverk T, Bakke-McKellep A-M, Ringø E, Sundby A, Shearer KD, Krogdahl Å (2006) Digestive capacity, intestinal morphology, and microflora of 1-year and 2-year old Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) fed standard or bioprocessed soybean meal. Aquaculture 261:269–284
Salim M, Aziz I, Sultan JI, Mustafa I (2004) Evaluation of apparent digestibility of fishmeal sunflower meal and rice polishings for Labeo rohita Pak. J Life Soc Sci 2:139–144
Stevens CE, Hume ID (1995) The digestive system of fish amphibians reptiles and birds. Comparative physiology of the vertebrate digestive system. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Stone D (2003) Carbohydrate utilization in fish. Rev Fisheries Sci 1:337–369
van den Ingh TSGAM, Olli JJ, Krogdahl Å (1996) Alcohol-soluble components in soybeans cause morphological changes in the distal intestine of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J Fish Dis 19:47–53
Zambonino Infante JL, Cahu CL (2001) Ontogeny of the gastrointestinal tract of marine fish larvae. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 130:477–487
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the technical staff at EWOS Innovation research institute in Dirdal, Norway, for their help in fish management and care and Ellen Hage (NMBU) for skillful sample preparation, analyses of trypsin, lipase and LAP activities, and chyme DM and element content. The present study was funded by Norwegian Research Council project no. 187264/S40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartviksen, M., Bakke, A.M., Vecino, J.G. et al. Evaluation of the effect of commercially available plant and animal protein sources in diets for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): digestive and metabolic investigations. Fish Physiol Biochem 40, 1621–1637 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9953-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9953-4