Abstract
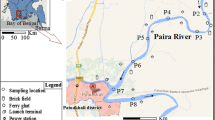
The objective of the study is to reveal the seasonal variations in the river water and sediment quality with respect to heavy metal contamination. To get the extent of trace metals contamination, water and sediment samples were collected from five different sites along the course of Sabarmati River and its tributary Kharicut canal in pre-monsoon, monsoon and post-monsoon seasons. The concentration of trace metals such as chromium, copper, lead, nickel and zinc was determined using inductively coupled plasma spectroscopy. The concentrations of heavy metals were found to be higher in the pre-monsoon season than in the monsoon and post-monsoon seasons in water samples. The pollution load index, contamination factor and degree of contamination (C d) in sediments were calculated to know the extent of anthropogenic pressures. The values of C d clearly indicated very high degree of contamination at Kharicut canal (S-4: 32.25 and S-5: 54.52) and considerable degree of contamination at three sites of Sabarmati river viz; S-1, S-2 and S-3 with values 14.30, 14.42 and 17.21, respectively. Lead and nickel could not be traced in any of the river water samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abida Begum, Ramaiah, M., Harikrishna, Khan, I. & Veena, K. (2009). Heavy metal pollution and chemical profile of Cauvery river water. E-Journal of Chemistry. 6 (1): 47–52.
Aboud, S. J., & Nandini, N. (2009). Heavy metal analysis and sediment quality values in urban lakes. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 5(6), 678–687.
APHA, Clescerl, L. S., Greenberg, A. E., Eaton A. D. (1998). Standard Methods for Examination of Water & Wastewater (20th edn.). Washington, DC.
Dalai, T. K., Rengarajan, R., & Patel, P. P. (2004). Sediment geochemistry of the Yamuna river systems in the Himalaya: Implications to weathering and transport. Geochemical Journal, 38, 441–453.
Datta, D. K., & Subramanian, V. (1998). Distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Ganges-Brahamputra-Meghna river system in the Bengal basin. Environmental Geology, 36, 93–101.
Davies, C. A., Tomlinson, K., & Stephenson, T. (1991). Heavy metals in river Tees estuary sediments. Environmental Technology, 12, 961–972.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control—A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Interim Freshwater sediment quality guidelines (ISQGs). (1999). Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the protection of Aquatic life, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, updated 2001. ISBN 1-896997-34-1.
Khaiwal, R., Ameena, M., Monika, R., & Kaushik, A. (2003). Seasonal variations in physico-chemical characteristics of River Yamuna in Haryana and its ecological best-designated use. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 5, 419–426.
Kucuksezgin, F., Uluturrhan, E., & Batki, H. (2008). Distribution of heavy metals in water, particulate matter and sediment of Gediz River (Eastern Aegean). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 141, 213–225.
Kumar, N. J. I., Kumar, R. N., George, B., Sajish, P. R., & Viyol, S. (2009). An assessment of heavy metal distribution at lower reaches of three permanent estuaries of Gulf of Khambhat, India. Pollution Research, 28(4), 597–601.
Lohani, M. B., Singh, A., Rupainwar, D. C., & Dhar, D. N. (2008). Seasonal variations of heavy metal contamination in river Gomti of Lukhnow city region. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 147, 253–263.
Maiti S. K. (2001). Hand book of methods in environmental studies, vol. I. Water and waste water analysis. ABD Publication, Jaipur, pp 24, 25.
Papafilippaki, A. K., Kotti, M. E., & Stavroulakis, G. G. (2008). Seasonal variations in dissolved heavy metals in the Keritis River, Chania, Greece. Global NEST Journal, 10(3), 320–325.
Reza, R., & Singh, G. (2010). Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for river water. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 7(4), 785–792.
Saha, S. B., Mitra, A., Bhattacharya, S. B., & Choudhary, A. (2001). Status of Sediment with special reference to heavy metal pollution of a brackishwater tidal ecosystem in northern Sundarbans of West Bengal. Tropical Ecology, 42(1), 127–132.
Saison, C., Schwartz, & Morel, J. L. (2004). Hyperaccumulation of metals by Thlapsi caerulescence as affected by root development and Cd–Zn/Ca–Mg interaction. International Journal of Phytology, 6(1), 49–61.
Sankar, R., Ramkumar, L., Rajkumar, M., Sun, J., & Ananthan, G. (2010). Seasonal variations in physico-chemical parameters and heavy metals in water and sediments of Uppanar estuary, Nagapattinam, India. Journal of Environmental Biology, 31(5), 681–686.
Shah, A. N., Ghariya, Puranik, A. S., A. D. & Suthar, M. B. (2008). A preliminary study on water quality from Kharicut Canal passing through Vatva area of Ahmedabad city, Gujarat State. Electronic Journal of Environmental Sciences, 1, 49–56.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192.
Venugopal, T., Giridharan, L., & Jayaprakash, M. (2009). Characterization and risk assessment studies of bed sediments of River Adyar—An application of speciation study. International Journal of Environmental Research, 3(4), 581–598.
WHO (1998). Global fresh water quality assessment report. WHO Int. Rept/PEP/88, Geneva.
WHO (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn., World Health Organization, ISBN: 92-4-154638-7, pp 516.
Wilken, R. D., & Hintelmann, H. (1991). Mercury and methylmercury in sediments and suspended particles from the River Elbe, North Germany. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 56, 427–437.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to University Grants Commission, New Delhi for providing financial assistance. We are also thankful to Sophisticated Instrumentation Centre for Applied Research and Testing, Vallabh Vidyanagar, Gujarat, for their assistance in sample analyses using inductively coupled plasma spectroscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R.N., Solanki, R. & Kumar, J.I.N. Seasonal variation in heavy metal contamination in water and sediments of river Sabarmati and Kharicut canal at Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Environ Monit Assess 185, 359–368 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2558-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2558-4