Abstract
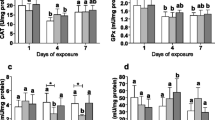
Prostaglandin H synthetases (cyclooxygenases) catalyze the initial reactions leading to prostanoids in animals. They form interesting links between diet and fish physiology as the type and nature of eicosanoids are affected by dietary lipid sources. Their expression is likely to be affected by tissues and environmental conditions leading to altered amount and ratio of eicosanoids. These mechanisms are, however, poorly understood in fish. In the present study, Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. (1,000 g, 10°C, seawater) were subjected to acute chasing stress. Liver, kidney, spleen, gill, muscle, midgut and hindgut were extracted before and 1 h post-stress and analyzed for mRNA expression of cox1, cox2a and cox2b. Intestinal samples were further sampled over 24 h for both cox expression and analysis of 15 eicosanoids and isoprostanes of the n-3 and n-6 series. Results show a highly variable but consecutively expression of cox1, cox2a and cox2b in most of the tissues analyzed. Low levels were only found for cox2a in liver and cox2b in liver and kidney. The study reveals the general trend that cox1 is about 10 times the level of cox2b, which again is about 10 times the level of cox2a. Cox2b shows the highest level of expression in the gills indicating a possible higher requirement for this protein in gills. Imposing stress to the fish induces a temporal increase in the expression of cox2a in the midgut, while the gene expression of the other genes is not affected in any of the tissues analyzed. There is, however, a general tendency to increased expression of both cox2 genes that merits further studies. Stress had a profound effect on the intestinal eicosanoid content which showed a general decrease in midgut sections after stress that persisted for at least 24 h.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breder CD, Dewitt D, Kraig RP (1995) Characterization of inducible cyclooxygenase in rat brain. J Comp Neurol 355:296–315
Calder PC (2006) Polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammation. Prostagl Leukotr Ess Fatty Acids 75:197–202
de Pablo MA, de Cienfuegos GA (2000) Modulatory effects of dietary lipids on immune system functions. Immunol Cell Biol 78:31–39
Dinchuk JE, Car BD, Focht RJ, Johnston JJ, Jaffee BD, Covington MB, Contel NR, Eng VM, Collins RJ, Czerniak PM (1995) Renal abnormalities and an altered inflammatory response in mice lacking cyclooxygenase II. Nature 378:406–409
Ferrer R, Moreno JJ (2010) Role of eicosanoids on intestinal epithelial homeostasis. Biochem Pharmacol 80:431–438
Gil-Martens L (2010) Inflammation as a potential risk factor for spinal deformities in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J Appl Ichthyol 26:350–354
Harris SI, Kuss M, Hubbard RC, Goldstein JL (2001) Upper gastrointestinal safety evaluation of parecoxib sodium, a new parenteral cyclooxygenase-2-specific inhibitor, compared with ketorolac, naproxen, and placebo. Clin Therap 23:1422–1428
Henderson RJ, Tocher DR (1987) The lipid composition and biochemistry of freshwater fish. Prog Lipid Res 26:281–347
Hodeify RF, Kreydiyyeh SI (2007) PGE2 reduces net water and chloride absorption from the rat colon by targeting the Na+/H+ exchanger and the Na+K+2Cl− cotransporter. Prostag Leukot Ess Fatty Acids 76:285–292
Homaidan FR, Chakroun I, Haidar HA (2002) Protein regulators of eicosanoid synthesis: role in inflammation. Curr Protein Peptide Sci 3:467–484
Ingerslev HC, Cunningham C, Wergeland HI (2006) Cloning and expression of TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and COX-2 in an anadromous and landlocked strain of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) during the smolting period. Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:450–461
Ishikawa TO, Herschman HR (2007) Two inducible, functional cyclooxygenase-2 genes are present in the rainbow trout genome. J Cell Biochem 102:1486–1492
Ishikawa T, Griffin KJP, Banerjee U, Herschman HR (2007) The zebrafish genome contains two inducible, functional cyclooxygenase-2 genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:181–187
Langenbach R, Morham SG, Tiano HF, Loftin CD, Ghanayem BI, Chulada PC, Mahler JF, Lee CA, Goulding EH, Kluckman KD (1995) Prostaglandin synthase 1 gene disruption in mice reduces arachidonic acid-induced inflammation and indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration. Cell 83:483–492
Lebman DA, Spiegel S (2008) Thematic review series: sphingolipids—cross-talk at the crossroads of sphingosine-1-phosphate, growth factors, and cytokine signaling. J Lipid Res 49:1388–1394
Liu W, Cao DZ, Oh SF, Serhan CN, Kulmacz RJ (2006) Divergent cyclooxygenase responses to fatty acid structure and peroxide level in fish and mammalian prostaglandin H synthases. FASEB J 20:1097–1108
Masferrer JL, Seibert K (1994) Regulation of prostaglandin synthesis by glucocorticoids. Receptor 4:25–30
Masoodi M, Nicolaou A (2006) Lipidomic analysis of twenty-seven prostanoids and isoprostanes by liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:3023–3029
Morham SG, Langenbach R, Loftin CD, Tiano HF, Vouloumanos N, Jennette JC, Mahler JF, Kluckman KD, Ledford A, Lee CA (1995) Prostaglandin synthase 2 gene disruption causes severe renal pathology in the mouse. Cell 83:473–482
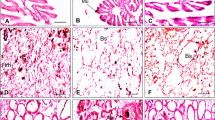
Olsen RE, Sundell K, Hansen T, Hemre GI, Myklebust R, Mayhew TM, Ringø E (2002) Acute stress alters the intestinal lining of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L.: an electron microscopical study. Fish Physiol Biochem 273:211–221
Olsen RE, Sundell K, Mayhew TM, Myklebust R, Ringø E (2005) Acute stress alters intestinal function of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquaculture 250:480–495
Olsvik PA, Lie KK, Jordal AE, Nilsen TO, Hordvik I (2005) Evaluation of potential reference genes in real-time RT-PCR studies of Atlantic salmon. BMC Mol Biol 6:21
Oxley A, Jolly C, Eide T, Jordal AE, Svardal A, Olsen RE (2010) The combined impact of plant-derived dietary ingredients and acute stress on the intestinal arachidonic acid cascade in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Br J Nutr 103:851–861
Rowley AF, Knight J, Lloyd-Evans P, Holland JW, Vickers PJ (1995) Eicosanoids and their role in immune modulation in fish: a brief overview. Fish Shellfish Immun 5:549–567
Russo-Marie F (2004) Antiinflammatory steroids. In: Curtis-Prior P (ed) The eicosanoids. Wiley, Chichester, pp 327–332
Smith WL (2008) Nutritionally essential fatty acids and biologically indispensable cyclooxygenases. Trends Biochem Sci 33:27–37
Tine M, McKenzie DJ, Bonhomme F, Durand JD (2011) Salinity-related variation in gene expression in wild populations of the black-chinned tilapia from various West African coastal marine estuarine and freshwater habitats. Est Coast Shelf Sci 91:102–109
Tocher DR (2003) Metabolism and function of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish. Rev Fish Sci 11:107–184
Vance JE (2008) Thematic review series: glycerolipids. Phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine in mammalian cells: two metabolically related aminophospholipids. J Lipid Res 49:1377–1387
Wang D, Mann JR, Dubois N (2005) The role of prostaglandins and other eicosanoids in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterol 128:1445–1461
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Wiseman S, Osachoff H, Bassett E, Malhotra J, Bruno J, VanAggelen G, Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM (2007) Gene expression pattern in the liver during recovery from an acute stressor in rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol D 2:234–244
Zakar T, Hirst JJ, Mijovic JE, Olson DM (1995) Glucocorticoids stimulate the expression of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-2 in amnion cells. Endocrinol 136:1610–1616
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the WEALTH project (Welfare and health in sustainable aquaculture, EU FP6 project no: No 501984). The authors are also indebted to Karen Anita Kvestad, IMR, Matre and Laila Unneland, IMR, Bergen, for excellent technical assistance and Dr. Anthony Oxley for assisting in the setup and sampling process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olsen, R.E., Svardal, A., Eide, T. et al. Stress and expression of cyclooxygenases (cox1, cox2a, cox2b) and intestinal eicosanoids, in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L.. Fish Physiol Biochem 38, 951–962 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9581-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9581-1