Abstract
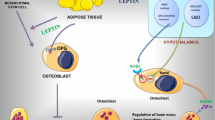
The role of bone marrow adipocytes in bone tissue is not yet understood. Adipocytes express enzymes for metabolism of free fatty acids and adipokines such as adiponectin, which have been shown to exert different effects on bone cells. Our aim was to find out whether triglyceride (TG) metabolism in bone tissue is associated with osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation by gene expression analysis of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), hormone sensitive lipase (HSL), fatty acid synthase (FASN), adiponectin, RUNX2, RANK, RANKL and OPG. Bone tissue was obtained from patients undergoing hip arthroplasty due to osteoporosis (OP) (50) or osteoarthritis (OA) (48) or from healthy autopsy controls (14). Lower bone mineral density and microstructural parameters were observed in OP compared to OA. The FASN expression did not differ between groups suggesting similar de novo lipogenesis. Lower LPL and HSL in OP suggest lower FFA release and uptake in OP bone tissue. Adiponectin expression was lower in OP than in OA and a trend was seen for controls. These results suggest OP bone has lower TG metabolism than OA and normal bone. In OP bone, lower osteoblastogenesis and higher osteoclast formation were observed and correlation analysis suggests adiponectin, LPL and HSL are associated with higher osteoblastogenesis and lower osteoclastogenesis. This study gives insights into TG metabolism in the human bone microenvironment. We conclude that OP bone tissue exhibits lower osteoblastogenesis, higher osteoclastogenesis and lower TG metabolism compared to OA or healthy controls.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen WJ, Liu LF, Patel S, Kraemer FB (2011) Hormone-sensitive lipase-knockout mice maintain high bone density during aging. FASEB J 25:2722–2730
Krings A, Rahman S, Huang S, Lu Y, Czernik PJ, Lecka-Czernik B (2011) Bone marrow fat has brown adipose tissue characteristics, which are attenuated with aging and diabetes. Bone 50:546–552
Wang H, Eckel RH (2009) Lipoprotein lipase: from gene to obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297:E271–E288
Lass A, Zimmermann R, Oberer M, Zechner R (2011) Lipolysis: a highly regulated multi-enzyme complex mediates the catabolism of cellular fat stores. Prog Lipid Res 50:14–27
Liu H, Liu JY, Wu X, Zhang JT (2010) Biochemistry, molecular biology, and pharmacology of fatty acid synthase, an emerging therapeutic target and diagnosis/prognosis marker. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 1:69–89
Garbarino J, Sturley SL (2009) Saturated with fat: new perspectives on lipotoxicity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 12:110–116
Maurin A, Chavassieux P, Frappart L, Delmas P, Serre C, Meunier P (2000) Influence of mature adipocytes on osteoblast proliferation in human primary cocultures. Bone 26:485–489
Maurin A, Chavassieux P, Vericel E, Meunier P (2002) Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the inhibitory effect of human adipocytes on osteoblastic proliferation. Bone 31:260–266
Elbaz A, Wu X, Rivas D, Gimble J, Duque G (2009) Inhibition of fatty acid biosynthesis prevents adipocyte lipotoxicity on human osteoblasts in vitro. J Cell Mol Med 14:982–991
Cornish J, MacGibbon A, Lin J, Watson M, Callon K, Tong P, Dunford J, van der Does Y, Williams G, Grey A, Naot D, Reid I (2008) Modulation of osteoclastogenesis by fatty acids. Endocrinology 149:5688–5695
Oh SR, Sul OJ, Kim YY, Kim HJ, Yu R, Suh JH, Choi HS (2010) Saturated fatty acids enhance osteoclast survival. J Lipid Res 51:892–899
Ahima RS, Flier JS (2000) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11:327–332
Berner H, Lyngstadaas S, Spahr A, Monjo M, Thommesen L, Drevon C, Syversen U, Reseland J (2004) Adiponectin and its receptors are expressed in bone-forming cells. Bone 35:842–849
Shinoda Y, Yamaguchi M, Ogata N, Akune T, Kubota N, Yamauchi T, Terauchi Y, Kadowaki T, Takeuchi Y, Fukumoto S, Ikeda T, Hoshi K, Chung UI, Nakamura K, Kawaguchi H (2006) Regulation of bone formation by adiponectin through autocrine/paracrine and endocrine pathways. J Cell Biochem 99:196–208
Luo X, Guo L, Yuan L, Xie H, Zhou H, Wu X, Liao E (2005) Adiponectin stimulates human osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 309:99–109
Oshima K, Nampei A, Matsuda M, Iwaki M, Fukuhara A, Hashimoto J, Yoshikawa H, Shimomura I (2005) Adiponectin increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and activating osteoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331:520–526
Yamaguchi N, Kukita T, Li YJ, Kamio N, Fukumoto S, Nonaka K, Ninomiya Y, Hanazawa S, Yamashita Y (2008) Adiponectin inhibits induction of TNF-alpha/RANKL-stimulated NFATc1 via the AMPK signaling. FEBS Lett 582:451–456
Williams G, Wang Y, Callon K, Watson M, Lin J, Lam J, Costa J, Orpe A, Broom N, Naot D, Reid I, Cornish J (2009) In vitro and in vivo effects of adiponectin on bone. Endocrinology 150:3603–3610
Tu Q, Zhang J, Dong LQ, Saunders E, Luo E, Tang J, Chen J (2011) Adiponectin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via APPL1-mediated suppression of Akt1. J Biol Chem 286:12542–12553
Luo X, Guo L, Xie H, Yuan L, Wu X, Zhou H, Liao E (2006) Adiponectin stimulates RANKL and inhibits OPG expression in human osteoblasts through the MAPK signaling pathway. J Bone Miner Res 21:1648–1656
Biver E, Salliot C, Combescure C, Gossec L, Hardouin P, Legroux-Gerot I, Cortet B (2011) Influence of adipokines and ghrelin on bone mineral density and fracture risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:2703–2713
Barbour KE, Zmuda JM, Boudreau R, Strotmeyer ES, Horwitz MJ, Evans RW, Kanaya AM, Harris TB, Bauer DC, Cauley JA (2011) Adipokines and the risk of fracture in older adults. J Bone Miner Res 26:1568–1576
Dequeker J, Boonen S, Aerssens J, Westhovens R (1996) Inverse relationship osteoarthritis-osteoporosis: what is the evidence? What are the consequences? Br J Rheumatol 35:813–818
Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L (2009) Osteoarthritis and risk of fractures. Calcif Tissue Int 84:249–256
Dragojevic J, Logar DB, Komadina R, Marc J (2011) Osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis are higher in osteoarthritic than in osteoporotic bone tissue. Arch Med Res 42:392–397
Arvidsson S, Kwasniewski M, Riano-Pachon DM, Mueller-Roeber B (2008) Quantprime: a flexible tool for reliable high-throughput primer design for quantitative pcr. BMC Bioinf 9:465
Chang MK, Raggatt LJ, Alexander KA, Kuliwaba JS, Fazzalari NL, Schroder K, Maylin ER, Ripoll VM, Hume DA, Pettit AR (2008) Osteal tissue macrophages are intercalated throughout human and mouse bone lining tissues and regulate osteoblast function in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 181:1232–1244
Marie P (2008) Transcription factors controlling osteoblastogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 473:98–105
Boyce BF, Xing L (2008) Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys 473:139–146
Fazzalari NL, Kuliwaba JS, Atkins GJ, Forwood MR, Findlay DM (2001) The ratio of messenger rna levels of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappab ligand to osteoprotegerin correlates with bone remodeling indices in normal human cancellous bone but not in osteoarthritis. J Bone Miner Res 16:1015–1027
Tsangari H, Findlay DM, Kuliwaba JS, Atkins GJ, Fazzalari NL (2004) Increased expression of IL-6 and RANK mRNA in human trabecular bone from fragility fracture of the femoral neck. Bone 35:334–342
Abdallah BM, Stilgren LS, Nissen N, Kassem M, Jorgensen HR, Abrahamsen B (2005) Increased RANKL/OPG mRNA ratio in iliac bone biopsies from women with hip fractures. Calcif Tissue Int 76:90–97
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by research programs P3-0298 and J3-2330 of the Research Agency of Slovenia. We thank the patients participating in our study for donating bone tissue. We thank Tina Žuran and Metka Košir for their help with RNA isolation and qPCR experiments, Viktor Jović for bone biopsies of autopsy cases and Franci Vindišar for OP and OA bone tissue.
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Dragojevič, J., Zupan, J., Haring, G. et al. Triglyceride metabolism in bone tissue is associated with osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation: a gene expression study. J Bone Miner Metab 31, 512–519 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0445-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0445-x