Abstract
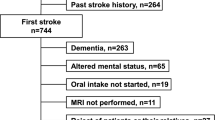
We aimed in this study to evaluate dysphagia in early stroke patients using a bedside screening test and flexible fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FFEES) and electrophysiological evaluation (EE) methods and to compare the effectiveness of these methods. Twenty-four patients who were hospitalized in our clinic within the first 3 months after stroke were included in this study. Patients were evaluated using a bedside screening test [including bedside dysphagia score (BDS), neurological examination dysphagia score (NEDS), and total dysphagia score (TDS)] and FFEES and EE methods. Patients were divided into normal-swallowing and dysphagia groups according to the results of the evaluation methods. Patients with dysphagia as determined by any of these methods were compared to the patients with normal swallowing based on the results of the other two methods. Based on the results of our study, a high BDS was positively correlated with dysphagia identified by FFEES and EE methods. Moreover, the FFEES and EE methods were positively correlated. There was no significant correlation between NEDS and TDS levels and either EE or FFEES method. Bedside screening tests should be used mainly as an initial screening test; then FFEES and EE methods should be combined in patients who show risks. This diagnostic algorithm may provide a practical and fast solution for selected stroke patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook IJ, Kahrilas PJ. AGA technical review on management of oropharyngeal dysphagia. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:455–78.
Walterfang M, Yu-Chien C, Imrie J, Rushton D, Schubiger D, Patterson MC. Dysphagia as a risk factor for mortality in Niemann–Pick disease type C: systematic literature review and evidence from studies with miglustat. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7(1):76.
Slattery J, Morgan A, Douglas J. Early sucking and swallowing problems as predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome in children with neonatal brain injury: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012;54(9):796–806.
Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis and pulmonary complications. Stroke. 2005;36:2756–63.
Daniels SK, Ballo LA, Mahoney MC, Foundas AL. Clinical predictors of dysphagia and aspiration risk: outcome measures in acute stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000;81:1030–3.
Mann G, Hankey GJ, Cameron D. Swallowing disorders following acute stroke: prevalence and diagnostic accuracy. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2000;10:380–6.
Daniels SK, Brailey K, Priestly DH, Herrington LR, Weisberg LA, Foundas AL. Aspiration in patients with acute stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79:14–9.
Groher ME, Bukatman R. The prevalence of swallowing disorders in two teaching hospitals. Dysphagia. 1986;1:3–6.
Perry L, Love CP. Screening for dysphagia and aspiration in acute stroke: a systematic review. Dysphagia. 2001;16:7–18.
Farneti D. La valutazione videoendoscopica. In: Schindler O, Ruoppolo G, Schindler A, editors. Deglutologia. 1st ed. Torino: Edizioni Omega; 2001. p. 167–88.
Antonios N, Carnaby-Mann G, Crary M, Miller L, Hubbard H, Hood K, Sambandam R, Xavier A, Silliman S. Analysis of a physician tool for evaluating dysphagia on an inpatient stroke unit: the modified Mann assessment of swallowing ability. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010;19(1):49–57.
Bours GJJW, Speyer R, Lemmens J, Limburg M, De Wit R. Bedside screening tests versus videofluoroscopy or fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing to detect dysphagia in patients with neurological disorders: systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2009;65(3):477–93.
Parker C, Power M, Hamdy S, Bowen A, Tyrrell P, Thompson DG. Awareness of dysphagia by patients following stroke predicts swallowing performance. Dysphagia. 2004;19:28–35.
Warnecke T, Teismann I, Oelenberg S, Hamacher C, Ringelstein EB, Schäbitz WR, Dziewas R. Towards a basic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in acute stroke–identification of salient findings by the inexperienced examiner. BMC Med Educ. 2009;9(13):1–7.
Vaiman M. Standardization of surface electromyography utilized to evaluate patients with dysphagia. Head Face Med. 2007;3(26):1–7.
Kucukdeveci AA, Yavuzer G, Elhan AH, Sonel B. Adaptation of the functional independence measure for use in Turkey. Clin Rehabil. 2001;15:311–8.
Dziewas R, Warnecke T, Olenberg S, Teismann I, Zimmermann J, Kramer C, Ritter M, Ringelstein EB, Schabitz WR. Towards a basic endoscopic assessment of swallowing in acute stroke–development and evaluation of a simple dysphagia score. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;26:41–7.
Horner J, Massey RW, Brazer SR. Aspiration in bilateral stroke patients. Neurology. 1990;40:1686–8.
Linden P, Kuhlemeier KV, Patterson C. The probability of correctly predicting subglottic penetration from clinical observations. Dysphagia. 1993;8:170–9.
Farneti D, Consolmagno P. The Swallowing Centre: rationale for a multidisciplinary management. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2007;27(4):200–7.
The European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Executive Committee and the ESO Writing Committee. Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;25:457–507.
Adams HP, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2007;38:1655–711.
Karaca Umay E, Gurcay E, Unlu E, Eksioglu E, Cakci A. Functional and nutritional effects of dysphagia in early stroke patients. Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci. 2010;30(3):925–31.
Hamdy S, Aziz Q, Rothwell JC, Crone R, Hughes D, Tallis RC, Thompson DG. Explaining oropharyngeal dysphagia after unilateral hemispheric stroke. Lancet. 1997;350:686–92.
Terre R, Mearin F. Oropharyngeal dysphagia after the acute phase of stroke: predictors of aspiration. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2006;18(3):200–5.
Colodny N. Comparison of dysphagics and nondysphagics on pulse oximetry during oral feeding. Dysphagia. 2000;15:68–73.
Smithard DG. Assessment of swallowing following acute stroke. Stroke Rev. 2002;6:7–10.
Turner-Lawrence DE, Peebles M, Price MF, Singh SJ, Asimos AW. A feasibility study of the sensitivity of emergency physician. Dysphagia screening in acute stroke patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2009;54:344–8.
Ramsey DJ, Smithard DG, Kalra L. Can pulse oximetry or a bedside swallowing assessment be used to detect aspiration after stroke? Stroke. 2006;37:2984–8.
Wu MC, Chang YC, Wang TG, Lin LC. Evaluating swallowing dysfunction using a 100-ml water swallowing test. Dysphagia. 2004;19:43–7.
Lim SH, Lieu PK, Phua SY, Seshadri R, Venketasubramanian N, Lee SH, Choo PW. Accuracy of bedside clinical methods compared with fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing (FEES) in determining the risk of aspiration in acute stroke patients. Dysphagia. 2001;16(1):1–6.
Chong MS, Lieu PK, Sitoh YY, Meng YY, Leow LP. Bedside clinical methods useful as screening test for aspiration in elderly patients with recent and previous strokes. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2003;32(6):790–4.
González-Fernández M, Sein MT, Palmer JB. Clinical experience using the Mann assessment of swallowing ability for identification of patients at risk for aspiration in a mixed-disease population. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2011;20(4):331–6.
Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olsen N. Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: a new procedure. Dysphagia. 1988;2:216–9.
Cohen JT, Eini M, Belkovitz S, Manor Y, Fliss DM. Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing–the Tel Aviv Voice and Swallowing Disorders Clinic. Harefuah. 2006;145(8):572–576, 631.
Gerek M, Atalay A, Cekin E, Ciyiltepe M, Ozkaptan Y. The effectiveness of fiberoptic endoscopic swallow study and modified barium swallow study techniques in diagnosis of dysphagia. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2005;15(5–6):103–11.
Warnecke T, Teismann I, Meimann W, Zimmermann J, Kramer C, Ringelstein EB, Schäbitz WR, Dziewas R. Assessment of aspiration risk in acute ischaemic stroke–evaluation of the simple swallowing provocation test. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 2008;79:312–4.
Willging JP, Thompson DM. Pediatric FEESST: fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2005;7(3):240–3.
Doggett DL, Tappe KA, Mitchell MD, Chapell R, Coates V, Turkelson CM. Prevention of pneumonia in elderly stroke patients by systematic diagnosis and treatment of dysphagia: an evidence-based comprehensive analysis of the literature. Dysphagia. 2001;16(4):279–95.
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yüceyar N. Piecemeal deglutition and dysphagia limit in normal subjects and in patients with swallowing disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 1996;61(5):491–6.
Aydogdu I, Ertekin C, Tarlaci S, Turman B, Kiylioglu N, Secil Y. Dysphagia in lateral medullary infarction (Wallenberg’s syndrome): an acute disconnection syndrome in premotor neurons related to swallowing activity? Stroke. 2001;32:2081–7.
Perlman AL, Christenson J. Topography and functional anatomy of the swallowing structures. In: Perlman AL, Schulze-Delrieu KS, editors. Deglutition and its Disorders. 1st ed. San Diego: Singular Publication Group; 1997. p. 15–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umay, E.K., Unlu, E., Saylam, G.K. et al. Evaluation of Dysphagia in Early Stroke Patients by Bedside, Endoscopic, and Electrophysiological Methods. Dysphagia 28, 395–403 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-013-9447-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-013-9447-z