Abstract
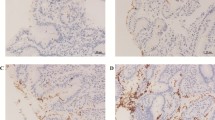
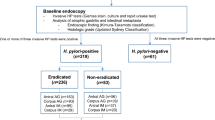
The endoscopic finding of nodular gastritis (NG) is highly associated with presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. How the endoscopic patterns and histopathology of NG change after eradication of H. pylori is unclear. Twenty-one adults (3 men and 18 women) with H. pylori-associated NG found on endoscopy were enrolled for this study. The histological findings included gastritis activity, bacterial colonization, and lymphoid follicles. Repeat endoscopy for the endoscopic as well as histopathological features of gastric biopsy specimens was performed 2 months later after eradication treatment. H. pylori was successfully eradicated in 19 patients. Endoscopic NG disappeared in 12, improved in 5, and was unchanged in 4. After treatment, there was significant improvement in scores for gastritis activity [P < 0.001, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.31–1.91], bacterial colonization (P < 0.001, 95% CI 0.71–1.14) and follicular gastritis (P = 0.047, 95% CI 0.04–0.52), primarily among patients whose endoscopic pattern resolved completely. The disappearance of nodularity on endoscopy was accompanied by a decrease in follicular gastritis score.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahu Mda G, da Silveira TR, Maguilnick I, Ulbrich-Kulczynski J (2003) Endoscopic nodular gastritis: an endoscopic indicator of high-grade bacterial colonization and severe gastritis in children with Helicobacter pylori. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 36:217–222
Chen MJ, Wang TE, Chang WH, Liao TC, Lin CC, Shih SC (2007) Nodular gastritis: an endoscopic indicator of Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Dis Sci 52:2662–2666
Luzza F, Pensabene L, Imeneo M, Mancuso M, Contaldo A, Giancotti L, La Vecchia AM, Costa MC, Strisciuglio P, Docimo C, Pallone F, Guandalini S (2001) Antral nodularity identifies children infected with Helicobacter pylori with higher grades of gastric inflammation. Gastrointest Endosc 53:60–64
Zaitoun AM (1995) The prevalence of lymphoid follicles in Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis in patients with ulcers and non-ulcer dyspepsia. J Clin Pathol 4:325–329
Chen XY, Liu WZ, Shi Y, Zhang DZ, Zhang DZ, Xiao SD, Tytgat GN (2002) Helicobacter pylori associated gastric diseases and lymphoid tissue hyperplasia in gastric antral mucosa. J Clin Pathol 55:133–137
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P (1996) Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated sydney system. International workshop on the histopathology of gastritis, Houston 1994. Am J Surg Pathol 20:1161–1181
Ernst P (1999) Review article: the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Therap 13:13–18
Hatakeyama M, Brzozowski T (2006) Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 11:14–20
Ohara H, Isomoto H, Wen CY, Ejima C, Murata M, Miyazaki M, Takeshima F, Mizuta Y, Murata I, Koji T, Nagura H, Kohno S (2003) Expression of mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 on vascular endothelium of gastric mucosa in patients with nodular gastritis. World J Gastroenterol 9:2701–2705
Luzza F, Pensabene L, Imeneo M, Mancuso M, Giancotti L, La Vecchia AM, Costa MC, Strisciuglio P, Pallone F (2002) Antral nodularity and positive CagA serology are distinct and relevant markers of severe gastric inflammation in children with Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 7:46–52
Rad R, Dossumbekova A, Neu B, Lang R, Bauer S, Saur D, Gerhard M, Prinz C (2004) Cytokine gene polymorphisms influence mucosal cytokine expression, gastric inflammation, and host specific colonisation during Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 53:1082–1089
Miyamoto M, Haruma K, Yoshihara M, Sumioka M, Nishisaka T, Tanaka S, Inoue K, Chayama K (2002) Five cases of nodular gastritis and gastric cancer: a possible association between nodular gastritis and gastric cancer. Dig Liver Dis 34:819–820
Ma ZQ, Tanizawa T, Nihei Z, Sugihara K, Nakamura K (2000) Follicular gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori. J Med Dent Sci 47:39–47
Miyamoto M, Haruma K, Hiyama T, Kamada T, Masuda H, Shimamoto F, Inoue K, Chayama K (2002) High incidence of B-cell monoclonality in follicular gastritis: a possible association between follicular gastritis and MALT lymphoma. Virchows Arch 440:376–380
Miyamoto M, Haruma K, Yoshihara M, Hiyama T, Sumioka M, Nishisaka T, Tanaka S, Chayama K (2003) Nodular gastritis in adults is caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Dis Sci 48:968–975
Genta RM, Hamner HW, Graham DY (1993) Gastric lymphoid follicles in Helicobacter pylori infection: frequency, distribution, and response to triple therapy. Hum Pathol 24:577–583
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Dr. Mary Jeanne Buttrey for critical reading and correction of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, MJ., Shih, SC., Wang, TE. et al. Endoscopic Patterns and Histopathological Features after Eradication Therapy in Helicobacter pylori-Associated Nodular Gastritis. Dig Dis Sci 53, 1893–1897 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0097-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0097-6