Abstract
Purpose
To assess the effect of signal strength (SS) on reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness measurement (measurement agreement) and its color-coded classification (classification agreement) by time-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Methods
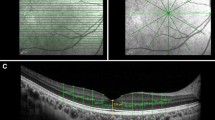
Two consecutive Stratus OCT scans with the Fast RNFL protocol were performed in 658 participants. Intraclass correlations and the linear-weighted kappa coefficient were calculated as indicators of RNFL measurement and classification agreement in participants grouped according to the difference in SS between consecutive OCT scans (interscan SS difference).
Results
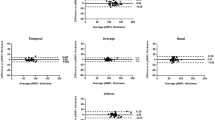
Groups with a larger interscan SS difference (= 2) had lower measurement agreement than those with a smaller interscan SS difference (0 or 1) for the temporal quadrant and total average RNFL. Classification agreement for the nasal quadrant was lower in the groups with a larger interscan SS difference (= 2) than in those with a smaller interscan SS difference. The tendency of SS to affect classification and measurement agreement remained similar in the group with thinner RNFL thickness (≤85 μm), but not in the group with thicker RNFL.
Conclusions
Careful attention should be paid when comparing two or more OCT scans for RNFL thickness measurement or its color-coded classification as the agreement may be sensitive to SS differences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budenz DL, Anderson DR, Varma R, et al. Determinants of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmology 2007;114:1046–1052.
Cheung CY, Leung CK, Lin D, Pang CP, Lam DS. Relationship between retinal nerve fiber layer measurement and signal strength in optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2008;115:1347–1351.
Wu Z, Huang J, Dustin L, Sadda SR. Signal strength is an important determinant of accuracy of nerve fiber layer thickness measurement by optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma 2009;18:213–216.
Wu Z, Vazeen M, Varma R, et al. Factors associated with variability in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements obtained by optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2007;114:1505–1512.
Barkana Y, Burgansky-Eliash Z, Gerber Y, et al. Inter-device variability of the Stratus optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2009;147:260–266.
Sung KR, Wollstein G, Schuman JS, et al. Advanced Imaging in Glaucoma Study Group. Scan quality effect on glaucoma discrimination by glaucoma imaging devices. Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93:1580–1584.
Nunnally JC. Psychometric theory. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company; 1978.
Altman DG. Practical statistics for medical research. London: Chapman and Hall; 1991.
Budenz DL, Chang RT, Huang X, Knighton RW, Tielsch JM. Reproducibility of retinal nerve fiber thickness measurements using the stratus OCT in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005;46:2440–2443.
Budenz DL, Fredette MJ, Feuer WJ, Anderson DR. Reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber thickness measurements with stratus OCT in glaucomatous eyes. Ophthalmology 2008;115:661–666.
Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a variability and diagnostic performance study. Ophthalmology 2009;116:1257–1263.
Knighton RW, Qian C. An optical model of the human retinal nerve fiber layer: implications of directional reflectance for variability of clinical measurements. J Glaucoma 2000;9:56–62.
Antón A, Castany M, Pazos-Lopez M, et al. Reproducibility of measurements and variability of the classification algorithm of Stratus OCT in normal, hypertensive, and glaucomatous patients. Clin Ophthalmol 2009;3:139–145.
Wu Z, Huang J, Sadda S. Signal strength and thickness measurements on optical coherence tomography. Author reply. J Glaucoma 2009;18:500.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, E.S., Kim, H. & Kim, J.M. Effect of signal strength on reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurement and its classification by time-domain optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol 54, 414–422 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-010-0850-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-010-0850-9