Abstract
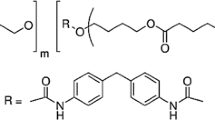
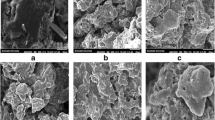
A polyurethane (PU) degrading bacterial strain MZA-75 was isolated from soil through enrichment technique. The bacterium was identified through 16S rRNA gene sequencing, the phylogenetic analysis indicated the strain MZA-75 belonged to genus Bacillus having maximum similarity with Bacillus subtilis strain JBE0016. The degradation of PU films by strain MZA-75 in mineral salt medium (MSM) was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy (FT-IR) and gel permeation chromatography (GPC). SEM revealed the appearance of widespread cracks on the surface. FTIR spectrum showed decrease in ester functional group. Increase in polydispersity index was observed in GPC, which indicates chain scission as a result of microbial treatment. CO2 evolution and cell growth increased when PU was used as carbon source in MSM in Sturm test. Increase in both cell associated and extracellular esterases was observed in the presence of PU indicated by p-Nitrophenyl acetate (pNPA) hydrolysis assay. Analysis of cell free supernatant by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) revealed that 1,4-butanediol and adipic acid monomers were produced. Bacillus subtilis strain MZA-75 can degrade the soft segment of polyester polyurethane, unfortunately no information about the fate of hard segment could be obtained. Growth of strain MZA-75 in the presence of these metabolites indicated mineralization of ester hydrolysis products into CO2 and H2O.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akutsu Y, Nakajima-Kambe T, Nomura N, Nakahara T (1998) Purification and properties of a polyester polyurethane degrading enzyme from Comamonas acidovorans TB-35. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:62–67
Allen A, Hilliard N, Howard GT (1999) Purification and characterization of a soluble polyurethane degrading enzyme from Comamonas acidovorans. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 43:37–41
Al-Sharidah A, Richardt A, Golecki JR, Dierstein R, Tadros MH (2000) Isolation and characterization of two hydrocarbon-degrading Bacillus subtilis strains from oil contaminated soil of Kuwait. Microbiol Res 155:157–164
Arora PK (2012) Decolourization of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol by a soil bacterium, Bacillus subtilis RKJ 700. PLoS One 7(12):e52012
Ashby RD, Solaiman DK (2008) Poly(hydroxyalkanoate) biosynthesis from crude Alaskan pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) oil. J Polym Environ 16:221–229
Barratt SR, Ennos AR, Greenhalgh M, Robson GD, Handley PS (2003) Fungi are the predominant micro-organisms responsible for degradation of soil-buried polyester polyurethane over a range of soil water holding capacities. J Appl Microbiol 95:78–85
Bentham RH, Morton LGH, Allen NG (1987) Rapid assessment of the microbial deterioration of polyurethanes. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 23:377–386
Christenson EM, Patel S, Anderson JM, Hiltner A (2006) Enzymatic degradation of poly(ether urethane) and poly(carbonate urethane) by cholesterol esterase. Biomaterials 27:3920–3926
Crabbe JR, Campbell JR, Thompson L, Walz SL, Schultz WW (1994) Biodegradation of a colloidal ester-based polyurethane by soil fungi. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 33:103–113
Gautam R, Bassi A, Yanful E (2007) Candida rugosa lipase catalyzed polyurethane degradation in aqueous medium. Biotechnol Lett 29:1081–1086
Hoang KC, Tseng M, Shu WJ (2007) Degradation of polyethylene succinate (PES) by a new thermophilic Microbispora strain. Biodegradation 18:333–342
Howard GT, Ruiz C, Hilliard NP (1999) Growth of Pseudomonas chlororaphis on a polyester-polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-esterase enzyme. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 43:7–12
Howard GT, Norton WN, Burks T (2012) Growth of Acinetobacter gerneri P7 on polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase enzyme. Biodegradation 23:561–573
Global polyurethane market: PU-foams and thermoplastic elastomers. Plastemart.com. http://www.plastemart.com/plastic-technical.article. Published on July 25, 2012
Kanwar SS, Verma HK, Kaushal RK, Kumar Y, Chimni SS, Chauhan GS (2005) Effect of solvents and kinetic parameters on synthesis of ethyl propionate catalyzed by poly (AAc-co-HPMA-cl-MBAm)-matrix-immobilized lipase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa BTS-2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1037–1044
Kathiresan K (2003) Polythene and plastics-degrading microbes from the mangrove soil. Rev Biol Trop 51:629–634
Kay MJ, Morton LHG, Prince EL (1991) Bacterial degradation of polyester polyurethane. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 27:205–222
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NI, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:165–275
Lu J, Hong CK, Wool RP (2004) Bio-based nanocomposites from functionalized plant oils and layered silicate. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 42:1441–1450
Mukherjee K, Tribedi P, Chowdhury A, Ray T, Joardar A, Giri S, Sil AK (2011) Isolation of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain from soil that can degrade polyurethane diol. Biodegradation 22:377–388
Muller RJ, Augusta J, Pantke M (1992) An interlaboratory investigation into biodegradation of plastics. Part I: a modified Sturm-test. Mater Organ 27:179–189
Nakajima-Kambe T, Onuma F, Kimpara N, Nakahara T (1995) Isolation and characterization of a bacterium which utilizes polyester polyurethane as a sole carbon and nitrogen source. FEMS Microbiol Lett 129:39–42
Nakajima-Kambe T, Onuma F, Akutsu Y, Nakahara T (1997) Determination of the polyester polyurethane breakdown products and distribution of the polyurethane degrading enzyme of Comamonas acidovorans strain TB-35. J Ferment Bioeng 83:456–460
Perreault NN, Manno D, Halasz A, Thiboutot S, Ampleman G et al (2012) Aerobic biotransformation of 2,4-dinitroanisole in soil and soil Bacillus sp. Biodegradation 23:287–295
Rowe L, Howard GT (2002) Growth of Bacillus subtilis on polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-lipase enzyme. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 50:33–40
Russell JR, Huang J, Anand P, Kucera K, Sandoval AG, Dantzler KW, Hickman DS, Jee J, Kimovec FM, Koppstein D, Marks DH, Mittermiller PA, Núñez SJ, Santiago M, Townes MA, Vishnevetsky M, Williams NE, Vargas MPN, Boulanger LA, Slack CB, Strobel SA (2011) Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by endophytic fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6076–6084
Sabev HA, Handley PS, Robson GD (2006) Fungal colonization of soil-buried plasticized polyvinyl chloride (pPVC) and the impact of incorporated biocides. Microbiology 152:1731–1739
Sauders JH, Frisch KC (1964) Polyurethanes: chemistry and technology, part II technology. Inter-science Publishers, New York
Shah AA, Hasan F, Akhter J, Hameed A, Ahmed S (2008) Degradation of polyurethane by novel bacterial consortium isolated from soil. Ann Microbiol 58:381–386
Shannon MJR, Unterman R (1993) Evaluating bioremediation: distinguishing fact from fiction. Ann Rev Microbiol 47:715–738
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1981) General characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA, Krieg NR, Phillips GB (eds) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 409–443
Usha R, Sangeetha T, Palaniswamy M (2011) Screening of polyethylene degrading microorganisms from garbage soil. Libyan Agric Res Cent J Int 2:200–204
Vega R, Main T, Howard GT (1999) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a polyurethane-degrading enzyme from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 43:49–55
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Higher Education Commission of Pakistan and University of Oklahoma, USA, for providing funds and utilization of lab facilities to accomplish this research, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, Z., Krumholz, L., Aktas, D.F. et al. Degradation of polyester polyurethane by a newly isolated soil bacterium, Bacillus subtilis strain MZA-75. Biodegradation 24, 865–877 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-013-9634-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-013-9634-5