Abstract
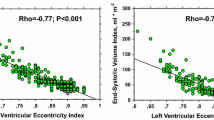
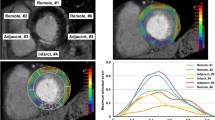
To assess whether global and regional myocardial strains from three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (3D-STE) correlate with myocardial infarction size (MIS) detected by single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). Fifty-seven patients with a history of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (MI) within 3–6 months were enrolled, alongside 24 healthy volunteers. Left ventricular (LV) global area strain, global longitudinal strain (GLS), global radial strain, global circumferential strain, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and wall motion score index (WMSI) were measured and compared with the corresponding SPECT-detected MISs. Patients were sub-grouped into massive MIS group (MIS ≥ 12 %) and small MIS group (MIS < 12 %). Myocardial strains of all the LV segments were compared with the corresponding MIS. Global myocardial strain parameters, LVEF and WMSI of the patients were significantly different from the control group (all P < 0.05) and correlated well with MISs, most significantly for GLS (r = 0.728, P < 0.01). Significant differences in myocardial strain parameters were found between the massive and small MIS groups (all P < 0.05). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis indicated that GLS had a highest diagnostic value and when the cutoff was −13.8 %, the area under the curve was 0.84, with the 70.6 % sensitivity and 87.5 % specificity. Significant differences of myocardial strain parameters were observed between segments with and without transmural MIs (P < 0.01). 3D-STE myocardial strain parameters evaluated LV global MIS, 3D GLS had the highest diagnostic value. It also preliminarily gauged the degree of ischemia and necrosis of regional myocardial segments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kastrati A, Mehilli J, Dirschinger J et al (2002) Myocardial salvage after coronary stenting plus abciximab versus fibrinolysis plus abciximab in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a randomised trial. Lancet 359(9310):920–925. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08022-4
Gibbons RJ, Valeti US, Araoz PA, Jaffe AS (2004) The quantification of infarct size. J Am Coll Cardiol 44(8):1533–1542. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.06.071
Burns RJ, Gibbons RJ, Yi Q, Roberts RS, Miller TD, Schaer GL, Anderson JL, Yusuf S, Investigators CS (2002) The relationships of left ventricular ejection fraction, end-systolic volume index and infarct size to six-month mortality after hospital discharge following myocardial infarction treated by thrombolysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 39(1):30–36
Leitman M, Lysyansky P, Sidenko S, Shir V, Peleg E, Binenbaum M, Kaluski E, Krakover R, Vered Z (2004) Two-dimensional strain—a novel software for real-time quantitative echocardiographic assessment of myocardial function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 17(10):1021–1029. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2004.06.019
Nesser HJ, Mor-Avi V, Gorissen W, Weinert L, Steringer-Mascherbauer R, Niel J, Sugeng L, Lang RM (2009) Quantification of left ventricular volumes using three-dimensional echocardiographic speckle tracking: comparison with MRI. Eur Heart J 30(13):1565–1573. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp187
Reant P, Barbot L, Touche C, Dijos M, Arsac F, Pillois X, Landelle M, Roudaut R, Lafitte S (2012) Evaluation of global left ventricular systolic function using three-dimensional echocardiography speckle-tracking strain parameters. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 25(1):68–79. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2011.10.009
Sjoli B, Orn S, Grenne B, Vartdal T, Smiseth OA, Edvardsen T, Brunvand H (2009) Comparison of left ventricular ejection fraction and left ventricular global strain as determinants of infarct size in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 22(11):1232–1238. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2009.07.027
Eek C, Grenne B, Brunvand H, Aakhus S, Endresen K, Hol PK, Smith HJ, Smiseth OA, Edvardsen T, Skulstad H (2010) Strain echocardiography and wall motion score index predicts final infarct size in patients with non-ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 3(2):187–194. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.109.910521
Munk K, Andersen NH, Nielsen SS, Bibby BM, Botker HE, Nielsen TT, Poulsen SH (2011) Global longitudinal strain by speckle tracking for infarct size estimation. Eur J Echocardiogr 12(2):156–165. doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jeq168
Sawada SG, Segar DS, Ryan T, Brown SE, Dohan AM, Williams R, Fineberg NS, Armstrong WF, Feigenbaum H (1991) Echocardiographic detection of coronary artery disease during dobutamine infusion. Circulation 83(5):1605–1614
Kim RJ, Wu E, Rafael A, Chen EL, Parker MA, Simonetti O, Klocke FJ, Bonow RO, Judd RM (2000) The use of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to identify reversible myocardial dysfunction. N Engl J Med 343(20):1445–1453. doi:10.1056/NEJM200011163432003
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V et al (2002) Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation 105(4):539–542
Berning J, Steensgaard-Hansen F (1990) Early estimation of risk by echocardiographic determination of wall motion index in an unselected population with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 65(9):567–576
Thorstensen A, Dalen H, Hala P, Kiss G, D’Hooge J, Torp H, Stoylen A, Amundsen B (2013) Three-dimensional echocardiography in the evaluation of global and regional function in patients with recent myocardial infarction: a comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. Echocardiography 30(6):682–692. doi:10.1111/echo.12115
Zhu W, Liu W, Tong Y, Xiao J (2014) Three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography for the evaluation of the infarct size and segmental transmural involvement in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Echocardiography 31(1):58–66. doi:10.1111/echo.12284
Xu TY, Sun JP, Lee AP, Yang XS, Qiao Z, Luo X, Fang F, Li Y, Yu CM, Wang JG (2014) Three-dimensional speckle strain echocardiography is more accurate and efficient than 2D strain in the evaluation of left ventricular function. Int J Cardiol 176(2):360–366. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.07.015
Seo Y, Ishizu T, Aonuma K (2014) Current status of 3-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: a review from our experiences. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 22(2):49–57. doi:10.4250/jcu.2014.22.2.49
Serri K, Reant P, Lafitte M, Berhouet M, Le Bouffos V, Roudaut R, Lafitte S (2006) Global and regional myocardial function quantification by two-dimensional strain: application in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 47(6):1175–1181. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.10.061
Winter R, Jussila R, Nowak J, Brodin LA (2007) Speckle tracking echocardiography is a sensitive tool for the detection of myocardial ischemia: a pilot study from the catheterization laboratory during percutaneous coronary intervention. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 20(8):974–981. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2007.01.029
Langeland S, D’Hooge J, Wouters PF, Leather HA, Claus P, Bijnens B, Sutherland GR (2005) Experimental validation of a new ultrasound method for the simultaneous assessment of radial and longitudinal myocardial deformation independent of insonation angle. Circulation 112(14):2157–2162. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.554006
Braunwald E (1997) Heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 5th ed. W B Sounders, pp 360–680
Mizuguchi Y, Oishi Y, Miyoshi H, Iuchi A, Nagase N, Oki T (2008) The functional role of longitudinal, circumferential, and radial myocardial deformation for regulating the early impairment of left ventricular contraction and relaxation in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: a study with two-dimensional strain imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 21(10):1138–1144. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2008.07.016
Galderisi M, Esposito R, Schiano-Lomoriello V, Santoro A, Ippolito R, Schiattarella P, Strazzullo P, de Simone G (2012) Correlates of global area strain in native hypertensive patients: a three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 13(9):730–738. doi:10.1093/ehjci/jes026
Kleijn SA, Aly MF, Terwee CB, van Rossum AC, Kamp O (2011) Three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography for automatic assessment of global and regional left ventricular function based on area strain. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24(3):314–321. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2011.01.014
Monte IP, Mangiafico S, Buccheri S, Arcidiacono AA, Lavanco V, Privitera F, Leggio S, Deste W, Tamburino C (2014) Early changes of left ventricular geometry and deformational analysis in obese subjects without cardiovascular risk factors: a three-dimensional and speckle tracking echocardiographic study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 30(6):1037–1047. doi:10.1007/s10554-014-0429-5
Tadic M, Majstorovic A, Pencic B, Ivanovic B, Neskovic A, Badano L, Stanisavljevic D, Scepanovic R, Stevanovic P, Celic V (2014) The impact of high-normal blood pressure on left ventricular mechanics: a three-dimensional and speckle tracking echocardiography study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 30(4):699–711. doi:10.1007/s10554-014-0382-3
Zhang X, Wei X, Liang Y, Liu M, Li C, Tang H (2013) Differential changes of left ventricular myocardial deformation in diabetic patients with controlled and uncontrolled blood glucose: a three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography-based study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 26(5):499–506. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2013.02.016
Wu Z, Shu X, Fan B, Dong L, Pan C, Chen S (2013) Differentiation of transmural and nontransmural infarction using speckle tracking imaging to assess endocardial and epicardial torsion after revascularization. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29(1):63–70. doi:10.1007/s10554-012-0050-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of People’s Liberation Army General Hospital and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Qiushuang Wang and Chunhong Zhang have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Zhang, C., Huang, D. et al. Evaluation of myocardial infarction size with three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: a comparison with single photon emission computed tomography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 31, 1571–1581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0745-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0745-4