Abstract
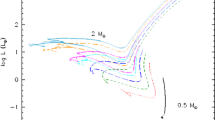
Habitable Zone (HZ) is defined as a life existence area, where water at the surface of the terrestrial planet is in liquid phase. This is caused by the balance of flux from the host star and effective radiative cooling with greenhouse effect of the planet. However, the flux varies according to evolutional phase of the host star. So, a simple but newest HZ model considering stellar mass range from 0.08 to 4.00 M⊙ has been proposed. It studies both at zero-age main sequence (ZAMS) and terminal-age main sequence (TMS) phases to examine persistence of HZ. By the way, it discusses the case of the metallicity like the Sun. Actually, it is interesting to study a HZ model considering host stars with low metallicity. So, we examine the effect of metallicity, following the precedent simple model. In our analysis, metallicity affects little for HZ orbital range at ZAMS, while it affects clearly in case of TMS. Since the inner and outer HZ boundaries at TMS are shifted outward especially in the mass range from 1.5 to 2.0 M⊙, we find persistent HZ is allowed above about 1.8 M⊙. The age of the universe is 13.8 Gyr, which is comparable to main sequence life time of about 0.8 M⊙ for the low metallicity case. Then, the effect of metallicity to estimate HZ of low metallicity host stars is important for the mass range from 0.8 to 1.8 M⊙.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, Y., Abe-Ouchi, A., Sleep, N.H., Zahnle, K.J.: Astrobiology 11, 443 (2011)
Barclay, T., et al. (57 coauthors): Nature 494, 452 (2013). (Erratum: Nature, 496, 252B)
Budyko, M.I.: Tellus 21, 611 (1969)
Campante, T.L., et al. (40 coauthors): CoRoT Symposium 3, Kepler KASC-7 Joint Meeting, id.02004. In: García, R.A., Ballot, J. (eds.) The Space Photometry Revolution, EPJ Web of Conferences, vol. 101 (2015)
Crossfield, I.J.M., et al. (26 coauthors): Astrophys. J. 804, 10 (2015)
Danchi, W.C., Lopez, B.: Astrophys. J. 782, 27 (2013)
Dole, S.H.: Habitable Planets for Man. Blaisdell Pub. Co., New York (1964)
Fogg, M.J.: J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 45, 3 (1992)
France, K., Linsky, J.L., Parke Loyd, R.O.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 354, 3 (2014)
Grenfell, J.L., Gebauer, S., Paris, P., Godolt, M., Rauer, H.: Planet. Space Sci. 98, 66 (2014)
Guo, J., Zhang, F., Chen, X., Han, Z.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 323, 367 (2009)
Guo, J., Zhang, F., Chen, X., Han, Z.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 325, 25 (2010)
Hart, M.H.: Icarus 37, 351 (1979)
Huang, S.-S.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 71, 421 (1959)
Hurley, J.R., Pols, O.R., Tout, C.A.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 315, 543 (2000)
Jones, B.W., Sleep, P.N., Underwood, D.R.: Astrophys. J. 649, 1010 (2006)
Kasting, J.F., Whitmire, D.P., Reynolds, R.T.: Icarus 101, 108 (1993)
Kopparapu, R.K.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 767, L8 (2013)
North, G.R.: J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 2033 (1975)
Orosz, J.A., et al. (38 coauthors): Science 337, 1511 (2012)
Ramirez, R.M., Kaltenegger, L.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 797, L25 (2014)
Rasool, I., De Bergh, C.: Nature 226, 1037 (1970)
Sellers, W.D.: J. Appl. Meteorol. 8, 392 (1969)
Shapley, H.: Climatic Change: Evidence, Causes, and Effects. Harvard University Press, Harvard (1953)
Spiegel, D.S., Raymond, S.N., Dressing, C.D., Scharf, C.A., Mitchell, J.L.: Astrophys. J. 721, 1308 (2010)
Strughold, H.: The Green and Red Planet: A Physiological Study of the Possibility of Life on Mars. University of New Mexico Press, New Mexico (1953)
Tout, C.A., Pols, O.R., Eggleton, P.P., Han, Z.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 281, 257 (1996)
Underwood, D.R., Jones, B.W., Sleep, P.N.: Int. J. Astrobiol. 2, 289 (2003)
Vladilo, G., Murante, G., Silva, L., Provenzale, A., Ferri, G., Ragazzini, G.: Astrophys. J. 767, 65 (2013)
Young, P.A., Kelley, L., Pagano, M.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 755, L31 (2012)
Zsom, A., Seager, S., de Wit, J., Stamenković, V.: Astrophys. J. 778, 109 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referee for useful and fruitful suggestions that helped us to improve the original manuscript very much.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oishi, M., Kamaya, H. A simple evolutional model of Habitable Zone around host stars with various mass and low metallicity. Astrophys Space Sci 361, 66 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2659-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2659-6