Abstract
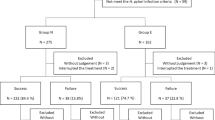
Ninety-one Helicobacter pylori-positive patients with nonulcer dyspepsia were randomized to receive either lansoprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin or lansoprazole and placebo. A validated questionnaire assessed dyspeptic symptoms at baseline and at 3, 6, and 12 months. Endoscopies and biopsies were performed at baseline and at 3 and 12 months. There was an overall trend, although not statistically significant, for a benefit of H. pylori eradication. Of the patients in the antibiotics group, 16 of 46 (35%) had symptomatic improvement, versus 9 of 43 (21%) in the control group (P = 0.164). In a secondary analysis, it was found that of the patients without endoscopic gastric erosions, 15 of 34 (44%) in the antibiotics group and 5 of 33 (15%) of controls had symptomatic improvement (P = 0.015). Helicobacter pylori eradication did not prove to be clinically beneficial, although a tendency to symptomatic benefit was detected. Further studies are necessary to confirm the implications of endoscopic gastric erosions in these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agreus L: Natural history of dyspepsia. Gut 50 (Suppl 4):IV2–IV9, 2002
Talley NJ, Stanghellini V, Heading RC, et al.: Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gut 45 (Suppl 2):II37–II42, 1999
Holtmann G, Gschossmann J, Neufang–Huber J, et al.: Differences in gastric mechanosensory function after repeated ramp distensions in nonconsulters with dyspepsia and healthy controls. Gut 47:332–336, 2000
Mearin F, Cucala M, Azpiroz F, et al.: The origin of symptoms on the brain–gut axis in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 101:999–1006, 1991
Fennerty MB: Is nonulcer dyspepsia related to Helicobacter pylori infection? Semin Gastrointest Dis 12:180–185, 2001
Nandurkar S, Talley NJ, Xia H, et al.: Dyspepsia in the community is linked to smoking and aspirin use but not to Helicobacter pylori infection. Arch Intern Med 158:1427–1433, 1998
Danesh J, Lawrence M, Murphy M, et al.: Systematic review of the epidemiological evidence on Helicobacter pylori infection and nonulcer or uninvestigated dyspepsia. Arch Intern Med 160:1192–1198, 2000
Bazzoli F, De Luca L, Pozzato P, et al.: Helicobacter pylori and functional dyspepsia: review of previous studies and commentary on new data. Gut 50 (Suppl 4):IV33–IV35, 2002
Blum AL, Talley NJ, O'Morain C, et al.: Lack of effect of treating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. Omeprazole plus Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin Effect One Year after Treatment (OCAY) Study Group. N Engl J Med 339:1875–1881, 1998
McColl K, Murray L, El Omar E, et al.: Symptomatic benefit from eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 339:1869–1874, 1998
Veldhuyzen van Zanten S, Fedorak R, Lambert J, et al.: Absence of symptomatic benefit of lansoprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin triple therapy in eradication of Helicobacter pylori positive, functional (nonulcer) dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol 98:1963–1969, 2003
Froehlich F, Gonvers JJ, Wietlisbach V, et al.: Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment does not benefit patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol 96:2329–2336, 2001
Talley NJ, Vakil N, Ballard ED, et al.: Absence of benefit of eradicating Helicobacter pylori in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 341:1106–1111, 1999
Greenberg PD, Cello JP: Lack of effect of treatment for Helicobacter pylori on symptoms of nonulcer dyspepsia. Arch Intern Med 159:2283–2288, 1999
Koskenpato J, Farkkila M, Sipponen P: Helicobacter pylori eradication and standardized 3-month omeprazole therapy in functional dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol 96:2866–2872, 2001
Oliveira AMR, Rocha GA, Queiroz DMM, et al.: Prevalence of H. pylori infection in a population from the rural area of Araćcua'i, MG, Brazil. Rev Microbiol 30:59–61, 1999
Mitchell A, Silva TMJ, Barrett LJ, et al.: Age–specific Helicobacter pylori seropositivity rates of children in an impoverished urban area of Northeast Brazil. J Clin Microbiol 41:1326–1328, 2003
Cunha RPA, Alves FP, Rocha AMC, et al.: Prevalence and risk factors associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in native populations from Brazilian Western Amazon. Trans Roy Soc Trop Med Hygiene 97:382–386, 2003
Talley NJ, Janssens J, Lauritsen K, et al.: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial with 12 month follow-up. The Optimal Regimen Cures Helicobacter Induced Dyspepsia (ORCHID) Study Group. BMJ 318:833–837, 1999
Talley NJ, Colin-Jones DG, Koch KI, et al.: Functional dyspepsia: a classification with guidelines for diagnosis and management. Gastroenterol Int 4:145–160, 1991
Tytgat GN: Role of endoscopy and biopsy in the work up of dyspepsia. Gut 50 (Suppl 4):IV13–IV16, 2002
Tytgat GN: The Sydney System: endoscopic division. Endoscopic appearances in gastritis/duodenitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:223–234, 1991
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, et al.: Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am J Surg Pathol 20:1161–1181, 1996
Sander GB, Mazzoleni LE, Francesconi CF, et al.: Development and validation of a cross-cultural questionnaire to evaluate nonulcer dyspepsia: the Porto Alegre Dyspeptic Symptoms Questionnaire (PADYQ). Dig Dis Sci 49:1822–1829, 2004
Buckley MJ, Scanlon C, McGurgan P, et al.: A validated dyspepsia symptom score. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:495–500, 1997
Veldhuyzen Van Zanten SJ, Tytgat KM, Pollak PT, et al.: Can severity of symptoms be used as an outcome measure in trials of nonulcer dyspepsia and Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis? J Clin Epidemiol 46:273–279, 1993
Streiner DL, Norman GR: Health Measurement Scales. 2nd ed. Oxford, Oxford Medical, 1995
Guyatt G, Walter S, Norman G: Measuring change over time: assessing the usefulness of evaluative instruments. J Chron Dis 40:171–178, 1987
Bruley DV, Flejou JF, Colin R, et al.: There are some benefits for eradicating Helicobacter pylori in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 15:1177–1185, 2001
Miwa H, Hirai S, Nagahara A, et al.: Cure of Helicobacter pylori infection does not improve symptoms in nonulcer dyspepsia patients—a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 14:317–324, 2000
Jaakkimainen RL, Boyle E, Tudiver F: Is Helicobacter pylori associated with nonulcer dyspepsia and will eradication improve symptoms? A meta-analysis. BMJ 319:1040–1044, 1999
Laine L, Schoenfeld P, Fennerty MB: Therapy for Helicobacter pylori in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann Intern Med 134:361–369, 2001
Moayyedi P, Soo S, Deeks J, et al.: Systematic review and economic evaluation of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment for nonulcer dyspepsia. Dyspepsia Review Group. BMJ 321:659–664, 2000
Laheij RJ, Van Rossum LG, Verbeek AL, et al.: Helicobacter pylori infection treatment of nonulcer dyspepsia: an analysis of meta-analyses. J Clin Gastroenterol 36:291–294, 2003
Schubert ML: H. pylori and nonulcer dyspepsia: not guilty as charged. Gastroenterology 117:270–272, 1999
Perri F, Andriulli A: Absence of benefit of eradicating Helicobacter pylori in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 342:589–590, 2000
Danesh J, Pounder RE: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori and nonulcer dyspepsia. Lancet 355:766–767, 2000
Puspok A, Oberhuber G: Helicobacter pylori and nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 340:1508–1509, 1999
Axon A: Management of uninvestigated dyspepsia: review and commentary. Gut 50 (Suppl 4):IV51–IV55, 2002
Malfertheiner P, Mössner J, Fischbach W, et al.: Helicobacter pylori eradication is beneficial in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 18:615–625, 2003
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al.: Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17(1):1–12, 1996
Moayyedi P, Soo S, Deeks J, et al.: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori for nonulcer dyspepsia (Cochrane Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD002096, 2003
Treiber G, Schwabe M, Ammon S, et al.: Dyspeptic symptoms associated with Helicobacter pylori infection are influenced by strain and host specific factors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19(2):219–231, 2004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abbott Laboratórios do Brasil Ltda. donated the drugs used in this clinical trial. The Research Incentive Fund (FIPE) and the Graduate Research Group at Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre provided editorial support. No member of the research team received any remuneration to conduct this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazzoleni, L.E., Sander, G.B., Ott, E.A. et al. Clinical Outcomes of Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in Nonulcer Dyspepsia in a Population with a High Prevalence of Infection: Results of a 12-Month Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Dig Dis Sci 51, 89–98 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3090-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3090-6