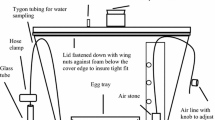
Abstract
Capelin (Mallotus villosus) displays alternative reproductive modes throughout its circumpolar distribution. This predicts divergent thermohaline tolerance of eggs because they are incubated in either a steady offshore or variable intertidal environment. We investigate herein thermohaline tolerance of eggs from the offshore spawning Barents Sea capelin. Subsequently, we compare our data with those previously published on other offshore and intertidal spawning capelin populations across the Northeast Atlantic Ocean, with the aim of determining possible patterns in the thermohaline tolerance of eggs from the alternative reproductive modes. In a 2 × 4 factorial design various combinations of salinities and temperatures had only negligible effect on the survival of eggs until first hatch. The embryonic development rate from fertilisation until first hatch across populations and between the two reproductive modes suggested non-local thermohaline tolerance towards the physical factors during development. Finally, no differences were observed in salinity tolerance from fertilisation to first hatch between populations representing different reproductive modes. The present findings demonstrate wide thermohaline tolerance of capelin eggs regardless of population origin and reproductive mode.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayson FG, Kaneko T, Hasegawa S, Hirano T (1994) Development of mitochondrion-rich cells in the yolk-sac membrane of embryos and larvae of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, in fresh-water and seawater. J Exp Zool 270:129–135. doi:10.1002/jez.1402700202
Baker JA, Cresko WA, Foster SA, Heins DC (2005) Life-history differentiation of benthic and limnetic ecotypes in a polytypic population of threespine stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Evol Ecol Res 7:121–131
Carscadden JE, Vilhjálmsson H (2002) Capelin - what are they good for? ICES J Mar Sci 59:863–869. doi:10.1006/jmsc.2002.1283
Carscadden JE, Frank KT, Miller DS (1989) Capelin (Mallotus villosus) spawning on the Southeast Shoal - Influence of physical factors past and present. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46:1743–1754
Caswell H (1983) Phenotypic plasticity in life-history traits: demographic effects and evolutionary consequences. Amer Zool 23:35–46
Christiansen JS, Præbel K, Siikavuopio SI, Carscadden JE (2008) Facultative semelparity in capelin Mallotus villosus (Osmeridae) - an experimental test of a life history phenomenon in a sub-arctic fish. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 360:47–55. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2008.04.003
Colbeck GJ, Turgeon J, Sirois P, Dodson JJ (2011) Historical introgression and the role of selective vs. neutral processes in structuring nuclear genetic variation (AFLP) in a circumpolar marine fish, the capelin (Mallotus villosus). Mol Ecol 20:1976–1987. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05069.x
Davenport J (1989) The effects of salinity and low temperature on eggs of the Icelandic capelin Mallotus villosus. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 69:1–9. doi:10.1017/S0025315400049055
Davenport J, Stene A (1986) Freezing resistance, temperature and salinity tolerance in eggs, larvae and adults of capelin, Mallotus villosus, from Balsfjord. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 66:145–157. doi:10.1017/S0025315400039710
Dodson JJ, Carscadden JE, Bernatchez L, Colombani F (1991) Relationship between spawning mode and phylogeographic structure in mitochondrial-DNA of North-Atlantic capelin Mallotus villosus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 76:103–113
Dodson JJ, Tremblay S, Colombani F, Carscadden JE, Lecomte F (2007) Trans-Arctic dispersals and the evolution of a circumpolar marine fish species complex, the capelin (Mallotus villosus). Mol Ecol 16:5030–5043. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03559.x
Frank KT, Leggett WC (1981) Wind regulation of emergence times and early larval survival in capelin (Mallotus villosus). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 38:215–223
Friðgeirsson E (1976) Observations on spawning behaviour and embryonic development of the Icelandic capelin. Rit Fiskideildar 5:1–35
Gjøsæter H (1998) The population biology and exploitation of capelin (Mallotus villosus) in the Barents Sea. Sarsia 83:453–496
Gjøsæter H, Gjøsæter J (1986) Observations on the embryonic development of capelin (Mallotus villosus Müller) from the Barents Sea. Fiskdir Skr Ser HavUnders 18:59–68
Holt RD (2003) On the evolutionary ecology of species’ ranges. Evol Ecol Res 5:159–178
Hutchings JA (2011) Old wine in new bottles: reaction norms in salmonid fishes. Heredity 106:421–437. doi:10.1038/hdy.2010.166
Jangaard PM (1974) The capelin (Mallotus villosus). Bull Fish Res Bd Can 186:68
Jeffers GW (1931) The life history of the capelin Mallotus villosus (O. F. Müller). Department of Biology, University of Toronto, Toronto
Kamler E (2002) Ontogeny of yolk-feeding fish: an ecological perspective. Rev Fish Biol Fish 12(1):79–103. doi:10.1023/A:1022603204337
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric-estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Koskinen MT, Haugen TO, Primmer CR (2002) Contemporary fisherian life-history evolution in small salmonid populations. Nature 419:826–830. doi:10.1038/nature01029
Kuparinen A, Hutchings JA (2012) Consequences of fisheries-induced evolution for population productivity and recovery potential. Proc R Soc B 279:2571–2579. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.0120
Mork J, Friis-Sørensen E (1983) Genetic variation in capelin Mallotus villosus from Norwegian waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 12:199–205
Nakashima BS, Wheeler JP (2002) Capelin (Mallotus villosus) spawning behaviour in Newfoundland waters - the interaction between beach and demersal spawning. ICES J Mar Sci 59:909–916. doi:10.1006/jmsc.2002.1261
Nyholmen O, Hopkins CCE (1988) Some observations on the population biology of capelin (Mallotus villosus) from Balsfjord, northern Norway. J Cons int Explor Mer 44:264–276
Penton PM, Davoren GK, Montevecchi WA, Andrews DW (2012) Beach and demersal spawning in capelin (Mallotus villosus) on the northeast Newfoundland coast: egg developmental rates and mortality. Can J Zool 90:248–256. doi:10.1139/z11-132
Peterson BJ, Holmes RM, McClelland JW, Vörösmarty CJ, Lammers RB, Shiklomanov AI, Shiklomanov IA, Rahmstorf S (2002) Increasing river discharge to the Arctic Ocean. Science 298:2171–2173. doi:10.1126/science.1077445
Pfennig DW, Wund MA, Snell-Rood EC, Cruickshank T, Schlichting CD, Moczek AP (2010) Phenotypic plasticity’s impacts on diversification and speciation. Trends Ecol Evol 25:459–467. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2010.05.006
Præbel K, Christiansen JS, Fevolden S-E (2004) Spawning habitat and egg mortality in capelin, Mallotus villosus (Müller) - responses to extreme abiotic conditions. ICES CM 2004/DD:1-14
Præbel K, Westgaard J-I, Fevolden S-E, Christiansen JS (2008) Circumpolar genetic population structure of capelin, Mallotus villosus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 360:189–199. doi:10.3354/meps07363
Præbel K, Christiansen JS, Fevolden SE (2009) Temperature and salinity conditions in a sub-Arctic intertidal spawning habitat for capelin. Mar Biol Res 5:511–514. doi:10.1080/17451000902729670
Sætre R, Gjøsæter J (1975) Ecological investigations on the spawning grounds of the Barents Sea capelin. Fiskdir Skr Ser HavUnders 16:203–227
Stergiou KI (1989) Capelin Mallotus villosus (Pisces, Osmeridae), glaciations, and speciation - a nomothetic approach to fisheries ecology and reproductive-biology. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 56(3):211–224
Templeman W (1948) The life history of the capelin (Mallotus villosus O. F. Müller) in Newfoundland waters. Bull Nfld Gov Lab 17:151
Todd H, Schluter D (1999) Ecological speciation in sticklebacks: environment-dependent hybrid fitness. Evolution 53:866–873
Turrero P, Horreo JL, Garcia-Vazquez E (2012) Same old Salmo? Changes in life history and demographic trends of North Iberian salmonids since the Upper Palaeolithic as revealed by archaeological remains and beast analyses. Mol Ecol 21:2318–29. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05508.x
Vila-Gispert A, Moreno-Amich R, Garcia-Berthou E (2002) Gradients of life-history variation: an intercontinental comparison of fishes. Rev Fish Biol Fish 12:417–427
Vilhjálmsson H (1994) The Icelandic capelin stock. Capelin, Mallotus villosus (Müller) in the Iceland-Greenland-Jan Mayen area. Rit Fiskideildar 13:1–281
Vilhjálmsson H (2002) Capelin (Mallotus villosus) in the Iceland-East Greenland-Jan Mayen ecosystem. ICES J Mar Sci 59:870–883. doi:10.1006/jmsc.2002.1233
Vonlanthen P, Bittner D, Hudson AG, Young KA, Müller R, Lundsgaard-Hansen B, Roy D, Di Piazza S, Largiader CR, Seehausen O (2012) Eutrophication causes speciation reversal in whitefish adaptive radiations. Nature 482:357–363. doi:10.1038/nature10824
Whitman DW, Agrawal AA (2009) What is phenotypic plasticity and why is it important? In: Whitman DW, Ananthakrishnan TN (eds) Phenotypic plasticity of insects. Enfield, Science Publishers, pp 1–63
Acknowledgements
We thank J. W. Behrens, N. Brundtland, L. L. Hansen, O. Nordgård, T. F. Sørensen and the crew onboard the R/V Jan Mayen for assistance in the field. I.-B. Falk-Petersen, the late H. Vilhjálmsson and four anonymous reviewers are thanked for many valuable comments on an earlier draft. The study is a contribution to the BASECOEX-Programme, grant no. 140290/140, partly funded by the Norwegian Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Præbel, K., Christiansen, J.S., Kettunen-Præbel, A. et al. Thermohaline tolerance and embryonic development in capelin eggs (Mallotus villosus) from the Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Environ Biol Fish 96, 753–761 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-012-0069-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-012-0069-3