Abstract
Study Design
A report of two cases with complex cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) and review of the literature.
Objective
To describe two unique patients with complex CSM due to simultaneous anomalies as anteroposterior compressions of the spinal cord in both upper and lower cervical spine, caused by hypertrophic transverse ligament of atlas (TLA), dysplasia of the posterior arch of atlas, disc herniation, hypertrophic ligamentum flavum and osteophytes.
Methods
We present such two cases with clinical, imageological presentations, and describe the surgical procedure, to which both patients responded favorably.
Results
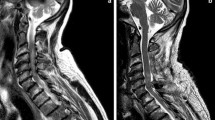
The neurological functions of both patients gradually improved according to the JOA scores and VAS scores in preoperative clumsiness and gait disturbance during the mean follow-up period lasted for 18 months. The latest plain radiographs and computed tomography (CT) revealed good fusion without instrumental failure and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed good decompression of C1–7 spinal cord of both patients. Both patients are progressively followed-up.
Conclusion
Posterior surgical approach as C1–7 laminectomy with fixations or occipital-cervical fusions may obtain better reconstructions of the cervical spine and good neurological recovery for the patients with complex CSM we present. However, the incidence and ethnic predisposition for the patients with complex CSM are still unclear.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsuruta W, Yanaka K, Okazaki M et al (2003) Cervical myelopathy caused by hypoplasia of the atlas and ossification of the transverse ligament—case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43(1):55–59
Tang JG, Hou SX, Shang WL et al (2010) Cervical myelopathy caused by anomalies at the level of atlas. Spine 35(3):E77–E79
Kasliwal MK, Traynelis VC (2012) Hypertrophic posterior arch of atlas causing cervical myelopathy. Asian Spine J 6(4):284–286
Motosuneya T, Hirabayashi S, Yamada H et al (2008) Posterior atlantoaxial subluxation due to os odontoideum combined with cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a case report. Eur Spine J 17:S275–S279
Sasaji Tatsuro, Kawahara Chikashi, Matsumoto Fujio (2011) Ossification of transverse ligament of atlas causing cervical myelopathy: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Med 2011:238748
Bokhari Rakan, Baeesa Saleh (2012) Atlas hypoplasia and ossification of the transverse atlantal ligament: a rare cause of cervical myelopathy. Case Rep Neurol Med 2012:893284
Proietti L, Scaramuzzo L, Sessa S et al (2012) Cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the transverse atlantal ligament: a Caucasian case report operated on and literature analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 98(4):470–474
Connor SE, Chandler C, Robinson S et al (2001) Congenital midline cleft of the posterior arch of atlas: a rare cause of symptomatic cervical canal stenosis. Eur Radiol 11(9):1766–1769
Phan N, Marras C, Midha R (1998) Cervical myelopathy caused by hypoplasia of the atlas: two case reports and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 43(3):629–633
Kotil K, Ozyuvaci E (2011) Multilevel decompressive laminectomy and transpedicular instrumented fusion for cervical spondylotic radiculopathy and myelopathy: a minimum follow-up of 3 years. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine 2:27–31
Anderson PA, Matz PG, Groff MW et al (2009) Laminectomy and fusion for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 11(2):150–156
Du W, Zhang P, Shen Y et al (2014) Enlarged laminectomy and lateral mass screw fixation for multilevel cervical degenerative myelopathy associated with kyphosis. Spine J 14:57–64
Ryken TC, Heary RF, Matz PG et al (2009) Cervical laminectomy for the treatment of cervical degenerative myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 11:142–149
Du W, Wang L, Shen Y et al (2013) Long-term impacts of different posterior operations on curvature, neurological recovery and axial symptoms for multilevel cervical degenerative myelopathy. Eur Spine J 22:1594–1602
Nurboja B, Kachramanoglou C, Choi D (2012) Cervical laminectomy vs laminoplasty: is there a difference in outcome and postoperative pain? Neurosurgery 70(4):965–970
Barbagallo GM, Certo F, Visocchi M et al (2013) Disappearance of degenerative, non-inflammatory, retro-odontoid pseudotumor following posterior C1–C2 fixation: case series and review of the literature. Eur Spine J Suppl 6:S879–S888
Kakutani K, Doita M, Yoshikawa M et al (2013) C1 laminectomy for retro-odontoid pseudotumor without atlantoaxial subluxation: review of seven consecutive cases. Eur Spine J 22(5):1119–1126
Klimo P Jr, Blumenthal DT, Couldwell WT (2003) Congenital partial aplasia of the posterior arch of the atlas causing myelopathy: case report and review of the literature. Spine 28(12):E224–E228
Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Kobayashi T et al (2014) Comparison between bilateral C2 pedicle screwing and unilateral C2 pedicle screwing, combined with contralateral C2 laminar screwing, for atlantoaxial posterior fixation. Asian Spine J 8(6):777–785
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Ma, X., Yang, H. et al. Complex cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a report of two cases and literature review. Eur Spine J 25 (Suppl 1), 27–32 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-4038-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-4038-3