Abstract
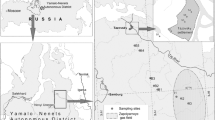
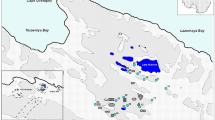
To investigate the distribution and source pathways of environmentally critical trace metals in coastal Antarctica, trace elemental concentrations were analyzed in 36 surface snow samples along a coast to inland transect in the Ingrid Christensen Coast of East Antarctica. The samples were collected and analyzed using the clean protocols and an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. Within the coastal ice-free and ice-covered region, marine elements (Na, Ca, Mg, K, Li, and Sr) revealed enhanced concentrations as compared with inland sites. Along with the sea-salt elements, the coastal ice-free sites were also characterized by enhanced concentrations of Al, Fe, Mn, V, Cr, and Zn. The crustal enrichment factors (Efc) confirm a dominant crustal source for Fe and Al and a significant source for Cr, V, Co, and Ba, which clearly reflects the influence of petrological characteristics of the Larsemann Hills on the trace elemental composition of surface snow. The Efc of elements revealed that Zn, Cu, Mo, Cd, As, Se, Sb, and Pb are highly enriched compared with the known natural sources, suggesting an anthropogenic origin for these elements. Evaluation of the contributions to surface snow from the different sources suggests that while contribution from natural sources is relatively significant, local contamination from the increasing research station and logistic activities within the proximity of study area cannot be ignored.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argentini, S., Viola, A., Sempreviva, A., & Petenko, I. (2005). Summer PBL height at the plateau site of Dome C, Antarctica. Boundary Layer Meteorology, 115(3), 409–422.
Barbante, C., Turetta, C., Gambaro, A., Capodaglio, G., & Scarponi, G. (1998). Sources and origins of aerosols reaching Antarctica as revealed by lead concentration profiles in shallow snow. Annals of Glaciology, 27, 674–678.
Bargagli, R. (2000). Trace metals in Antarctica related to climate change and increasing human impact. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 166, 129–73.
Berg, T., Royset, O., & Steinnes, E. (1994). Trace elements in atmospheric precipitation at Norwegian background stations (1989–1990) measured by ICP-MS. Atmospheric Environment, 28(21), 3519–3536.
Bertler, N., Mayewski, P. A., Aristarain, A., Barrett, P., Becagli, S., Bernardo, R., et al. (2005). Snow chemistry across Antarctica. Annals of Glaciology, 41, 167–179.
Boutron, C. F., & Wolff, E. W. (1989). Heavy metal and sulphur emissions to the atmosphere from human activities in Antarctica. Atmospheric Environment, 23, 1669–1675.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1979). Environmental chemistry of the elements (p. 333). Elsevier: New York.
Coplen, T. B. (1996). New guidelines for reporting stable hydrogen, carbon and oxygen isotope ratio data. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 3359–3360.
Coplen, T. B., Wildman, J. D., & Chen, J. (1991). Improvements in the gaseous hydrogen–water equilibration technique for hydrogen isotope ratio analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 63(9), 910–912.
Cunningham, W. C., & Zoller, W. H. (1981). The chemical composition of remote area aerosols. Journal of Aerosol Science, 12(4), 367–384.
Delmotte, M. V., Hou, S., Ekaykin, A., Jouzel, J., Aristarain, A., Bernardo, R. T., et al. (2008). A review of Antarctic surface snow isotopic composition: observations, atmospheric circulation, and isotopic modeling. Journal of Climate, 21, 3359–3387.
Ding, M. H., Xiao, C. D., Jin, B., Ren, J. W., Qin, D., & Sun, W. Z. (2010). Distribution of δ 18O in surface snow along a transect from Zhongshan Station to Dome A, East Antarctica. Chinese Science Bulletin, 5(24), 2709–2714. doi:10.1007/s114340103179-3.
Epstein, S., & Mayeda, T. (1953). Variations of O18 contents of waters from natural sources. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 4, 213–224.
Gabriell, P., Barbante, C., Boutron, C., Cozzi, G., Gaspari, V., Planchon, F., et al. (2005). Variations in atmospheric trace elements in Dome C (East Antarctica) ice over the last two climatic cycles. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 6420–6429.
Gasparon, M., & Burgess, J. S. (2000). Human impacts in Antarctica: trace element geochemistry of freshwater lakes in the Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica. Environmental Geology, 39, 963–976.
Gasparon, M., & Matschullat, J. (2006a). Trace metals in Antarctic ecosystems: results from the Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica. Applied Geochemistry, 2, 1593–1612.
Gasparon, M., & Matschullat, J. (2006b). Geogenic sources and sinks of trace metals in the Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica: natural processes and human impact. Applied Geochemistry, 21, 318–334.
Grotti, M., Soggia, F., Ardini, F., & Magi, E. (2011). Major and trace element partitioning between dissolved and particulate phases in Antarctic surface snow. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 13, 2511–2520. doi:10.1039/C1EM10215J.
Hinkley, T., Lamothe, P. J., Wilson, S. A., Finnegan, D. L., & Gerlach, T. M. (1999). Metal emission from Kilauea, and a suggested revision of the estimated worldwide metal output by quiescent degassing of volcanoes. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 170, 315–325.
Hong, S., Lluberas, A., & Rodriguez, F. (2000). A clean protocol for determining ultralow heavy metal concentrations: its application to the analysis of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn and Mn in Antarctic snow. Korean Journal of Polar Research, 11, 35–47.
Hong, S., Lluberas, A., Lee, G., & Park, J. K. (2002). Natural and anthropogenic heavy metal deposition to the Snow in King George Island, Antarctic Peninsula. Ocean and Polar Research, 24(3), 279–287.
Hur, S. D., Cunde, X., Hong, S., Barbante, C., Gabrielli, P., Lee, K., et al. (2007). Seasonal patterns of heavy metal deposition to the snow on Lambert Glacier basin, East Antarctica. Atmospheric Environment, 41(38), 8567–8578.
Ikegawa, M., Kimura, M., Honda, K., Makita, K., Fujii, Y., & Itokawa, Y. (1997). Springtime peaks of trace metals in Antarctic snow. Environmental Health Perspectives, 105(6), 654–659.
Ikegawa, M., Kimura, M., Honda, K., Akabane, I., Makita, K., Motoyama, H., et al. (1999). Geographical variations of major and trace elements in East Antarctica. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 1457–1467.
Jianjun, W., Liqi, C., Xulin, Y., & Yuanhui, Z. (2010). Characteristics of metals in the aerosols of Zhongshan Station, Antarctica. Advances in Polar science, 21(1), 46–59. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1085.2010.00046.
Jouzel, J., & Merlivat, L. (1984). Deuterium and oxygen 18 in precipitation: modeling of the isotopic effects during snow formation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89, 11749–11757.
Jouzel, J., Alley, R. B., Cuffey, K. M., Dansgaard, W., Grootes, P., Hoffmann, P., et al. (1997). Validity of the temperature reconstruction from water isotopes in ice cores. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102, 2647–26487.
Lambert, G., Ardouin, B., & Sanak, J. (1990). Atmospheric transport of trace elements towards Antarctica. Tellus, 42B, 76–82.
Legrand, M., & Mayewski, P. A. (1997). Glaciochemistry of polar ice cores: a review. Reviews of Geophysics, 35, 219–243.
Martin, J. M., & Whitfield, M. (1983). The significance of the river input of chemical elements to the ocean. In C. S. Wong, E. Boyle, K. W. Bruland, J. D. Bourton, & E. D. Goldberg (Eds.), Trace metals in sea water (pp. 265–296). New York: Plenum.
Nriagu, J. O. (1989). A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature, 338, 47–49.
Planchon, F. A. M., Boutron, C. F., Barbante, C., Cozzi, G., Gasperi, V., Wolff, E. W., et al. (2002). Changes in atmospheric heavy metals in Antarctic snow from Coats Land since the mid-nineteenth century. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 200(1–2), 207–222.
Röthlisberger, R., Mulvaney, R., Wolff, E. W., Hutterli, M. A., Bigler, M., Sommer, S., et al. (2002). Dust and sea-salt variability in central East Antarctica (Dome C) over the last 45 k years and its implications for southern high-latitude climate. Geophysical Research Letters, 29(20). doi:10.1029/2002GL015186.
Shouzhen, F., Zuo, X., & Wanqing, C. (2008). Topographic features around Zhongshan Station, Southeast of Prydz Bay. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 26(4), 467–472. doi:10.1007/s00343-008-0467-8.
Sodeau, J. (2010). Snow matters in the Polar Regions. Environmental Research Letters, 5(1). doi:10.1088/1748-9326-5-1-01100.
Stuwe, K., & Powell, R. (1989). Low pressure granulite facies metamorphism in the Larsemann Hills Area, East Antarctica; petrology and tectonic implications for the Prydz Bay area. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 7, 465–48.
Suttie, E. D., & Wolff, E. W. (1992). Seasonal input of heavy metals to Antarctic snow. Tellus, 44B, 351–357.
Thamban, M., Laluraj, C. M., Mahalinganathan, K., Redkar, B. L., Naik, S. S., & Shrivastava, P. K. (2010). Glaciochemistry of surface snow from the Ingrid Christensen Coast, East Antarctica, and its environmental implications. Antarctic Science, 22(4), 435–441.
Tin, T., Fleming, Z. L., Hughes, K. A., Ainley, D. G., Convey, P., Moreno, C. A., et al. (2009). Impacts of local human activities on the Antarctic environment. Antarctic Science, 21(1), 3–33. doi:10.1017/S09541020090017.
Tuncel, G., Aras, N. K., & Zoller, W. H. (1989). Temporal variations and sources of elements in the South Pole atmosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 94(D10), 13025–13038.
Vallelonga, P., Van de Velde, K., Candelone, J. P., Morgan, V. I., Boutron, C. F., & Rosman, K. J. R. (2002). The lead pollution history of Law Dome, Antarctica, from isotopic measurements on ice cores: 1500 ad to 1989 ad. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 203, 291–306.
Van de Velde, K., Vallelonga, P., Candelone, J. P., Rosman, K. J. R., Gaspari, V., Cozzi, G., et al. (2005). Pb isotope record over one century in snow from Victoria Land, Antarctica. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 232, 95–108.
Wedepohl, K. H. (1995). The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta, 59(7), 1217–1232.
Williamson, B. R., Kreutz, K. J., Mayewski, P. A., Bertler, N. A. N., Sneed, S., Handley, M., et al. (2007). A coastal transect of McMurdo Dry Valleys (Antarctica) snow and firn: marine and terrestrial influences on glaciochemistry. Journal of Glaciology, 53(183), 681–693.
Wolff, E. W., & Suttie, E. D. (1994). Antarctic snow record of Southern Hemisphere lead pollution. Geophysical Research Letters, 21, 781–784.
Wolff, E. W., Suttie, E. D., & Peel, D. A. (1999). Antarctic snow record of cadmium, copper and zinc content during the twentieth century. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 1535–1541.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India for the project support. We thank Rasik Ravindra, Director, NCAOR, Goa, for his encouragement and interest in this study. Sincere thanks are extended to B. L Redkar for his assistance with sample processing and analysis as well as C.M. Laluraj for support. NOAA Air Resource Laboratory is acknowledged for the HYSPLIT meteorological model used in this paper. This is NCAOR contribution No. 23/2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 10
Back trajectory data from NOAA for two different months (February and March 2007) at 10 m level for four different sampling sites along the sampling transect (JPEG 93 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thamban, M., Thakur, R.C. Trace metal concentrations of surface snow from Ingrid Christensen Coast, East Antarctica—spatial variability and possible anthropogenic contributions. Environ Monit Assess 185, 2961–2975 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2764-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2764-0