Abstract
Object
To propose a fast and robust acquisition and post-processing pipeline that is time-compatible with clinical explorations to obtain a proton density (ρ) map used as a reference for metabolic map normalization. This allows inter-subject and inter-group comparisons of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) data and longitudinal follow-up for single subjects.
Materials and methods
A multi-echo T *2 mapping sequence, the XEP sequence for B +1 -mapping and Driven Equilibrium Single Pulse Observation of T 1—an optimized variable flip angle method for T 1 mapping used for both B −1 -mapping and M 0 calculation—were used to determine correction factors leading to quantitative water proton density maps at 3T. Normalized metabolite maps were obtained on a phantom and nine healthy volunteers. To show the potential use of this technique at the individual level, we also explored one patient with low-grade glioma.
Results
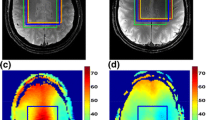
Accurate ρ maps were obtained both on phantom and volunteers. After signal normalization with the generated ρ maps, metabolic concentrations determined by the present method differed from theory by <7 % in the phantom and were in agreement with data from the literature for the healthy controls. Using these normalized metabolic values, it was possible to demonstrate in the patient with brain glioma, metabolic abnormalities in normalized N-acetyl aspartate, choline and creatine levels; illustrating the potential for direct use of this technique in clinical studies.
Conclusion
The proposed combination of sequences provides a robust ρ map that can be used to normalize metabolic maps in clinical MRSI studies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu WJ, Delbello MP, Jarvis KB, Norris MM, Kim MJ, Weber W, Lee JH, Strakowski SM, Adler CM (2013) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging of lactate in patients with bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res 213:230–234
Stagg CJ, Knight S, Talbot K, Jenkinson M, Maudsley AA, Turner MR (2013) Whole-brain magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging measures are related to disability in ALS. Neurology 80:610–615
Siger M, Schuff N, Zhu X, Miller BL, Weiner MW (2009) Regional myo-inositol concentration in mild cognitive impairment using 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 23:57–62
Ernst T, Kreis R, Ross BD (1993) Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the human brain. I. Compartments and water. J Magn Reson Ser B 102:1–8
Kreis R, Ernst T, Ross BD (1993) Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the human brain. II. Metabolite concentrations. J Magn Reson Ser B 102:9–19
Maudsley AA, Darkazanli A, Alger JR, Hall LO, Schuff N, Studholme C, Yu Y, Ebel A, Frew A, Goldgof D, Gu Y, Pagare R, Rousseau F, Sivasankaran K, Soher BJ, Weber P, Young K, Zhu X (2006) Comprehensive processing, display and analysis for in vivo MR spectroscopic imaging. NMR Biomed 19:492–503
Spoto GP, Press GA, Hesselink JR, Solomon M (1990) Intracranial ependymoma and subependymoma: mR manifestations. Am J Neuroradiol 11:83–91
Warntjes JB, Dahlqvist O, Lundberg P (2007) Novel method for rapid, simultaneous T1, T*2, and proton density quantification. Magn Reson Med 57:528–537
Volz S, Noth U, Deichmann R (2012) Correction of systematic errors in quantitative proton density mapping. Magn Reson Med 68:74–85
Volz S, Noth U, Jurcoane A, Ziemann U, Hattingen E, Deichmann R (2012) Quantitative proton density mapping: correcting the receiver sensitivity bias via pseudo proton densities. Neuroimage 63:540–552
Kover F, Schwarcz A, Pal J, Bogner P, Vajna T, Vadon G, Doczi T (2004) Fast method for longitudinal relaxation time and water content mapping of the human brain on a clinical MR scanner. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:1341–1346
Venkatesan R, Lin W, Haacke EM (1998) Accurate determination of spin-density and T1 in the presence of RF-field inhomogeneities and flip-angle miscalibration. Magn Reson Med 40:592–602
Newbould RD, Skare ST, Alley MT, Gold GE, Bammer R (2010) Three-dimensional T (1), T (2) and proton density mapping with inversion recovery balanced SSFP. Magn Reson Imaging 28:1374–1382
Neeb H, Ermer V, Stocker T, Shah NJ (2008) Fast quantitative mapping of absolute water content with full brain coverage. Neuroimage 42:1094–1109
Sabati M, Maudsley AA (2013) Fast and high-resolution quantitative mapping of tissue water content with full brain coverage for clinically-driven studies. Magn Reson Imaging 31:1752–1759
Amadon A, Boulant N, Cloos MA, Giacomini E, Wiggins CJ, Luong M, Ferrand G, Fautz H-P (2010) Mapping of an 8-channels TX-array over a human-head like volume in less than 2 minutes: the XEP sequence. Proceedings of the 18th scientific meeting, International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Stockholm, p 2828
Deoni SC, Rutt BK, Peters TM (2003) Rapid combined T1 and T2 mapping using gradient recalled acquisition in the steady state. Magn Reson Med 49:515–526
Fautz H-P, Vogel M, Gross P, Kerr A, Zhu Y (2008) B1 mapping of coil arrays for parallel transmission. Proceedings of the 16th scientific meeting, International Society dor Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Toronto, p 1247
Haacke EM, Brown RW, Thompson MR, Venkatesan R (1999) Physical principles and sequence design. Wiley-Liss, New York
Schabel MC, Morrell GR (2009) Uncertainty in T (1) mapping using the variable flip angle method with two flip angles. Phys Med Biol 54:N1–N8
Deoni SC, Peters TM, Rutt BK (2004) Determination of optimal angles for variable nutation proton magnetic spin-lattice, T1, and spin–spin, T2, relaxation times measurement. Magn Reson Med 51:194–199
Wang J, Qiu M, Constable RT (2005) In vivo method for correcting transmit/receive nonuniformities with phased array coils. Magn Reson Med 53:666–674
Duc CO, Weber OM, Trabesinger AH, Meier D, Boesiger P (1998) Quantitative 1H MRS of the human brain in vivo based on the stimulation phantom calibration strategy. Magn Reson Med 39:491–496
Jansen JF, Backes WH, Nicolay K, Kooi ME (2006) 1H MR spectroscopy of the brain: absolute quantification of metabolites. Radiology 240:318–332
Buchli R, Boesiger P (1993) Comparison of methods for the determination of absolute metabolite concentrations in human muscles by 31P MRS. Magn Reson Med 30:552–558
Mlynarik V, Gruber S, Moser E (2001) Proton T (1) and T (2) relaxation times of human brain metabolites at 3 Tesla. NMR Biomed 14:325–331
Tsai SY, Posse S, Lin YR, Ko CW, Otazo R, Chung HW, Lin FH (2007) Fast mapping of the T2 relaxation time of cerebral metabolites using proton echo-planar spectroscopic imaging (PEPSI). Magn Reson Med 57:859–865
Brooks RA, Di Chiro G, Keller MR (1980) Explanation of cerebral white-gray contrast in computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 4:489–491
Torack RM, Alcala H, Gado M, Burton R (1976) Correlative assay of computerized cranial tomography CCT, water content and specific gravity in normal and pathological postmortem brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 35:385–392
Rieth KG, Fujiwara K, Di Chiro G, Klatzo I, Brooks RA, Johnston GS, O’Connor CM, Mitchell LG (1980) Serial measurements of CT attenuation and specific gravity in experimental cerebral edema. Radiology 135:343–348
Le Fur Y, Nicoli F, Guye M, Confort-Gouny S, Cozzone PJ, Kober F (2010) Grid-free interactive and automated data processing for MR chemical shift imaging data. Magn Reson Mater Phy 23:23–30
Mattei JP, Fur YL, Cuge N, Guis S, Cozzone PJ, Bendahan D (2006) Segmentation of fascias, fat and muscle from magnetic resonance images in humans: the DISPIMAG software. Magn Reson Mater Phy 19:275–279
Galanaud D, Le Fur Y, Nicoli F, Denis B, Confort-Gouny S, Ranjeva JP, Viout P, Pelletier J, Cozzone PJ (2001) Regional metabolite levels of the normal posterior fossa studied by proton chemical shift imaging. Magn Reson Mater Phy 13:127–133
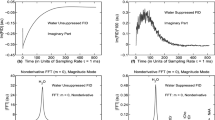
Le Fur Y, Cozzone PJ (2013) FID modulus: a simple and efficient technique to phase and align MR spectra. Magn Reson Mater Phy. doi:10.1007/s10334-013-0381-8
Vanhamme L, van den Boogaart A, Van Huffel S (1997) Improved method for accurate and efficient quantification of MRS data with use of prior knowledge. J Magn Reson 129:35–43
Pijnappel WWF, Van Den Boogaart A, De Beer R, Van Ormondt D (1992) SVD-based quantification of magnetic resonance signals. J Magn Reson 97:122–134
Tisell A, Leinhard OD, Warntjes JB, Lundberg P (2012) Procedure for quantitative (1) H magnetic resonance spectroscopy and tissue characterization of human brain tissue based on the use of quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.24554
Gasparovic C, Neeb H, Feis DL, Damaraju E, Chen H, Doty MJ, South DM, Mullins PG, Bockholt HJ, Shah NJ (2009) Quantitative spectroscopic imaging with in situ measurements of tissue water T1, T2, and density. Magn Reson Med 62:583–590
Lu H, Nagae-Poetscher LM, Golay X, Lin D, Pomper M, van Zijl PC (2005) Routine clinical brain MRI sequences for use at 3.0 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:13–22
De Graaf RA (2007) In vivo NMR spectroscopy principles and techniques, 2nd edn. Wiley-Liss, Chichester, pp 302–303
Ethofer T, Mader I, Seeger U, Helms G, Erb M, Grodd W, Ludolph A, Klose U (2003) Comparison of longitudinal metabolite relaxation times in different regions of the human brain at 1.5 and 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 50:1296–1301
Preibisch C, Deichmann R (2009) T1 mapping using spoiled FLASH-EPI hybrid sequences and varying flip angles. Magn Reson Med 62:240–246
Wright PJ, Mougin OE, Totman JJ, Peters AM, Brookes MJ, Coxon R, Morris PE, Clemence M, Francis ST, Bowtell RW, Gowland PA (2008) Water proton T1 measurements in brain tissue at 7, 3, and 1.5 T using IR-EPI, IR-TSE, and MPRAGE: results and optimization. Magn Reson Mater Phy 21:121–130
Wansapura JP, Holland SK, Dunn RS, Ball WS Jr (1999) NMR relaxation times in the human brain at 3.0 tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:531–538
Stanisz GJ, Odrobina EE, Pun J, Escaravage M, Graham SJ, Bronskill MJ, Henkelman RM (2005) T1, T2 relaxation and magnetization transfer in tissue at 3T. Magn Reson Med 54:507–512
Gussew A, Erdtel M, Hiepe P, Rzanny R, Reichenbach JR (2012) Absolute quantitation of brain metabolites with respect to heterogeneous tissue compositions in (1) H-MR spectroscopic volumes. Magn Reson Mater Phy 25:321–333
Gasparovic C, Song T, Devier D, Bockholt HJ, Caprihan A, Mullins PG, Posse S, Jung RE, Morrison LA (2006) Use of tissue water as a concentration reference for proton spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 55:1219–1226
Chadzynski GL, Klose U (2010) Chemical shift imaging without water suppression at 3 T. Magn Reson Imaging 28:669–675
Chadzynski GL, Klose U (2013) Proton CSI without solvent suppression with strongly reduced field gradient related sideband artifacts. Magn Reson Mater Phy 26:183–192
Dong Z, Dreher W, Leibfritz D (2006) Toward quantitative short-echo-time in vivo proton MR spectroscopy without water suppression. Magn Reson Med 55:1441–1446
Serrai H, Clayton DB, Senhadji L, Zuo C, Lenkinski RE (2002) Localized proton spectroscopy without water suppression: removal of gradient induced frequency modulations by modulus signal selection. J Magn Reson 154:53–59
Hernando D, Vigen KK, Shimakawa A, Reeder SB (2012) R (2) mapping in the presence of macroscopic B (0) field variations. Magn Reson Med 68:830–840
Preibisch C, Deichmann R (2009) Influence of RF spoiling on the stability and accuracy of T1 mapping based on spoiled FLASH with varying flip angles. Magn Reson Med 61:125–135
Morrell GR (2008) A phase-sensitive method of flip angle mapping. Magn Reson Med 60:889–894
Akoka S, Franconi F, Seguin F, Le Pape A (1993) Radiofrequency map of an NMR coil by imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 11:437–441
Nehrke K, Versluis MJ, Webb A, Bornert P (2013) Volumetric B (1) (+) mapping of the brain at 7T using DREAM. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.24667
Yoshida K, Furuse M, Kaneoke Y, Saso K, Inao S, Motegi Y, Ichihara K, Izawa A (1989) Assessment of T1 time course changes and tissue-blood ratios after Gd-DTPA administration in brain tumors. Magn Reson Imaging 7:9–15
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Angèle Viola for the preparation of phantoms. Angèle Lecocq is the recipient of a PhD Grant (CIFRE) supported by Siemens France and the French Ministry of Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lecocq, A., Le Fur, Y., Amadon, A. et al. Fast water concentration mapping to normalize 1H MR spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Mater Phy 28, 87–100 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-014-0451-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-014-0451-6