Abstract
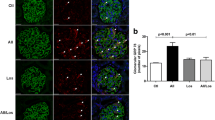
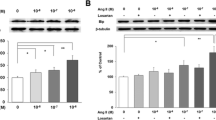
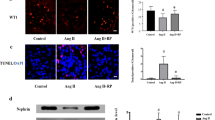
Increasing data have shown that angiotensin II (Ang II) perpetuates podocyte injury and promotes progression to end-stage kidney disease. The mechanism underlying Ang II-induced podocyte apoptosis has not been established. C-terminal Src kinase (Csk) is a cytoplasmic kinase that interacts with scaffolding proteins involved in cell growth, adhesion, and polarization, and the role of Csk in regulating cellular apoptosis has gradually attracted attention. This study evaluates the role of Csk in Ang II-induced podocyte apoptosis. In vivo, Wistar rats were randomly subjected to a normal saline or Ang II infusion. In vitro, we exposed differentiated mouse podocytes to Ang II. Ang II increased Csk expression and induced podocyte apoptosis, stimulated Csk translocation and binding to Caveolin-1, and stimulated decreased Fyn pY416, increased Fyn pY529, and nephrin dephosphorylation. Csk knockdown prevented Ang II-induced podocyte apoptosis, reduced Fyn kinase inactivation, and increased the interaction between nephrin and the activated form of Fyn, accompanied by a reduced interaction between Csk and Caveolin-1. These findings indicate that Ang II induces podocyte injury via a Csk-dependent pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
US Renal Data System (USRDS) (2012) USRDS 2012 Annual data report: atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda
Garg P, Holzman LB (2012) Podocytes: gaining a foothold. Exp Cell Res 318:955–963. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.02.030
New LA, Keyvani Chahi A, Jones N (2013) Direct regulation of nephrin tyrosine phosphorylation by Nck adaptor proteins. J Biol Chem 288:1500–1510. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.439463
Arif E, Rathore YS, Kumari B, Ashish F, Wong HN, Holzman LB, Nihalani D (2014) Slit diaphragm protein Neph1 and its signaling: a novel therapeutic target for protection of podocytes against glomerular injury. J Biol Chem 289:9502–9518. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.505743
Oshima Y, Kinouchi K, Ichihara A, Sakoda M, Kurauchi-Mito A, Bokuda K, Narita T, Kurosawa H, Sun-Wada GH, Wada Y, Yamada T, Takemoto M, Saleem MA, Quaggin SE, Itoh H (2011) Prorenin receptor is essential for normal podocyte structure and function. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:2203–2212. doi:10.1681/ASN.2011020202
Greka A, Mundel P (2012) Cell biology and pathology of podocytes. Annu Rev Physiol 74:299–323. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-020911-153238
Kapodistria K, Tsilibary EP, Politis P, Moustardas P, Charonis A, Kitsiou P (2015) Nephrin, a transmembrane protein, is involved in pancreatic beta-cell survival signaling. Mol Cell Endocrinol 400:112–128. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2014.11.003
Ren Z, Liang W, Chen C, Yang H, Singhal PC, Ding G (2012) Angiotensin II induces nephrin dephosphorylation and podocyte injury: role of caveolin-1. Cell Signal 24:443–450. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.09.022
Liu Y, Liang W, Yang Y, Pan Y, Yang Q, Chen X, Singhal PC, Ding G (2015) IQGAP1 regulates actin cytoskeleton organization in podocytes through interaction with nephrin. Cell Signal 27:867–877. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.01.015
Denhez B, Lizotte F, Guimond MO, Jones N, Takano T, Geraldes P (2015) Increased SHP-1 protein expression by high glucose levels reduces Nephrin phosphorylation in podocytes. J Biol Chem 290:350–358. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.612721
Gagliardini E, Perico N, Rizzo P, Buelli S, Longaretti L, Perico L, Tomasoni S, Zoja C, Macconi D, Morigi M, Remuzzi G, Benigni A (2013) Angiotensin II contributes to diabetic renal dysfunction in rodents and humans via Notch1/Snail pathway. Am J Pathol 183:119–130. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.03.025
Register AC, Leonard SE, Maly DJ (2014) SH2-catalytic domain linker heterogeneity influences allosteric coupling across the SFK family. Biochemistry 53:6910–6923. doi:10.1021/bi5008194
Elliott J, Zheleznova NN, Wilson PD (2011) c-Src inactivation reduces renal epithelial cell-matrix adhesion, proliferation, and cyst formation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301:C522–C529. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00163.2010
Mezquita B, Mezquita P, Pau M, Mezquita J, Mezquita C (2014) Unlocking doors without keys: activation of Src by truncated C-terminal intracellular receptor tyrosine kinases lacking tyrosine kinase activity. Cells 3:92–111. doi:10.3390/cells3010092
Yeatman TJ (2004) A renaissance for SRC. Nat Rev Cancer 4:470–480. doi:10.1038/nrc1366
Roskoski R (2015) Src protein-tyrosine kinase structure, mechanism, and small molecule inhibitors. Pharmacol Res 94:9–25. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2015.01.003
Okada M (2012) Regulation of the Src family kinases by CSK. Int J Biol Sci 8:1385–1397. doi:10.7150/ijbs.5141
Wong L, Lieser SA, Miyashita O, Miller M, Tasken K, Onuchic JN, Adams JA, Woods VL, Jennings PA (2005) Coupled motions in the SH2 and kinase domains of CSK control Src phosphorylation. J Mol Biol 351:131–143. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.05.042
Nuche-Berenguer B, Moreno P, Jensen RT (2015) Elucidation of the roles of the Src kinases in pancreatic acinar cell signaling. J Cell Biochem 116:22–36. doi:10.1002/jcb.24895
Vang T, Liu WH, Delacroix L, Wu S, Vasile S, Dahl R, Yang L, Musumeci L, Francis D, Landskron J, Tasken K, Tremblay ML, Lie BA, Page R, Mustelin T, Rahmouni S, Rickert RC, Tautz L (2012) LYP inhibits T-cell activation when dissociated from CSK. Nat Chem Biol 8:437–446. doi:10.1038/nchembio.916
Li J, Zelenin S, Aperia A, Aizman O (2006) Low doses of ouabain protect from serum deprivation-triggered apoptosis and stimulate kidney cell proliferation via activation of NF-γB. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1848–1857. doi:10.1681/ASN.2005080894
Ding G, Reddy K, Kapasi AA, Franki N, Gibbons N, Kasinath BS, Singhal PC (2002) Angiotensin II induces apoptosis in rat glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F173–F180. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00240.2001
Liu Y, Liang W, Yang Q, Ren Z, Chen X, Zha D, Singhal PC, Ding G (2013) IQGAP1 mediates angiotensin II-induced apoptosis of podocytes via the ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway. Am J Nephrol 38:430–444. doi:10.1159/000355970
Dodd DA, Worth RG, Rosen MK, Grinstein S, van Oers NS, Hansen EJ (2014) The Haemophilus ducreyi LspA1 protein inhibits phagocytosis by using a new mechanism involving activation of C-terminal Src kinase. MBio 5:e1114–e1178. doi:10.1128/mBio.01178-14
Naik MU, Caplan JL, Naik UP (2014) Junctional adhesion molecule-A suppresses platelet integrin αIIbβ3 signaling by recruiting Csk to the integrin-c-Src complex. Blood 123:1393–1402. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-04-496232
Kwon HJ, Waghmare I, Verghese S, Singh A, Singh A, Kango-Singh M (2015) Drosophila C-terminal Src kinase regulates growth via the Hippo signaling pathway. Dev Biol 397:67–76. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.10.010
Tanaka H, Akagi K, Oneyama C, Tanaka M, Sasaki Y, Kanou T, Lee YH, Yokogawa D, Dobenecker MW, Nakagawa A, Okada M, Ikegami T (2013) Identification of a new interaction mode between the Src homology 2 domain of C-terminal Src kinase (CSK) and CSK-binding protein/phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid microdomains. J Biol Chem 288:15240–15254. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.439075
Yang KC, Rutledge CA, Mao M, Bakhshi FR, Xie A, Liu H, Bonini MG, Patel HH, Minshall RD, Dudley SC (2014) Caveolin-1 modulates cardiac gap junction homeostasis and arrhythmogenecity by regulating cSrc tyrosine kinase. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 7:701–710. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.113.001394
Tan YX, Manz BN, Freedman TS, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Weiss A (2014) Inhibition of the kinase CSK in thymocytes reveals a requirement for actin remodeling in the initiation of full TCR signaling. Nat Immunol 15:186–194. doi:10.1038/ni.2772
Yu L, Lin Q, Feng J, Dong X, Chen W, Liu Q, Ye J (2013) Inhibition of nephrin activation by c-mip through Csk-Cbp-Fyn axis plays a critical role in Angiotensin II-induced podocyte damage. Cell Signal 25:581–588. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.11.017
Jo A, Park H, Lee SH, Ahn SH, Kim HJ, Park EM, Choi YH (2014) SHP-2 binds to caveolin-1 and regulates Src activity via competitive inhibition of CSK in response to H2O2 in astrocytes. PLoS One 9:e91582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0091582
Jones N, Blasutig IM, Eremina V, Ruston JM, Bladt F, Li H, Huang H, Larose L, Li SS, Takano T, Quaggin SE, Pawson T (2006) Nck adaptor proteins link nephrin to the actin cytoskeleton of kidney podocytes. Nature 440:818–823. doi:10.1038/nature04662
Verma R, Wharram B, Kovari I, Kunkel R, Nihalani D, Wary KK, Wiggins RC, Killen P, Holzman LB (2003) Fyn binds to and phosphorylates the kidney slit diaphragm component Nephrin. J Biol Chem 278:20716–20723. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301689200
Jeon BK, Kwon K, Kang JL, Choi YH (2015) Csk-induced phosphorylation of Src at tyrosine 530 is essential for H2O2-mediated suppression of ERK1/2 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Sci Rep 5:12725. doi:10.1038/srep12725
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China (81300559 to Z. Ren and 81270762 to G. Ding).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Lu Zhang and Zhilong Ren have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Ren, Z., Yang, Q. et al. Csk regulates angiotensin II-induced podocyte apoptosis. Apoptosis 21, 846–855 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1256-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1256-z