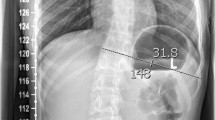
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the inter- and intra-observer variability of the computerized radiologic measurements using Keops® and to determine the bias between the software and the standard paper measurement.
Methods
Four individuals measured all frontal and sagittal variables on the 30 X-rays randomly selected on two occasions (test and retest conditions). The Bland–Altman plot was used to determine the degree of agreement between the measurement on paper X-ray and the measurement using Keops® for all reviewers and for the two measures; the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was calculated for each pair of analyses to assess interobserver reproducibility among the four reviewers for the same patient using either paper X-ray or Keops® measurement and finally, concordance correlation coefficient (rc) was calculated to assess intraobserver repeatability among the same reviewer for one patient between the two measure using the same method (paper or Keops®).
Results
The mean difference calculated between the two methods was minimal at −0, 4° ± 3.41° [−7.1; 6.4] for frontal measurement and 0.1° ± 3.52° [−6.7; 6.8] for sagittal measurement. Keops® has a better interobserver reproducibility than paper measurement for determination of the sagittal pelvic parameter (ICC = 0.9960 vs. 0.9931; p = 0.0001). It has a better intraobserver repeatability than paper for determination of Cobbs angle (rc = 0.9872 vs. 0.9808; p < 0.0001) and for pelvic parameter (rc = 0.9981 vs. 0.9953; p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
We conclude that Keops® has no bias compared to the traditionally paper measurement, and moreover, the repeatability and the reproducibility of measurements with this method is much better than with similar standard radiologic measures done manually in both frontal and sagittal plane and that the use of this software can be recommended for clinical application.
Level of evidence
Diagnostic, level III.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Been E, Kalichman L (2013) Lumbar lordosis. Spine J [Internet]; Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1529943013013855
Cobb JR (1960) The problem of the primary curve. J Bone Joint Surg Am 42-A:1413–1425
Le Huec JC, Saddiki R, Franke J, Rigal J, Aunoble S (2011) Equilibrium of the human body and the gravity line: the basics. Eur Spine J 20(S5):558–563
Vaz G, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J (2002) Sagittal morphology and equilibrium of pelvis and spine. Eur Spine J 11(1):80–87
Le Huec JC, Roussouly P (2011) Sagittal spino-pelvic balance is a crucial analysis for normal and degenerative spine. Eur Spine J 20(S5):556–557
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, Marty C (1998) Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J 7(2):99–103
Hwang J-H, Modi HN, Suh S-W, Hong J-Y, Park Y-H, Park J-H et al (2010) Reliability of lumbar lordosis measurement in patients with spondylolisthesis: a case–control study comparing the Cobb, centroid, and posterior tangent methods. Spine 35(18):1691–1700
Vrtovec T, Janssen MMA, Likar B, Castelein RM, Viergever MA, Pernuš F (2013) Evaluation of pelvic morphology in the sagittal plane. Spine J 13(11):1500–1509
Bland JM, Altman DG (1999) Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res 8(2):135–160
Pruijs JEH, Hageman MAPE, Keessen W, van der Meer R, van Wieringen JC (1994) Variation in Cobb angle measurements in scoliosis. Skeletal Radiol 23(7):517–520
Polly DW Jr, Kilkelly FX, McHale KA, Asplund LM, Chang AS (1996) Measurement of lumbar lordosis. Evaluation of intraobserver, interobserver, and technique variability. Spine 21(13):1530–1535 (discussion 1535–1536)
Morrissy RT, Goldsmith GS, Hall EC, Kehl D, Cowie GH (1990) Measurement of the Cobb angle on radiographs of patients who have scoliosis. Evaluation of intrinsic error. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72(3):320–327
Vrtovec T, Janssen MMA, Likar B, Castelein RM, Viergever MA, Pernuš F (2012) A review of methods for evaluating the quantitative parameters of sagittal pelvic alignment. Spine J 12(5):433–446
Duval-Beaupère G, Schmidt C, Cosson P (1992) A barycentre metric study of the sagittal shape of spine and pelvis: the conditions required for an economic standing position. Ann Biomed Eng 20(4):451–462
Lazennec JY, Ramaré S, Arafati N, Laudet CG, Gorin M, Roger B et al (2000) Sagittal alignment in lumbosacral fusion: relations between radiological parameters and pain. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 9(1):47–55
Peleg S, Dar G, Medlej B, Steinberg N, Masharawi Y, Latimer B et al (2007) Orientation of the human sacrum: anthropological perspectives and methodological approaches. Am J Phys Anthropol 133(3):967–977
Peleg S, Dar G, Steinberg N, Peled N, Hershkovitz I, Masharawi Y (2007) Sacral orientation revisited. Spine 32(15):E397–E404
Jackson RP, Phipps T, Hales C, Surber J (2003) Pelvic lordosis and alignment in spondylolisthesis. Spine 28(2):151–160
Curylo LJ, Edwards C, DeWald RW (2002) Radiographic markers in spondyloptosis: implications for spondylolisthesis progression. Spine 27(18):2021–2025
Jackson RP, Kanemura T, Kawakami N, Hales C (2000) Lumbopelvic lordosis and pelvic balance on repeated standing lateral radiographs of adult volunteers and untreated patients with constant low back pain. Spine 25(5):575–586
Jackson RP, Hales C (2000) Congruent spinopelvic alignment on standing lateral radiographs of adult volunteers. Spine 25(21):2808–2815
Aubin C-E, Bellefleur C, Joncas J, de Lanauze D, Kadoury S, Blanke K et al (2011) Reliability and accuracy analysis of a new semiautomatic radiographic measurement software in adult scoliosis. Spine 36(12):E780–E790
Berthonnaud E, Labelle H, Roussouly P, Grimard G, Vaz G, Dimnet J (2005) A variability study of computerized sagittal spinopelvic radiologic measurements of trunk balance. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(1):66–71
Bolesta MJ, Winslow L, Gill K (2010) A comparison of film and computer workstation measurements of degenerative spondylolisthesis: intraobserver and interobserver reliability. Spine 35(13):1300–1303
Dimar JR, Carreon LY, Labelle H, Djurasovic M, Weidenbaum M, Brown C et al (2008) Intra- and inter-observer reliability of determining radiographic sagittal parameters of the spine and pelvis using a manual and a computer-assisted methods. Eur Spine J 17(10):1373–1379
Guglielmi G, Stoppino LP, Placentino MG, D’Errico F, Palmieri F (2009) Reproducibility of a semi-automatic method for 6-point vertebral morphometry in a multi-centre trial. Eur J Radiol 69(1):173–178
Kim CH, Chung CK, Hong HS, Kim EH, Kim MJ, Park BJ (2012) Validation of a simple computerized tool for measuring spinal and pelvic parameters. J Neurosurg Spine 16(2):154–162
Pearson AM, Spratt KF, Genuario J, McGough W, Kosman K, Lurie J et al (2011) Precision of lumbar intervertebral measurements: does a computer-assisted technique improve reliability? Spine 36(7):572–580
Sardjono TA, Wilkinson MH, Veldhuizen AG, van Ooijen PM, Purnama KE, Verkerke GJ (2013) Automatic Cobb angle determination from X-ray images. Spine Jun 1
Tanure MC, Pinheiro AP, Oliveira AS (2010) Reliability assessment of Cobb angle measurements using manual and digital methods. Spine J 10(9):769–774
Wang Z, Parent S, de Guise JA, Labelle H (2010) A variability study of computerized sagittal sacral radiologic measures. Spine 35(1):71–75
Zhang J, Lou E, Shi X, Wang Y, Hill DL, Raso JV et al (2010) A computer-aided Cobb angle measurement method and its reliability. J Spinal Disord Tech 23(6):383–387
Vialle R, Ilharreborde B, Dauzac C, Guigui P (2006) Intra and inter-observer reliability of determining degree of pelvic incidence in high-grade spondylolisthesis using a computer assisted method. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 15(10):1449–1453
Dimar JR 2nd, Carreon LY, Labelle H, Djurasovic M, Weidenbaum M, Brown C et al (2008) Intra- and inter-observer reliability of determining radiographic sagittal parameters of the spine and pelvis using a manual and a computer-assisted methods. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 17(10):1373–1379
Boulay C, Tardieu C, Hecquet J, Benaim C, Mitulescu A, Marty C et al (2005) Anatomical reliability of two fundamental radiological and clinical pelvic parameters: incidence and thickness. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 15(3):197–204
Chaise FO, Candotti CT, Torre ML, Furlanetto TS, Pelinson PPT, Loss JF (2011) Validation, repeatability and reproducibility of a noninvasive instrument for measuring thoracic and lumbar curvature of the spine in the sagittal plane. Rev Bras Fisioter São Carlos São Paulo Braz 15(6):511–517
Czaprowski D, Pawłowska P, Gębicka A, Sitarski D, Kotwicki T (2012) Intra- and interobserver repeatability of the assessment of anteroposterior curvatures of the spine using Saunders digital inclinometer. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 14(2):145–153
Yeager MS, Cook DJ, Cheng BC (2013) Reliability of computer-assisted lumbar intervertebral measurements using a novel vertebral motion analysis system. Spine J Off J North Am Spine Soc. Nov 12
Somoskeöy S, Tunyogi-Csapó M, Bogyó C, Illés T (2012) Accuracy and reliability of coronal and sagittal spinal curvature data based on patient-specific three-dimensional models created by the EOS 2D/3D imaging system. Spine J Off J North Am Spine Soc 12(11):1052–1059
Mieritz RM, Bronfort G, Kawchuk G, Breen A, Hartvigsen J (2012) Reliability and measurement error of 3-dimensional regional lumbar motion measures: a systematic review. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 35(8):645–656
Hioki A, Miyamoto K, Shimizu K, Inoue N (2011) Test–retest repeatability of lumbar sagittal alignment and disc height measurements with or without axial loading: a computed tomography study. J Spinal Disord Tech 24(2):93–98
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J.-C. Le Huec is the past president of Eurospine, ISASS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maillot, C., Ferrero, E., Fort, D. et al. Reproducibility and repeatability of a new computerized software for sagittal spinopelvic and scoliosis curvature radiologic measurements: Keops® . Eur Spine J 24, 1574–1581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3817-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3817-1