Abstract
Background
This study aimed to evaluate the perioperative outcomes and pathology of patients undergoing laparoscopic splenectomy for splenic masses.
Methods
The records for 174 patients who underwent laparoscopic splenectomy from May 1994 to August 2006 were reviewed. Patient demographics, preoperative imaging, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, body mass index (BMI), estimated blood loss (EBL), operative time, spleen size, complications, hospital length of stay (LOS), pathology, and mortality were extracted from the records. Data are expressed as means ± standard deviation. Statistical significance (p < 0.05) was determined using a two-tailed t-test and Fisher’s exact test.
Results
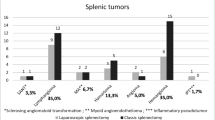
A splenic mass was diagnosed preoperatively for 18 patients (10.3%) (7 males and 11 females). The mean patient age was 51.4 ± 13.7 years. The mean ASA was 2.3 ± 0.8, and the mean BMI was 27.3 ± 5.8 kg/m2. Computed tomography scans demonstrated splenic masses in all the patients. The mean mass size was 4.3 ± 3.3 cm (range, 1.0–11.0 cm), and the mean spleen length was 14.6 ± 7.5 cm (range, 5.5–40.2 cm). Total laparoscopic splenectomy was completed for 15 patients, and hand-assisted splenectomy was performed for 3 patients (2 converted). The mean operative time was 128.3 ± 38.5 min, and the mean EBL was 110 ± 137.5 ml. There were no intraoperative complications or 30-day mortalities. The postoperative complication rate was 11.1%, and the mean LOS was 1.9 ± 1.0 days. The pathology for six patients (33.3%) was malignant (5 lymphomas and 1 adenocarcinoma). There were three false-positive positron emission tomography (PET) scans. Compared with 73 patients undergoing laparoscopic splenectomy for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, there was no significant difference in mean EBL, operative time, conversion rate, complication rate, LOS, or 30-day mortality rate (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Laparoscopic splenectomy is appropriate for patients whose indication for surgery is splenic mass. Suspicious splenic masses should be removed due to the relatively high incidence of malignant pathology, most commonly lymphoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burch M, Misra M, Phillips EH (2005) Splenic malignancy: a minimally invasive approach. Cancer J 11:36–42
Narang S, Wolf BC, Neiman RS (1985) Malignant lymphoma presenting with prominent splenomegaly: a clinicopathologic study with special reference to intermediate cell lymphoma. Cancer 55:1948–1957
Klein B, Stein M, Kuten A, Steiner M, Barshalom D, Robinson E, Gal D (1987) Splenomegaly and solitary spleen metastasis in solid tumors. Cancer 60:100–102
Kawashima A, Fishman EK (1994) Benign and malignant splenic lesions. In: Gore RM, Levine MS, Laufer I (eds) Textbook of gastrointestinal radiology. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 2276–2285
Moriyama S, Inayoshi A, Kurano R (2000) Inflammatory pseudotumor of the spleen: report of a case. Surg Today 30:942–946
Uchida H, Ohta M, Shibata K, Endo Y, Iwaki K, Tominaga M, Ishio T, Kitano S (2006) Laparoscopic splenectomy in patients with inflammatory pseudotumor of the spleen: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 16:182–186
The Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Therapy Study Group (2004) A comparison of laparoscopically assisted and open colectomy for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2050–2059
Yano H, Nakano Y, Tono T, Ohnishi T, Iwazawa T, Kimura Y, Kanoh T, Monden T (2004) Hand-assisted laparoscopic splenectomy for splenic tumors. Dig Surg 21:215–222
Silecchia G, Fantini A, Raparelli L, De LA, Vitolo D, Monarca B, Bezzi M, Rosato P, Basso N (1999) Management of abdominal lymphoproliferative diseases in the era of laparoscopy. Am J Surg 177:325–330
Hahn PF, Weissleder R, Stark DD, Saini S, Elizondo G, Ferrucci JT (1988) MR imaging of focal splenic tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 150:823–827
Caslowitz PL, Labs JD, Fishman EK, Siegelman SS (1990) Nontraumatic focal lesions of the spleen: assessment of imaging and clinical evaluation. Comput Med Imaging Graph 14:133–141
Noguchi H, Kondo H, Kondo M, Shiraiwa M, Monobe Y (2000) Inflammatory pseudotumor of the spleen: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol 30:196–203
Di VG, Soresi M, Patti R, Carroccio A, Leo P, Franco V, Montalto G (2001) Concomitant inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver and spleen. Liver 21:217–222
Caraway NP, Fanning CV (1997) Use of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the evaluation of splenic lesions in a cancer center. Diagn Cytopathol 16:312–316
Keogan MT, Freed KS, Paulson EK, Nelson RC, Dodd LG (1999) Imaging-guided percutaneous biopsy of focal splenic lesions: update on safety and effectiveness. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:933–937
Bellows CF, Sweeney JF (2006) Laparoscopic splenectomy: present status and future perspective. Expert Rev Med Devices 3:95–104
Heniford BT, Matthews BD, Answini GA, Walsh RM (2000) Laparoscopic splenectomy for malignant diseases. Semin Laparosc Surg 7:93–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented at the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES), Las Vegas, NV, 20 April 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tessier, D.J., Pierce, R.A., Brunt, L.M. et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy for splenic masses. Surg Endosc 22, 2062–2066 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-9748-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-9748-8