Abstract
Introduction
Traditional treatment for the esophageal motility disorder, achalasia, ranges from endoscopic botulinum toxin (Botox) injections or balloon dilatation, to laparoscopic or open surgical myotomy. Recent advances in endoscopic therapy have led to peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) as a viable alternative to traditional techniques for myotomy. Uncertainty exists as to whether the procedure is feasible for patients who have already received prior endoscopic or surgical procedures for therapy, as these groups experience higher failure rates as well as intraoperative mucosal perforations and technical difficulty during Heller myotomy. We describe our first 40 patients who have undergone POEM and compare outcomes between patients who have or have not received previous treatment for achalasia.
Methods and procedures
We evaluated our prospectively collected database of POEM procedures performed by two surgeons (JLP and JMM) at a single institution. Perioperative data was collected for operative and hospital outcomes. Patients completed pre- and postoperative GERD-Health-Related Quality of Life Questionnaires (GERD-HRQL) and SF-12 surveys for symptom scoring.
Results
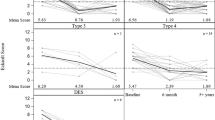
Forty patients received a POEM procedure between 2011 and 2013. Of these, 40 % (n = 16) had had at least one prior endoscopic or surgical procedure. Nine had prior Botox injections, 7 had balloon dilations, 3 had both Botox and dilations, and 3 received prior laparoscopic Heller myotomy (two with Dor fundoplication). Mean operative time was 102 min for patients with prior procedures (Prior Tx) and 118 min for patients without any prior procedure (No Tx) (p = 0.07). Intraoperative complication rates for the Prior Tx group were 12.5 versus 16.7 % for the No Tx group. Mean follow-up was 10 months. Both groups independently demonstrated clinical improvement in both the GERD-HRQL and SF-12 scores following POEM. There were no statistical differences between the two groups for GERD-HRQL reflux and dysphagia subset scores, or SF-12 mental component summary.
Conclusion
We found favorable outcomes following POEM in patients who have had prior endoscopic or surgical treatments for achalasia, as well as for patients without prior intervention. There were no significant differences between these two groups with regards to operative times, GERD-HRQL scores, and mental component SF-12 scores. One complication requiring intervention occurred in a patient that had received multiple prior Botox injections and balloon dilatations. POEM appears to be a viable alternative for treatment of achalasia compared to traditional techniques, however, long-term data are needed to establish the durability of this technique and to determine whether symptoms will recur necessitating re-intervention.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eckardt AJ, Eckardt VF (2011) Treatment and surveillance strategies in achalasia: an update. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:311–319
Chen Z, Bessell JR, Chew A, Watson DI (2010) Laparoscopic cardiomyotomy for achalasia: clinical outcomes beyond 5 years. J Gastrointest Surg 14:594–600
Pasricha PJ, Hawari R, Ahmed I, Chen J, Cotton PB, Hawes RH, Kalloo AN, Kantsevoy SV, Gostout CJ (2007) Submucosal endoscopic esophageal myotomy: a novel experimental approach for the treatment of achalasia. Endoscopy 39:761–764
Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H, Kudo S (2010) Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy 42:265–271
Ponsky JL, Marks JM, Pauli EM (2012) how i do it: per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). J Gastrointest Surg 16:1251–1255
Heller E (1914) Extramukose Kardioplastik beim chronischen Kardiospasmus mil Dilatation des Oesophagus. Mitt Grenzgeb Med Chir 27:141–149
Shimi S, Nathanson LK, Cuschieri A (1991) Laparoscopic cardiomyotomy for achalasia. J R Coll Surg Edinb 36:152–154
Pellegrini C, Wetter LA, Patti M, Leichter R, Mussan G, Mori T, Bernstein G, Way L (1992) Thoracoscopic esophagomyotomy. Initial experience with a new approach for the treatment of achalasia. Ann Surg 216:291–296 discussion 296-299
Ware J Jr, Kosinski M, Keller SD (1996) A 12-item short-form Health Survey: construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med Care 34:220–233
Velanovich V, Vallance SR, Gusz JR, Tapia FV, Harkabus MA (1996) Quality of life scale for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 183:217–224
Onimaru M, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Yoshida A, Santi EG, Sato H, Ito H, Maselli R, Kudo SE (2013) Peroral endoscopic myotomy is a viable option for failed surgical esophagocardiomyotomy instead of redo surgical Heller myotomy: a single center prospective study. J Am Coll Surg 217:598–605
Zhou PH, Li QL, Yao LQ, Xu MD, Chen WF, Cai MY, Hu JW, Li L, Zhang YQ, Zhong YS, Ma LL, Qin WZ, Cui Z (2013) Peroral endoscopic remyotomy for failed Heller myotomy: a prospective single-center study. Endoscopy 45:161–166
Sharata A, Kurian AA, Dunst CM, Bhayani NH, Reavis KM, Swanstrom LL (2013) Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is safe and effective in the setting of prior endoscopic intervention. J Gastrointest Surg 17:1188–1192
Smith CD, Stival A, Howell DL, Swafford V (2006) Endoscopic therapy for achalasia before Heller myotomy results in worse outcomes than heller myotomy alone. Ann Surg 243:579–584 discussion 584-576
Wang L, Li YM (2008) Recurrent achalasia treated with Heller myotomy: a review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol 14:7122–7126
Beckingham IJ, Callanan M, Louw JA, Bornman PC (1999) Laparoscopic cardiomyotomy for achalasia after failed balloon dilatation. Surg Endosc 13:493–496
Gorecki PJ, Hinder RA, Libbey JS, Bammer T, Floch N (2002) Redo laparoscopic surgery for achalasia. Surg Endosc 16:772–776
Iqbal A, Tierney B, Haider M, Salinas VK, Karu A, Turaga KK, Mittal SK, Filipi CJ (2006) Laparoscopic re-operation for failed Heller myotomy. Dis Esophagus 19:193–199
Grotenhuis BA, Wijnhoven BP, Myers JC, Jamieson GG, Devitt PG, Watson DI (2007) Reoperation for dysphagia after cardiomyotomy for achalasia. Am J Surg 194:678–682
James DR, Purkayastha S, Aziz O, Amygdalos I, Darzi AW, Hanna GB, Zacharakis E (2012) The feasibility, safety and outcomes of laparoscopic re-operation for achalasia. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 21:161–167
Rosemurgy AS, Morton CA, Rosas M, Albrink M, Ross SB (2010) A single institution’s experience with more than 500 laparoscopic Heller myotomies for achalasia. J Am Coll Surg 210:637–645
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by institutional support from University Hospitals Case Medical Center.
Disclosures
Dr. Ponsky has received consulting and/or speaking fees from US Endoscopy. Dr. Marks has received consulting and/or speaking fees from Olympus, Merck, and Apollo Endosurgery. Dr. Orenstein, Mr. Raigani, Drs. Wu, Pauli, and Phillips have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orenstein, S.B., Raigani, S., Wu, Y.V. et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) leads to similar results in patients with and without prior endoscopic or surgical therapy. Surg Endosc 29, 1064–1070 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3782-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3782-5