Abstract
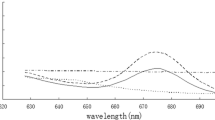
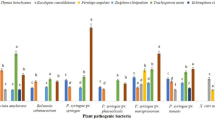
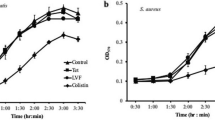
We prepared an ethanol extract from Laminaria japonica, and obtained five fractions from the extract using various solvents. We investigated the antibacterial activities of the fractions against Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus (Spieckermann & Kotthoff) Davis et al., the causal agent of bacterial ring rot of potato (BRR). Among all the fractions, the petroleum ether fraction showed the strongest (P < 0.05) antibacterial activity against C. michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus. We analyzed the petroleum ether fraction to detect the components with antibacterial activity, and identified 24 compounds. The main constituents of the petroleum ether extract were esters (35.28 %) and acids (44.84 %). Cell membrane permeability assays, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses revealed that the petroleum ether fraction caused drastic ultrastructural changes in the cells of the pathogen. The petroleum ether fraction caused envelope disruption, cell deformation, the separation of the cell wall from the cell membrane, and the formation of vacuoles. These results clearly indicate that the petroleum ether fraction obtained from L. japonica shows strong antibacterial activity against the causal agent of BRR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar, Y., Yeoung, Y. R., & Isman, M. B. (2008). Comparative bioactivity of selected extracts from Meliaceae and some commercial botanical insecticides against two noctuid caterpillars, Trichoplusia ni and Pseudaletia unipuncta. Phytochemistry Reviews, 7(1), 77–88.
Alakomi, H. L., Skyttä, E., Saarela, M., Mattila-Sandholm, T., Latva-Kala, K., & Helander, I. M. (2000). Lactic acid permeabilizes Gram-negative bacteria by disrupting the outer membrane. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(5), 2001–2005.
Axe, D. D., & Bailey, J. E. (1995). Transport of lactate and acetate through the energized cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coil. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 47(1), 8–19.
Bajpai, V. K., Shukla, S., & Kang, S. C. (2008). Chemical composition and antifungal activity of essential oil and various extract of Silene armeria L. Bioresource Technology, 99(18), 8903–8908.
Bajpai, V. K., Sharma, A., & Baek, K. H. (2013). Antibacterial mode of action of Cudrania tricuspidata fruit essential oil, affecting membrane permeability and surface characteristics of food-borne pathogens. Food Control, 32(2), 582–590.
Barnard, M., Padgitt, M., & Uri, N. D. (1997). Pesticide use and its measurement. International Pest Control, 39, 161–164.
Bendimerad, N., Taleb Bendiab, S. A., Benabadji, A. B., Fernandez, X., Valette, L., & Lizzani-Cuvelier, L. (2005). Composition and antibacterial activity of Pseudocytisus integrifolius (Salisb.) essential oil from Algeria. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(8), 2947–2952.
Blažević, I., Radonić, A., Mastelić, J., Zekić, M., Skočibušić, M., & Maravić, A. (2010). Hedge mustard (Sisymbrium officinale): chemical diversity of volatiles and their antimicrobial activity. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 7(8), 2023–2034.
Brul, S., & Coote, P. (1999). Preservative agents in foods: mode of action and microbial resistance mechanisms. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 50(1–2), 1–17.
Chao, L. K., Hua, K. F., Hsu, H. Y., Cheng, S. S., Liu, J. Y., & Chang, S. T. (2005). Study on the antiinflammatory activity of essential oil from leaves of Cinnamomum osmophloeum. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(18), 7274–7278.
Chen, Y., & Dai, G. (2012). Antifungal activity of plant extracts against Colletotrichum lagenarium, the causal agent of anthracnose in cucumber. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 92(9), 1937–1943.
Chen, Y., Yue, X. L., & Wang, Y. C. (2010). Features and integrated management of ring-rot in potato. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 38(7), 140–141.
Chen, L., Liu, S., Chen, X., & Peng, L. (2011). Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oils from Dalbergia odorifera T Chen. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 32(6), 1165–1167.
Cherrington, C. A., Hinton, M., Mead, G. C., & Chopra, I. (1991). Organic acids: chemistry, antibacterial activity and practical application. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 32, 87–108.
Choi, Y. S., Choi, J. H., Han, D. J., Kim, H. Y., Kim, H. W., Lee, M. A., et al. (2012). Effects of Laminaria japonica on the physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of reduced-fat pork patties. Meat Science, 91(1), 1–7.
Cowan, M. M. (1999). Plant products as antimicrobial agents. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 12(4), 564–582.
De Boer, S. H., & Slack, S. (1984). Current status and prospects for detecting and controlling bacterial ring rot of potatoes in North America. Plant Disease, 68, 841–844.
Deng, X., Qin, S., Zhang, Q., Jiang, P., Cui, Y., & Li, X. (2009). Microprojectile bombardment of Laminaria japonica gametophytes and rapid propagation of transgenic lines within a bubble-column bioreactor. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 97(3), 253–261.
Derbalah, A. S., Dewir, Y. H., & El-Sayed, A. E. B. (2012). Antifungal activity of some plant extracts against sugar beet damping-off caused by Sclerotium rolfsii. Annals of Microbiology, 62(3), 1021–1029.
Devi, P. K., Nisha, S. A., Sakthivel, R., & Pandian, S. K. (2010). Eugenol (an essential oil of clove) acts as an antibacterial agent against Salmonella typhi by disrupting the cellular membrane. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 130(1), 107–115.
Elbadri, G. A., Lee, D. W., Park, J. C., Yu, H. B., & Choo, H. Y. (2008). Evaluation of various plant extracts for their nematicidal efficacies against juveniles of Meloidogyne incognita. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 11(2), 99–102.
Glombitza, K. W. (1979). Antibiotics from algae. In H. A. Hoppe, T. Levring, & Y. Tanaka (Eds.), Marine algae in pharmaceutical science (pp. 303–342). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Go, H., Hwang, H. J., & Nam, T. J. (2010). A glycoprotein from Laminaria japonica induces apoptosis in HT-29 colon cancer cells. Toxicology in Vitro, 24(6), 1546–1553.
Guo, D., Yang, S., Zhang, X., & Shen, H. (2004). Primary research on the antifungal compositions in the root of Stellera chamaejasme. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 39(3), 325–329.
Harish, S., Saravanakumar, D., Radjacommare, R., Ebenezar, E. G., & Seetharaman, K. (2008). Use of plant extracts and biocontrol agents for the management of brown spot disease in rice. BioControl, 53, 555–567.
Ifesan, B. O., Joycharat, N., & Voravuthikunchai, S. P. (2009). The mode of antistaphylococcal action of Eleutherine americana. FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology, 57(2), 193–201.
Kagale, S., Marimuthu, T., Thayumanavan, B., Nandakumar, R., & Samiyappan, R. (2004). Antimicrobial activity and induction of systemic resistance in rice by leaf extract of Datura metel against Rhizoctonia solani and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 65(2), 91–100.
Karabay-Yavasoglu, N. U., Sukatar, A., Ozdemir, G., & Horzum, Z. (2007). Antimicrobial activity of volatile components and various extracts of the red alga Jania rubens. Phytotherapy Research, 21(2), 153–156.
Kim, Y. H., Kim, J. H., Jin, H. J., & Lee, S. Y. (2013). Antimicrobial activity of ethanol extracts of Laminaria japonica against oral microorganisms. Anaerobe, 21, 34–38.
Knight, S. C., Anthony, V. M., Brady, A. M., Greenland, A. J., Heaney, S. P., Murray, D. C., et al. (1997). Rationale and perspectives on the development of fungicides. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 35, 349–372.
Li, N., Zhang, Q., & Song, J. (2005). Toxicological evaluation of fucoidan extracted from Laminaria japonica in Wistar rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 43(3), 421–426.
Li, L. Y., Li, L. Q., & Guo, C. H. (2010). Evaluation of in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Laminaria japonica polysaccharides. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 4(21), 2194–2198.
Lin, J. B., Zhao, H. Q., Hang, B., & Aisa, H. A. (2013). Antimicrobial and antitumor activities of crude extracts and isolated compounds from euphorbia humifusa. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 25(7), 3957–3960.
Luo, S., You, X., Ding, C., Li, Z., Lin, G., Yu, Z., et al. (2012). Antimicrobial activities and chemical compositions of Dictyophora indusia fisscher and Dictyophora echinovolvata. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 21, 70–73.
Marino, M., Bersani, C., & Comi, G. (2001). Impedance measurements to study the antimicrobial activity of essential oils from Lamiaceae and Compositae. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 67(3), 187–195.
Meillisa, A., Siahaan, E. A., Park, J. N., Woo, H. C., & Chun, B. S. (2013). Effect of subcritical water hydrolysate in the brown seaweed Saccharina japonica as a potential antibacterial agent on food-borne pathogens. Journal of Applied Phycology, 25(3), 763–769.
Michielin, E. M. Z., Salvador, A. A., Riehl, C. A. S., Smânia, A., Jr., Smânia, E. F. A., & Ferreira, S. R. S. (2009). Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of Cordia verbenacea extracts obtained by different methods. Bioresource Technology, 100(24), 6615–6623.
Muthukumar, A., Eswaran, A., Nakkeeran, S., & Sangeetha, G. (2010). Efficacy of plant extracts and biocontrol agents against Pythium aphanidermatum inciting chilli damping-off. Crop Protection, 29(12), 1483–1488.
Pastrik, K. H. (2000). Detection of Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus in potato tubers by multiplex PCR with coamplification of host DNA. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 106(2), 155–165.
Perminow, J. I. S., Akselsen, I. L. W., Borowski, E., Ruden, Ø., & Grønås, W. (2012). Potato ring rot in norway: occurrence and control. Potato Research, 55, 241–247.
Pieterse, B., Leer, R. J., Schuren, F. H., & van der Werf, M. J. (2005). Unravelling the multiple effects of lactic acid stress on Lactobacillus plantarum by transcription profiling. Microbiology, 151, 3881–3894.
Qiu, Y. E. (2004). The occurrence and control of ring-rot in potato. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 41, 88–89.
Rasch, M. (2002). The influence of temperature, salt and pH on the inhibitory effect of reuterin on Escherichia coli. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 72(3), 225–231.
Roe, A. J., O’byrne, C., Mclaggan, D., & Booth, I. R. (2002). Inhibition of Escherichia coli growth by acetic by acetic acid: a problem with methionine biosythesis and homocysteine toxicity. Microbiology, 148, 2215–2222.
Schmutterer, H. (1990). Properties and potential of natural pesticides from the neem tree Azadirachta indica. Annual Review Entomology, 35, 271–297.
Secor, G. A., De Buhr, L., & Gudmestad, N. C. (1987). Chemical sanitation for bacterial ring rot control. American Potato Journal, 64, 699–700.
Shao, X., Cheng, S., Wang, H., Yu, D., & Mungai, C. (2013). The possible mechanism of antifungal action of tea tree oil on Botrytis cinerea. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 114(6), 1642–1649.
Sikkema, J., de Bont, J. A., & Poolman, B. (1995). Mechanisms of membrane toxicity of hydrocarbons. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 59(2), 201–222.
Singh, G., Maurya, S., Catalan, C., & de Lampasona, M. P. (2004). Chemical constituents, antifungal and antioxidative effects of ajwain essential oil and its acetone extract. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52(11), 3292–3296.
Smânia, A., Jr., Monache, F. D., Smânia, E. F. A., & Cuneo, R. S. (1999). Antibacterial activity of steroidal compounds isolated from Ganoderma applanatum (Pers.) Pat. (Aphyllophoromycetideae) fruit body. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 1(4), 325–330.
Smith, N. C., Hennessy, J., & Stead, D. E. (2001). Repetitive sequence-derived PCR profiling using the BOX-A1R primer for rapid identification of the plant pathogen Clavibacter michiganensis subspecies sepedonicus. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 107(7), 739–748.
Tabanca, N., Demirci, B., Baser, K. H. C., Aytac, Z., Ekici, M., Khan, S. I., et al. (2006). Chemical composition and antifungal activity of Salvia macrochlamys and Salvia recognita essential oils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54(18), 6593–6597.
Tegegne, G., & Pretorius, J. C. (2007). In vitro and in vivo antifungal activity of crude extracts and powdered dry material from Ethiopian wild plants against economically important plant pathogens. BioControl, 52(6), 877–888.
Tseng, C. K. (2001). Algal biotechnology industries and research activities in China. Journal of Applied Phycology, 13(4), 375–380.
Urbanek, A., Szadziewski, R., Stepnowski, P., Boros-Majewska, J., Gabriel, I., Dawgul, M., et al. (2012). Composition and antimicrobial activity of fatty acids detected in the hygroscopic secretion collected from the secretory setae of larvae of the biting midge Forcipomyia nigra (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Journal of Insect Physiology, 58(9), 1265–1276.
Vukovic, N., Sukdolak, S., Solujic, S., & Niciforovic, N. (2009). Antimicrobial activity of the essential oil obtained from roots and chemical composition of the volatile constituents from the roots, stems, and leaves of Ballota nigra from Serbia. Journal of Medicinal Food, 12(2), 435–441.
Zhen, Y., Jiang, H. X., & Lin, X. P. (2004). Chemical analysis of lipid compound and its antibacterial and antifungal activities in Pachydictyon coriaceum. Marine Sciences, 28(10), 42–44.
Acknowledgments
We thank Edanz Editing Company for critical reviews of the manuscript and editorial assistance with the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, J., Feng, J., Wang, F. et al. Antibacterial activity of petroleum ether fraction from Laminaria japonica extracts against Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus . Eur J Plant Pathol 140, 291–300 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0462-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0462-1