Abstract
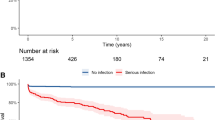
Infection is a major cause of morbidity and mortality among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). To describe the pattern of serious infections in patients with SLE and to identify the predictors of infection-related mortality among SLE patients with serious infections, we prospectively studied all SLE patients who were hospitalized with infections in Sarawak General Hospital during 2011–2015. Demographic data, clinical features, and outcomes were collected. Cox regression analysis was carried out to determine the independent predictors of infection-related mortality. There were a total of 125 patients with 187 episodes of serious infections. Our patients were of multiethnic origins with female predominance (89.6%). Their mean age was 33.4 ± 14.2 years. The patients had a mean disease duration of 66.8 ± 74.0 months. The most common site of infection was pulmonary (37.9%), followed by septicemia (22.5%). Gram-negative organisms (38.2%) were the predominant isolates within the cohort. There were 21 deaths (11.2%) during the study period. Independent predictors of infection-related mortality among our cohort of SLE patients were flare of SLE (HR 3.98, CI 1.30–12.21) and the presence of bacteremia (HR 2.54, CI 0.98–6.59). Hydroxychloroquine was protective of mortality from serious infections (HR 9.26, CI 3.40–25.64). Pneumonia and Gram-negative organisms were the predominant pattern of infection in our SLE cohort. The presence of flare of SLE and bacteremia were independent prognostic predictors of infection-related mortality, whereas hydroxychloroquine was protective of infection-related mortality among SLE patients with serious infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee J, Dhillon N, Pope J (2013) All-cause hospitalizations in systemic lupus erythematosus from a large Canadian referral centre. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52:905–909
Feldman CH, Hiraki LT, Winkelmayer WC, Marty FM, Franklin JM, Kim SC, Costenbader KH (2015) Serious infections among adult Medicaid beneficiaries with systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 7(6):1577–1585
Goldblatt F, Chambers S, Rahman A, Isenberg DA (2009) Serious infections in British patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: hospitalisations and mortality. Lupus 18:682–689
Gladman DD, Hussain F, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) The nature and outcome of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 11:234–239
Petri M, Genovese M (1992) Incidence of and risk factors for hospitalizations in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective study of the Hopkins lupus cohort. J Rheumatol 19:1559–1565
Chen D, Xie J, Chen H, Yang Y, Zhan Z, Liang L, Yang X (2016) Infection in southern Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: spectrum, drug resistance, outcomes, and risk factors. J Rheumatol 43(9):1650–1656
Alarcon GS, Jr MGG, Bastian HM, Roseman J, Lisse J, Fessler BJ et al (2001) For the LUMINA study Group Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. VIII. Predictors of early mortality in the LUMINA cohort. Arthritis Rheum 45:191–202
Dubula T, Mody GM (2015) Spectrum of infections and outcome among hospitalized south Africans with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 34(3):479–488
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Olivares N, Ruiz-Arruza I, Martinez-Berriotxoa A, Egurbide MV, Aguirre C (2009) Predictors of major infections in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R109
Tektonidou MG, Wang Z, Dasgupta A, Ward MM (2015) Burden of serious infections in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus: a National Population-Based Study, 1996–2011. Arthritis Care Res 67(8):1078–1085
Yurkovich M, Vostretsova K, Chen W, Avina-Zubieta JA (2014) Overall and cause-specific mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Care Res 66:608–616
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, Mcshane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) The committee on prognosis studies in SLE. The development and validation of the SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI). Arthritis Rheum 35:630–640
Buyon JP, Petri MA, Kim MY, Kalunian KC, Grossman J, Hahn BH et al (2005) The effect of combined estrogen and progesterone hormone replacement therapy on disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 142:953–962
Gladman D, Ginzler E, Goldsmith C, Fortin P, Liang M, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Urowitz M, Bacon P, Bombardieri S, Hanly J, Jones J, Hay E, Symmons D, Isenberg D, Kalunion K, Maddison P, Nived O, Sturfelt G, Petri M, Richter M, Snaith M, Zoma A (1996) The development and initial validation of the SLICC/ACR damage index for SLE. Arthritis Rheum 39:363–369
Lim E, Koh WH, Loh SF, Lam MS, Howe HS (2001) Nonthyphoidal salmonellosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. A study of fifty patients and a review of the literature. Lupus 10:87–92
Gerona JG, Navarra SV (2009) Salmonella infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case series. Int J Rheum Dis 12(4):319–323
Yun JE, Lee SW, Kim TH, Jun JB, Jung S, Bae SC, Kim TY, Yoo DH (2002) The incidence and clinical characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection among systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis patients in Korea. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:127–132
Sayarlioglu M, Inanc M, al KS (2004) Tuberculosis in Turkish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: increased frequency of extrapulmonary localization. Lupus 13:274–278
Lim CC, Liu PY, Tan HZ, Lee P, Chin YM, Mok IY, Chan CM, Choo JC (2016) Severe infections in patients with lupus nephritis treated with immunosuppressants: a retrospective cohort study. Nephrology
Hellmann DB, Petri M, Whiting-O’Keefe Q (1987) Fatal infections in systemic lupus erythematosus: the role of opportunistic organisms. Medicine (Baltimore) 66(5):341–348
Zonana-Nacach A, Yañez P, Jiménez-Balderas FJ, Camargo-Coronel A (2007) Disease activity, damage and survival in Mexican patients with acute severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 16(12):997–1000
Paton NI, Cheong IK, Kong NC, Segasothy M (1996) Risk factors for infection in Malaysian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. QJM 89(7):531–538
Bosch X, Guilabert A, Pallares L et al (2006) Infections in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective and controlled study of 110 patients. Lupus 15:584–589
Rúa-Figueroa Í, López-Longo J, Galindo-Izquierdo M, Calvo-Alén J, Del Campo V, Olivé-Marqués A et al (2017) Incidence, associated factors and clinical impact of severe infections in a large, multicentric cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum
Chen MJ, Tseng HM, Huang YL, Hsu WN, Yeh KW, Wu TL, See LC, Huang JL (2008) Long-term outcome and short-term survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus after bacteraemia episodes: 6-yr follow-up. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:1352–1357
Marcos M, Fernández C, Soriano A, Fernández C, Soriano À, Marco F, Martínez JA, Almela M, Cervera R, Mensa J, Espinosa G (2011) Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of bloodstream infections among lupus patients. Lupus 20:965–971
Feldman CH, Marty FM, Winkelmayer WC, Guan H, Franklin JM, Solomon DH, Costenbader KH, Kim SC (2017) Comparative rates of serious infections among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus receiving immunosuppressive medications. Arthritis Rheumatol 69(2):387–397
Herrinton LJ, Liu L, Goldfien R, Michaels MA, Tran TN (2016) Risk of serious infection for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus starting glucocorticoids with or without antimalarials. J Rheumatol 43(8):1503–1509
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the support of the Ministry of Health, Malaysia, for the technical support of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were in involved in conception or design, or analysis and interpretation of data, or both. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teh, C.L., Wan, S.A. & Ling, G.R. Severe infections in systemic lupus erythematosus: disease pattern and predictors of infection-related mortality. Clin Rheumatol 37, 2081–2086 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4102-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4102-6