Abstract
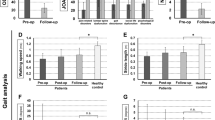
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) combined with posterior column osteotomy (PCO) may be effective to achieve ideal lumbar curve correction in lumbar flat-back deformity (LFD). We aimed to investigate the radiographic and clinical outcomes of patients with primary degenerative LFD treated with multi-level ALIFs combined with PCOs. Seventy patients with primary degenerative LFD who underwent corrective surgery were divided into three groups according to the 1-month postoperative pelvic incidence/lumbar lordosis (PI-LL) angles (≤ − 10°, from − 9° to 9°, and ≥ 10°). The spinopelvic parameters, including thoracic kyphosis, LL, pelvic tilt, T1 pelvic angle, and sagittal vertical axis, were analyzed at the preoperative, postoperative follow-up periods. The clinical outcomes, including the Oswestry disability index (ODI), visual analog scale (VAS), and Scoliosis Research Society (SRS)-22r, were also evaluated. Further, the paraspinal muscles were qualitatively and quantitatively examined, preoperatively. All spinopelvic parameters were corrected as close to the normal values at the 1-month postoperative period. The spinopelvic parameters in the PI-LL ≤ − 10° group were better corrected and maintained than those in the other groups. The ODI, VAS, and SRS-22r scores improved at the final follow-up in all groups. The PI-LL ≤ − 10° group showed better clinical outcomes than the other groups. In the paraspinal muscle examination, the mean lumbar muscularity value and fatty degeneration ratio were 236.7% and 20.7%, respectively. Multi-level ALIFs with PCOs in patients with LFD are effective in restoring sagittal balance and improving clinical symptoms. In addition, the postoperative LL angles should be larger than PI + 10° to achieve good overall outcomes in patients with severe degenerative back muscle.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames CP, Smith JS, Scheer JK, Bess S, Bederman SS, Deviren V, Lafage V, Schwab F, Shaffrey CI (2012) Impact of spinopelvic alignment on decision making in deformity surgery in adults: a review. J Neurosurg Spine 16:547–564. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.2.SPINE11320
Berjano P, Langella F, Ismael MF, Damilano M, Scopetta S, Lamartina C (2014) Successful correction of sagittal imbalance can be calculated on the basis of pelvic incidence and age. Eur Spine J 23(Suppl 6):587–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3556-8
Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Rinella A, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K (2004) Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(Suppl 1):44–50
Cho KJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Berra A, Baldus C (2005) Comparison of Smith-Petersen versus pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of fixed sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:2030–2037; discussion 2038
Choi MK, Kim SM (2017) Nontraumatic multiple vertebral compression fractures induced by primary hyperparathyroidism: a case report and literature review. World Neurosurg 108:992 e995–992 e999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.08.157
Crandall DG, Revella J (2009) Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion as an adjunct to posterior instrumented correction of degenerative lumbar scoliosis: three year clinical and radiographic outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:2126–2133. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181b612db
Deukmedjian AR, Dakwar E, Ahmadian A, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2012) Early outcomes of minimally invasive anterior longitudinal ligament release for correction of sagittal imbalance in patients with adult spinal deformity. ScientificWorldJournal 2012:789698. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/789698
Deukmedjian AR, Le TV, Baaj AA, Dakwar E, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2012) Anterior longitudinal ligament release using the minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach: a cadaveric feasibility study and report of 4 clinical cases. J Neurosurg Spine 17:530–539. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.8.SPINE12432
Hsieh PC, Koski TR, O'Shaughnessy BA, Sugrue P, Salehi S, Ondra S, Liu JC (2007) Anterior lumbar interbody fusion in comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: implications for the restoration of foraminal height, local disc angle, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine 7:379–386. https://doi.org/10.3171/SPI-07/10/379
Jang JS, Lee SH, Min JH, Maeng DH (2007) Changes in sagittal alignment after restoration of lower lumbar lordosis in patients with degenerative flat back syndrome. J Neurosurg Spine 7:387–392. https://doi.org/10.3171/SPI-07/10/387
Janssen ME, Lam C, Beckham R (2001) Outcomes of allogenic cages in anterior and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J 10(Suppl 2):S158–S168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005860100292
Jun HS, Kim JH, Ahn JH, Chang IB, Song JH, Kim TH, Park MS, Chan Kim Y, Kim SW, Oh JK, Yoon DH (2016) The effect of lumbar spinal muscle on spinal sagittal alignment: evaluating muscle quantity and quality. Neurosurgery 79:847–855. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001269
Kim HJ, Bridwell KH, Lengke LG, Park MS, Song KS, Piyaskulkaew C, Chuntarapas T (2014) Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis requiring revision surgery have higher postoperative lumbar lordosis and larger balance correction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20;39(9):E576–E580. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.00000000000000246
Lafage V, Bharucha NJ, Schwab F, Hart RA, Burton D, Boachie-Adjei O, Smith JS, Hostin R, Shaffrey C, Gupta M, Akbarnia BA, Bess S (2012) Multicenter validation of a formula predicting postoperative spinopelvic alignment. J Neurosurg Spine 16:15–21. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.8.SPINE11272
Lee CS, Lee CK, Kim YT, Hong YM, Yoo JH (2001) Dynamic sagittal imbalance of the spine in degenerative flat back: significance of pelvic tilt in surgical treatment. Spine 26:2029–2035
Lee JC, Cha JG, Kim Y, Kim YI, Shin BJ (2008) Quantitative analysis of back muscle degeneration in the patients with the degenerative lumbar flat back using a digital image analysis: comparison with the normal controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:318–325. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318162458f
Manwaring JC, Bach K, Ahmadian AA, Deukmedjian AR, Smith DA, Uribe JS (2014) Management of sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity with minimally invasive anterolateral lumbar interbody fusion: a preliminary radiographic study. J Neurosurg Spine 20:515–522. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.2.SPINE1347
Pezolato A, de Vasconcelos EE, Defino HL, Nogueira-Barbosa MH (2012) Fat infiltration in the lumbar multifidus and erector spinae muscles in subjects with sway-back posture. Eur Spine J 21:2158–2164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2286-z
Rajaraman V, Vingan R, Roth P, Heary RF, Conklin L, Jacobs GB (1999) Visceral and vascular complications resulting from anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg 91:60–64
Ramieri A, Miscusi M, Domenicucci M, Raco A, Costanzo G (2017) Surgical management of coronal and sagittal imbalance of the spine without PSO: a multicentric cohort study on compensated adult degenerative deformities. Eur Spine J 26(Suppl 4):442–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5042-6
Ranson CA, Burnett AF, Kerslake R, Batt ME, O'Sullivan PB (2006) An investigation into the use of MR imaging to determine the functional cross sectional area of lumbar paraspinal muscles. Eur Spine J 15:764–773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-005-0909-3
Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V (2010) Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine 35:2224–2231. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ee6bd4
Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, Hostin R, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS, Boachie-Adjei O, Burton DC, Akbarnia BA, Mundis GM, Ames CP, Kebaish K, Hart RA, Farcy JP, Lafage V, International Spine Study G (2013) Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:E803–E812. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318292b7b9
Smith JS, Bess S, Shaffrey CI, Burton DC, Hart RA, Hostin R, Klineberg E, International Spine Study G (2012) Dynamic changes of the pelvis and spine are key to predicting postoperative sagittal alignment after pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a critical analysis of preoperative planning techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:845–853. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31823b0892
Smith JS, Klineberg E, Schwab F, Shaffrey CI, Moal B, Ames CP, Hostin R, Fu KM, Burton D, Akbarnia B, Gupta M, Hart R, Bess S, Lafage V, International Spine Study G (2013) Change in classification grade by the SRS-Schwab Adult Spinal Deformity Classification predicts impact on health-related quality of life measures: prospective analysis of operative and nonoperative treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:1663–1671. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31829ec563
Takemitsu Y, Harada Y, Iwahara T, Miyamoto M, Miyatake Y (1988) Lumbar degenerative kyphosis. Clinical, radiological and epidemiological studies. Spine 13:1317–1326
Uribe JS, Smith DA, Dakwar E, Baaj AA, Mundis GM, Turner AW, Cornwall GB, Akbarnia BA (2012) Lordosis restoration after anterior longitudinal ligament release and placement of lateral hyperlordotic interbody cages during the minimally invasive lateral transpsoas approach: a radiographic study in cadavers. J Neurosurg Spine 17:476–485. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.8.SPINE111121
Funding
This work was supported by research grants from Daegu Catholic University in 2018 IRB approval: KMC IRB 2016-01-207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The first author (MK Choi) has received research grants from Catholic University of Daegu. The other authors (SM Kim and DJ Jo) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval retrospective studies
The study was approved by the institutional review board (KMC 2016-01-207).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, M.K., Kim, S.M. & Jo, D.J. Anterior lumbar interbody fusions combined with posterior column osteotomy in patients who had sagittal imbalance associated with degenerative lumbar flat-back deformity: a retrospective case series. Neurosurg Rev 43, 1117–1125 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01129-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01129-w