Abstract
Background
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) is a relatively rare, malignant disease of the esophagus. The prognosis of patients with BSCC is thought to be poorer than that of typical squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), but the treatment strategy for BSCC is generally the same as that for typical SCC. This study examined the diagnosis, the clinical and pathological characteristics, and the results of therapy in patients with BSCC.
Methods
The medical records for 13 patients with pathologically confirmed esophageal BSCC were extracted. The pretreatment endoscopic diagnosis and the pathological diagnosis after resection were reviewed for each patient, and the histological features and patient outcome were examined. We especially focus on histological difference and endoscopic findings of the 13 patients with BSCC.
Results
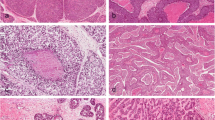
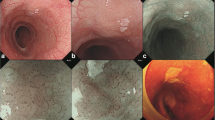
Macroscopically, BSCC was mainly visualized as an elevated lesion with normal epithelium on the surface layer which indicated the tumor growth into submucosa. Further pathological examination allowed the 13 BSCC patients to be grouped into 2 groups according to differences in the microscopic appearances of the BSCC cancer cells: a typical BSCC pattern and a pattern similar to that of poorly differentiated SCC. Six of the patients who received an esophagectomy as the primary treatment died, and only 1 patient survived. Two patients who received chemoradiotherapy before an esophagectomy did not develop recurrences. Almost all the patients who died as a result of the recurrence of esophageal cancer had a lymph node recurrence. Prognoses of BSCCs with a pattern similar to that of poorly differentiated SCC without preoperative chemotherapy were poorer than BSCCs with a typical BSCC pattern, while BSCC with a pattern similar to poorly differentiated SCC with preoperative chemotherapy showed good prognoses than BSCC without preoperative chemotherapy.
Conclusions
BSCC esophageal cancer mainly appears as an elevated lesion with submucosal growth, which can be diagnosed preoperatively by understanding of macroscopic characteristics of esophageal BSCC. The outcome of the BSCC patients in the present study was relatively poor, while pretreatment diagnosis of BSCC influences the strategy of treatment and pathological diagnosis including histological difference of BSCC may lead to appropriate treatment and better prognosis of esophageal BSCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takubo K, Mafune K, Tanaka Y, Miyama T, Fujita K. Basaloid-squamous carcinoma of the esophagus with marked deposition of basement membrane substance. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1991;41:59–64.
Rubio CA, Liu FS. The histogenesis of microinvasive basal cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Pathol Res Pract. 1990;186:223–7.
Abe K, Sasano H, Itakura Y, Nishihira T, Mori S, Nagura H. Basaloid-squamous carcinoma of the esophagus. A clinicopathologic, DNA ploidy, and immunohistochemical study of seven cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996;20:453–61.
Vaaudev P, Boutross-Tadross O, Radhi J. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma: two case reports. Cases J. 2009;2:9351.
Cho KJ, Jang JJ, Lee SS, Zo JI. Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the oesophagus: a distinct neoplasm with multipotential differentiation. Histopathology. 2000;36(4):331–40.
Schaefer IM, Enders C, Polten A, Haller F, Frölich AM, Cameron S, et al. Common genomic aberrations in basaloid squamous cell carcinoma and carcinosarcoma of the esophagus detected by CGH and array CGH. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135(4):579–86.
Chen SB, Weng HR, Wang G, Yang JS, Yang WP, et al. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:1165–71.
Imamhasan A, Mitomi H, Saito T, Hayashi T, Takahashi M, Kajiyama Y, et al. Immunohistochemical and oncogenetic analyses of esophageal basaloid squamous cell carcinoma in comparison with conventional squamous cell carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2012;43:2012–23.
Wain SL, Kier R, Vollmer RT, Bossen EH. Basaloid-squamous carcinoma of the tongue, hypopharynx, and larynx: report of 10 cases. Hum Pathol. 1986;17:1158–66.
The Japan Esophageal Society. Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer. 10th ed 2008 (Revised version).
Ohashi K, Horiguchi S, Moriyama S, Hishima T, Hayashi Y, Momma K, et al. Superficial basaloid squamous carcinoma of the esophagus. A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 12 cases. Pathol Res Pract. 2003;199(11):713–21.
Zhang XH, Sun GQ, Ahou XJ, Guo HF, Zhang TH. Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the esophagus: a clinicopathological, immunohistological and electron microscopic study of sixteen cases. World J Gastroenterol. 1998;4:297–403.
Sarbia M, Verreet P, Bittinger F, Dutkowski P, Heep H, Willers R, et al. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer. 1997;79:1871–8.
Li TJ, Zhang YX, Wen J, Cowan DF, Hart J, Xiao SY. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus with and without adenoid cystic features. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128:1124–30.
Zhang BH, Cheng GY, Xue Q, Gao SG, Sun KL, Wang YG, et al. Clinical outcomes of Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a retrospective analysis of 142 cases. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(3):1889–94.
Lam KY, Law S, Luk JM, Wong J. Oesophageal basaloid squamous cell carcinoma: a unique clinicopathological entity with telomerase activity as prognostic indicator. J Pathol. 2001;195:435–42.
Ohashi K, Horiguchi S, Moriyama S, Hishima T, Hayashi Y, Momma K, et al. Superficial basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. A clinicopathological and immunohistological study of the 12 cases. Pathol Res Pract. 2003;199(11):713–21.
The Japanese society for esophageal diseases:comprehensive registry of Esophageal cancer in Japan(1998,1999). 3rd ed, 2002.
Luna MA, Parichatikanond P, Weber RS. BatsakisJG: Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. Clinicopathologic and DNA flow cytometric analysis. Cancer. 1990;66:537–42.
Kobayashi Y, Nakanishi Y, Taniguchi H, Sekine S, Igaki H, Tachimori Y, et al. Histological diversity in basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Disease of the esophagus. 2009;22:231–8.
Ethical Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any authors.
Conflict of interest
Author Rieko Nakamura, Author Tai Omori, Author Hiroya Takeuchi, Author Hirofumi Kawakubo, Author Tsunehiro Takahashi, Author Norihito Wada, Author Yoshiro Saikawa, Author Kaori Kameyama, and Author Yuko Kitagawa declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, R., Omori, T., Takeuchi, H. et al. Characteristics and diagnosis of esophageal basaloid squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus 13, 48–54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-015-0490-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-015-0490-8