Abstract
Background
Several novel biomarkers that predict acute kidney injury (AKI) have recently been proposed. We have evaluated the sequential patterns of biomarker elevation after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and determined their diagnostic accuracy.
Methods
We measured the ability of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), interleukin-18 (IL-18), liver type fatty-acid binding protein (L-FABP), kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2), and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7), to predict AKI (≥50% increase in serum creatinine from baseline). Areas under the receiver-operator characteristic curves (AUCs) were calculated for each biomarker and for various biomarker combinations at multiple time points after CPB.
Results
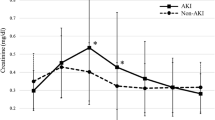
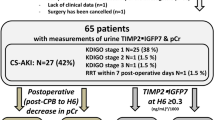
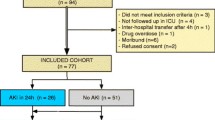
Of 150 patients examined, AKI had developed in 50 patients by 24 h after CPB, with an elevated NGAL concentration first noted at 2 h post-CPB, increases in IL-18, L-FABP, and the product of TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 first noted at 6 h, and an elevated KIM-1 level noted at 12 h. At each time point, urine NGAL remained the marker with the highest predictive ability (AUC > 0.9). The addition of any other biomarker did not increase the predictive accuracy of NGAL alone at 2 and 6 h. At 12 h, when compared to NGAL alone, the combination of NGAL, IL-18, and TIMP2 improved the AUC for AKI prediction (from 0.938 to 0.973).
Conclusions
While urine NGAL remains a superior stand-alone test at the 2 and 6 h time points after pediatric CPB, a panel of carefully selected biomarkers may prove optimal at later time points.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jefferies JL, Devarajan P (2016) Early detection of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery. Prog Pediatr Cardiol 41:9–16
Pederson K (2012) Acute kidney injury in children undergoing surgery for congenital heart disease. Eur J Pediatr Surg 22:426–433
Li S, Krawczeski CD, Zappitelli M, Devarajan P, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Coca SG, Kim RW, Parikh CR, TRIBE-AKI Consortium (2011) Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med 39:1493–1499
Morgan CJ, Zappitelli M, CMT R, Alton GY, Sauve RS, Joffe AR, Ross DB, Rebeyka IM, Western Canadian Complex Pediatric Therapies Follow-Up Group (2013) Risk factors for and outcomes of acute kidney injury in neonates undergoing complex cardiac surgery. J Pediatr 162:120–127
Devarajan P (2015) Genomic and proteomic characterization of acute kidney injury. Nephron 131:85–91
Supavekin S, Zhang W, Kucherlapati R, Kaskel FJ, Moore LC, Devarajan P (2003) Differential gene expression following early renal ischemia–reperfusion. Kidney Int 63:1714–1724
Bennett MR, Nehus E, Haffner C, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2015) Pediatric reference ranges for acute kidney injury biomarkers. Pediatr Nephrol 30:677–685
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365:1231–1238
Bennett M, Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Grenier F, Workman R, Syed H, Ali S, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2008) Urine NGAL predicts severity of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: a prospective study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:665–673
Krawczeski CD, Woo JG, Wang Y, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Pediatr 158:1009–1015
Krawczeski CD, Goldstein SL, Woo JG, Wang Y, Piyaphanee N, Ma Q, Bennett M, Devarajan P (2011) Temporal relationship and predictive value of urinary acute kidney injury biomarkers after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. J Am Coll Cardiol 58:2301–2309
Parikh CR, Mishra J, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Dursun B, Ma Q, Kelly C, Dent C, Devarajan P, Edelstein CL (2006) Urinary IL-18 is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 70:199–203
Han WK, Waikar SS, Johnson A, Betensky RA, Dent CL, Devarajan P, Bonventre JV (2009) Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 76:863–869
Portilla D, Dent C, Sugaya T, Nagothu KK, Kundi I, Moore P, Noiri E, Devarajan P (2008) Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 73:4654–4672
Kashani K, Al-Khafaji A, Ardiles T, Artigas A, Bagshaw SM, Bell M, Bihorac A, Birkhahn R, Cely CM, Chawla LS, Davison DL, Feldkamp T, Forni LG, Gong MN, Gunnerson KJ, Haase M, Hackett J, Honore PM, Hoste EA, Joannes-Boyau O, Joannidis M, Kim P, Koyner JL, Laskowitz DT, Lissauer ME, Marx G, McCullough PA, Mullaney S, Ostermann M, Rimmelé T, Shapiro NI, Shaw AD, Shi J, Sprague AM, Vincent JL, Vinsonneau C, Wagner L, Walker MG, Wilkerson RG, Zacharowski K, Kellum JA (2013) Discovery and validation of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in human acute kidney injury. Critical Care 17:R25. doi: 10.1186/cc12503
Meersch M, Schmidt C, Van Aken H, Rossaint J, Görlich D, Stege D, Malec E, Januszewska K, Zarbock A (2014) Validation of cell-cycle arrest biomarkers for acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery. PLoS One 9:e110865
Schuh MP, Nehus E, Ma Q, Haffner C, Bennett M, Krawczeski CD, Devarajan P (2016) Long-term stability of urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in children. Am J Kidney Dis 67(1):56–61
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Section 2: AKI definition. Kidney Int. Suppl 2:19–36
Jenkins KJ (2004) Risk adjustment for congenital heart surgery: the RACHS-1 method. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu 7:180–184
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44:837–845
Devarajan P (2006) Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1503–1520
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel urinary biomarker for ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 4:2534–2543
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2004) Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin (NGAL): a novel urinary biomarker for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Nephrol 24:307–315
Paragas N, Qiu A, Zhang Q, Samstein B, Deng SX, Schmidt-Ott KM, Viltard M, Yu W, Forster CS, Gong G, Liu Y, Kulkarni R, Mori K, Kalandadze A, Ratner AJ, Devarajan P, Landry DW, D'Agati V, Lin CS, Barasch J (2011) The NGAL reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to injury in real time. Nat Med 17:216–222
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Yang J, Mitsnefes M, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2004) Amelioration of ischemic acute renal injury by neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:3073–3082
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54:1012–1024
Haase-Fielitz A, Haase M, Devarajan P (2014) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury: a critical evaluation of current status. Ann Clin Biochem 51:335–351
Basu RK, Wong HR, Krawczeski CD, Wheeler DS, Manning PB, Chawla LS, Devarajan P, Goldstein SL (2014) Combining functional and tubular damage biomarkers improves diagnostic precision for acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:2753–2762
Parikh CR, Devarajan P, Zappitelli M, Sint K, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Li S, Kim RW, Koyner JL, Coca SG, Edelstein CL, Shlipak MG, Garg AX, Krawczeski CD, TRIBE-AKI Consortium (2011) Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after pediatric cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1737–1747
Devarajan P (2011) Biomarkers for the early detection of acute kidney Biomarkers for the early detection of acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Pediatr 23:194–200
Devarajan P (2010) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Biomark Med 4:265–280
Melnikov VY, Faubel S, Siegmund B, Lucia MS, Ljubanovic D, Edelstein CL (2002) Neutrophil-independent mechanisms of caspase-1- and IL-18-mediated ischemic acute tubular necrosis in mice. J Clin Invest 110:1083–1091
Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Obama A, Hiroi J, Miura H, Watanabe M, Kumai T, Ohtani-Kaneko R, Hirata K, Kimura K (2006) Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein attenuates renal injury induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Pathol 169:1107–1117
Parikh CR, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Garg AX, Kadiyala D, Shlipak MG, Koyner JL, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P, Patel UD, Zappitelli M, Krawczeski CD, Passik CS, Coca SG, TRIBE-AKI Consortium (2013) Performance of kidney injury molecule-1 and liver fatty acid-binding protein and combined biomarkers of AKI after cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1079–1088
Yang L, Brooks CR, Xiao S, Sabbisetti V, Yeung MY, Hsiao LL, Ichimura T, Kuchroo V, Bonventre JV (2015) KIM-1-mediated phagocytosis reduces acute injury to the kidney. J Clin Invest 125:1620–1636
Peco-Antić A, Ivanišević I, Vulićević I, Kotur-Stevuljević J, Ilić S, Ivanišević J, Miljković M, Kocev N (2013) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury in pediatric cardiac surgery. Clin Biochem 46:1244–1251
Hoste EA, McCullough PA, Kashani K, Chawla LS, Joannidis M, Shaw AD, Feldkamp T, Uettwiller-Geiger DL, McCarthy P, Shi J, Walker MG, Kellum JA, Investigators S (2014) Derivation and validation of cutoffs for clinical use of cell cycle arrest biomarkers. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:2054–2061
Vijayan A, Faubel S, Askenazi DJ, Cerda J, Fissell WH, Heung M, Humphreys BD, Koyner JL, Liu KD, Mour G, Nolin TD, Bihorac A, American Society of Nephrology Acute Kidney Injury Advisory Group (2016) Clinical use of the urine biomarker [TIMP-2]×[IGFBP7] for acute kidney injury risk assessment. Am J Kidney Dis 68:19–28
Lameire N, Vanmassenhove J, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R (2016) The cell cycle biomarkers: promising research, but do not oversell them. Clin Kidney J 9:353–358
Westhoff JH, Tönshoff B, Waldherr S, Pöschl J, Teufel U, Westhoff TH, Fichtner A (2015) Urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) • insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) predicts adverse outcome in Pediatric acute kidney injury. PLoS One 10:e0143628
Gist KM, Goldstein SL, Wrona J, Alten JA, Basu RK, Cooper DS, Soranno DE, Duplantis J, Altmann C, Gao Z, Faubel S (2017) Kinetics of the cell cycle arrest biomarkers (TIMP-2*IGFBP-7) for prediction of acute kidney injury in infants after cardiac surgery. Pediatr Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s00467-017-3655-y
Filho LT, Grande AJ, Colonetti T, Della ESP, da Rosa MI (2017) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury diagnosis in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s00467-017-3704-6
Acknowledgments
PD has received funding from the National Institutes of Health (grant number P50 DK096418). We are grateful to Dr. Jun Ying for assistance with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This single-center case–control study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Written informed consent from the legal guardian, and assent from the patient when appropriate, were obtained prior to enrollment.
Disclosures
P.D. is a co-inventor on patents (7,776,824 and 7,977,110) related to NGAL as a biomarker of kidney injury, and declares licensing agreements with BioPorto Diagnostics and Abbott Diagnostics. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 42 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Ma, Q., Bennett, M. et al. Urinary biomarkers of cell cycle arrest are delayed predictors of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. Pediatr Nephrol 32, 2351–2360 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3748-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3748-7