Abstract
Purpose
Female patients with breast cancer frequently develop arthralgia when treated with aromatase inhibitors (AI). Although the mechanism of AI-induced arthralgia is unknown, potential biomarkers have been identified. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical and genetic predictors of AI-induced arthralgia in a prospective cohort of patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.
Methods
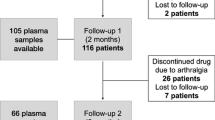
One hundred and ninety-six patients were enrolled at initiation of AI therapy with either letrozole or anastrozole. Patients completed two validated self-report questionnaires assessing pain, stiffness, and physical function at baseline, and repeated the questionnaires at two and at six months after the initiation of treatment with an AI. Germline DNA of all patients was genotyped for seven single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) previously identified by genetic screens and genome-wide association studies as associated with AI-induced arthralgia.
Results
More than 50% of the study group experienced arthralgia symptoms. Genetic analysis revealed that four SNPs, in CYP19A1 (rs4775936) and ESR1 (rs9322336, rs2234693, rs9340799), were associated with the development of arthralgia (adjusted P = 0.016, 0.018, 0.017, 0.047). High body mass index (BMI) was also associated with the development of arthralgia symptoms (adjusted P = 0.001). Patients prescribed letrozole were significantly more likely to develop arthralgia than patients on anastrozole (P = 0.018), and also more likely to discontinue AI therapy due to arthralgia. The CYP19A1 (rs4775936) SNP was significantly associated with discontinuation of therapy due to intolerable arthralgia.
Conclusions
Our results suggested that BMI and AI drug (letrozole versus anastrozole) were clinical predictors of arthralgia, while genetic variants rs4775936, rs9322336, rs2234693, and rs9340799 were genetic predictors of AI-induced arthralgia. Significantly, rs4775936 was also a predictor of discontinuation of therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others

Abbreviations
- ADR:
-
Adverse drug reactions
- AIs:
-
Aromatase inhibitors
- AUSCAN:
-
Australian/Canadian osteoarthritis hand index
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- WOMAC:
-
Western Ontario and McMaster osteoarthritis index
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics 2012. CA 65(2):87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, Jemal A (2014) Breast cancer statistics 2013. CA 64(1):52–62. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21203
Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative G (2015) Aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen in early breast cancer: patient-level meta-analysis of the randomised trials. Lancet 386(10001):1341–1352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61074-1
Bulun SE, Takayama K, Suzuki T, Sasano H, Yilmaz B, Sebastian S (2004) Organization of the human aromatase p450 (CYP19) gene. Seminars Reprod Med 22(1):5–9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-823022
Nelson LR, Bulun SE (2001) Estrogen production and action. J Am Acad Dermatol 45(3 Suppl):S116–124
Crew KD, Greenlee H, Capodice J, Raptis G, Brafman L, Fuentes D, Sierra A, Hershman DL (2007) Prevalence of joint symptoms in postmenopausal women taking aromatase inhibitors for early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(25):3877–3883. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.10.7573
Swenson KK, Nissen MJ, Henly SJ, Maybon L, Pupkes J, Zwicky K, Tsai ML, Shapiro AC (2013) Identification of tools to measure changes in musculoskeletal symptoms and physical functioning in women with breast cancer receiving aromatase inhibitors. Oncol Nurs Forum 40(6):549–557. https://doi.org/10.1188/13.ONF.549-557
Borrie AE, Kim RB (2017) Molecular basis of aromatase inhibitor associated arthralgia: known and potential candidate genes and associated biomarkers. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 13(2):149–156. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2017.1234605
Team RDC (2016) R: A language and environment for statistical computing (Version 3.3.1). R version 3.3.1 (2016–06–21) edn. R Development Core Team, Vienna, Austria
Henry NL, Azzouz F, Desta Z, Li L, Nguyen AT, Lemler S, Hayden J, Tarpinian K, Yakim E, Flockhart DA, Stearns V, Hayes DF, Storniolo AM (2012) Predictors of aromatase inhibitor discontinuation as a result of treatment-emergent symptoms in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 30(9):936–942. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0261
Garcia-Giralt N, Rodriguez-Sanz M, Prieto-Alhambra D, Servitja S, Torres-Del Pliego E, Balcells S, Albanell J, Grinberg D, Diez-Perez A, Tusquets I, Nogues X (2013) Genetic determinants of aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia: the B-ABLE cohort study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 140(2):385–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2638-3
Henry NL, Skaar TC, Dantzer J, Li L, Kidwell K, Gersch C, Nguyen AT, Rae JM, Desta Z, Oesterreich S, Philips S, Carpenter JS, Storniolo AM, Stearns V, Hayes DF, Flockhart DA (2013) Genetic associations with toxicity-related discontinuation of aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138(3):807–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2504-3
Wang J, Lu K, Song Y, Xie L, Zhao S, Wang Y, Sun W, Liu L, Zhao H, Tang D, Ma W, Pan B, Xuan Q, Liu H, Zhang Q (2013) Indications of clinical and genetic predictors for aromatase inhibitors related musculoskeletal adverse events in Chinese Han women with breast cancer. PLoS ONE 8(7):e68798. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068798
Hamilton KJ, Hewitt SC, Arao Y, Korach KS (2017) Estrogen Hormone Biology. Curr Top Dev Biol 125:109–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.12.005
Ingle JN, Schaid DJ, Goss PE, Liu M, Mushiroda T, Chapman JA, Kubo M, Jenkins GD, Batzler A, Shepherd L, Pater J, Wang L, Ellis MJ, Stearns V, Rohrer DC, Goetz MP, Pritchard KI, Flockhart DA, Nakamura Y, Weinshilboum RM (2010) Genome-wide associations and functional genomic studies of musculoskeletal adverse events in women receiving aromatase inhibitors. J Clin Oncol 28(31):4674–4682. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.28.5064
Wang J, Lu K, Song Y, Zhao S, Ma W, Xuan Q, Tang D, Zhao H, Liu L, Zhang Q (2015) RANKL and OPG Polymorphisms Are Associated with Aromatase Inhibitor-Related Musculoskeletal Adverse Events in Chinese Han Breast Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0133964. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133964
Dempsey JM, Xi J, Henry NL, Rae JM, Hertz DL (2018) Attempted replication of SNPs in RANKL and OPG with musculoskeletal adverse events during aromatase inhibitor treatment for breast cancer. Physiol Genomics 50(2):98–99. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00085.2017
Amir E, Seruga B, Niraula S, Carlsson L, Ocana A (2011) Toxicity of adjuvant endocrine therapy in postmenopausal breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(17):1299–1309. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djr242
Mao JJ, Stricker C, Bruner D, Xie S, Bowman MA, Farrar JT, Greene BT, DeMichele A (2009) Patterns and risk factors associated with aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia among breast cancer survivors. Cancer 115(16):3631–3639. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24419
Kanematsu M, Morimoto M, Honda J, Nagao T, Nakagawa M, Takahashi M, Tangoku A, Sasa M (2011) The time since last menstrual period is important as a clinical predictor for non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia. BMC Cancer 11:436. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-436
Acknowledgements
We thank all patients for their collaboration in this study. We would like to thank Cameron Ross, Maureen Trinnear, and James Sinfield for their coordinating assistance. We would also like to acknowledge the entire Breast Disease Site Team at the London Regional Cancer Program for their support of this research. Dr. Richard B. Kim holds the Wolfe Medical Research Chair in Pharmacogenomics at Western. This study was funded by the Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Research Chair Award (Tier-1) in Experimental Therapeutics (Richard B. Kim) and a Catalyst Grant from the London Regional Cancer Program (Richard B. Kim). Adrienne Borrie was supported by grant funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Breast Cancer Society of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borrie, A.E., Rose, F.A., Choi, YH. et al. Genetic and clinical predictors of arthralgia during letrozole or anastrozole therapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 183, 365–372 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05777-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05777-1