Abstract
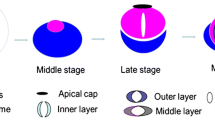
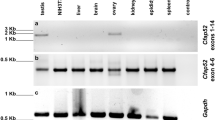
Spermatogenesis is a complicated process during which spermatogonia undergo proliferation and divisions leading, after a series of dramatic changes, to the production of mature spermatozoa. Many molecular motors are involved in this process. KIFC1, a C-terminal kinesin motor, participates in acrosome biogenesis and nuclear shaping. We report here the expression profile of KIFC1 during spermatogenesis in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. KIFC1 mainly localizes around the nucleus but is also present within the nucleus of the spermatogonium and spermatocyte. At the early spermatid stage, KIFC1 begins to be distributed on the nuclear membrane at the region where the proacrosomal vesicle is located. By the late spermatid stage, KIFC1 is found on the acrosome. Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural analyses have shown that KIFC1 localizes on the perforatorium, which is composed of an apical cap and an acrosomal tubule. We demonstrate that, during spermatogenesis in E. sinensis, KIFC1 probably plays important roles in the biogenesis of the acrosome and in its maintenance. KIFC1 may also be essential for the eversion of the acrosome during fertilization.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Haila A, Tulsiani DR (2000) Mammalian sperm acrosome: formation, contents, and function. Arch Biochem Biophys 379:173–182
Ajduk A, Yamauchi Y, Ward MA (2006) Sperm chromatin remodeling after intracytoplasmic sperm injection differs from that of in vitro fertilization. Biol Reprod 75:442–451
Ali MY, Lu H, Bookwalter CS, Warshaw DM, Trybus KM (2008) Myosin V and kinesin act as tethers to enhance each others' processivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:4691–4696
Benetti AS, Santos DC, Negreiros-Fransozo ML, Scelzo MA (2008) Spermatozoal ultrastructure in three species of the genus Uca Leach, 1814 (Crustacea, Brachyura, Ocypodidae). Micron 39:337–343
Bray JD, Chennathukuzhi VM, Hecht NB (2004) KIF2Abeta: a kinesin family member enriched in mouse male germ cells interacts with translin associated factor-X (TRAX). Mol Reprod Dev 69:387–396
Breed WG (2004) The spermatozoon of Eurasian murine rodents: its morphological diversity and evolution. J Morphol 261:52–69
Burkin HR, Zhao L, Miller DJ (2004) CASK is in the mammalian sperm head and is processed during epididymal maturation. Mol Reprod Dev 68:500–506
Cai Y, Singh BB, Aslanukov A, Zhao H, Ferreira PA (2001) The docking of kinesins, KIF5B and KIF5C, to Ran-binding protein 2 (RanBP2) is mediated via a novel RanBP2 domain. J Biol Chem 276:41594–41602
Christova Y, James P, Mackie A, Cooper TG, Jones R (2004) Molecular diffusion in sperm plasma membranes during epididymal maturation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 216:41–46
Diefenbach RJ, Mackay JP, Armati PJ, Cunningham AL (1998) The C-terminal region of the stalk domain of ubiquitous human kinesin heavy chain contains the binding site for kinesin light chain. Biochemistry 37:16663–16670
Du NS, Lai W, Xue LZ (1987) Studies on the sperm of Chinese mitten-handed crab, Eriocheir sinensis (Crustacea, Decapoda). I. The morphology and ultrastructure of mature sperm. Oceanol Limnol Sin 18:119–125
Du NS, Xue LZ, Lai W (1988) Studies on the sperm of Chinese mitten-handed crab, Eriocheir sinensis (Crustacea, Decapoda). II. Spermatogenesis. Oceanol Limnol Sin 19:71–75
Hehnly H, Stamnes M (2007) Regulating cytoskeleton-based vesicle motility. FEBS Lett 581:2112–2118
Hinsch GW (1980) Spermiogenesis in a hermit-crab, Coenobita clypeatus. II. Sertoli cells. Tissue Cell 12:255–262
Hirokawa N, Noda Y (2008) Intracellular transport and kinesin superfamily proteins, KIFs: structure, function, and dynamics. Physiol Rev 88:1089–1118
Hirokawa N, Takemura R (2004) Kinesin superfamily proteins and their various functions and dynamics. Exp Cell Res 301:50–59
Hyenne V, Harf JC, Latz M, Maro B, Wolfrum U, Simmler MC (2007) Vezatin, a ubiquitous protein of adherens cell-cell junctions, is exclusively expressed in germ cells in mouse testis. Reproduction 133:563–574
Ilango K (2005) Structure and function of the spermathecal complex in the phlebotomine sandfly Phlebotomus papatasi Scopoli (Diptera: Psychodidae). II. Post-copulatory histophysiological changes during the gonotrophic cycle. J Biosci 30:733–747
Kallio M, Sjoblom T, Lahdetie J (1995) Effects of vinblastine and colchicine on male rat meiosis in vivo: disturbances in spindle dynamics causing micronuclei and metaphase arrest. Environ Mol Mutagen 25:106–117
Kotaja N, De Cesare D, Macho B, Monaco L, Brancorsini S, Goossens E, Tournaye H, Gansmuller A, Sassone-Corsi P (2004a) Abnormal sperm in mice with targeted deletion of the act (activator of cAMP-responsive element modulator in testis) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10620–10625
Kotaja N, Kimmins S, Brancorsini S, Hentsch D, Vonesch JL, Davidson I, Parvinen M, Sassone-Corsi P (2004b) Preparation, isolation and characterization of stage-specific spermatogenic cells for cellular and molecular analysis. Nat Methods 1:249–254
Kremling H, Keime S, Wilhelm K, Adham IM, Hameister H, Engel W (1991) Mouse proacrosin gene: nucleotide sequence, diploid expression, and chromosomal localization. Genomics 11:828–834
Lawrence CJ, Dawe RK, Christie KR, Cleveland DW, Dawson SC, Endow SA, Goldstein LS, Goodson HV, Hirokawa N, Howard J, Malmberg RL, McIntosh JR, Miki H, Mitchison TJ, Okada Y, Reddy AS, Saxton WM, Schliwa M, Scholey JM, Vale RD, Walczak CE, Wordeman L (2004) A standardized kinesin nomenclature. J Cell Biol 167:19–22
Medina PM, Worthen RJ, Forsberg LJ, Brenman JE (2008) The actin-binding protein capulet genetically interacts with the microtubule motor kinesin to maintain neuronal dendrite homeostasis. PLoS ONE 3:e3054
Moreno RD, Ramalho-Santos J, Sutovsky P, Chan EK, Schatten G (2000) Vesicular traffic and Golgi apparatus dynamics during mammalian spermatogenesis: implications for acrosome architecture. Biol Reprod 63:89–98
Nath S, Bananis E, Sarkar S, Stockert RJ, Sperry AO, Murray JW, Wolkoff AW (2007) Kif5B and Kifc1 interact and are required for motility and fission of early endocytic vesicles in mouse liver. Mol Biol Cell 18:1839–1849
Navolanic PM, Sperry AO (2000) Identification of isoforms of a mitotic motor in mammalian spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 62:1360–1369
Ramalho-Santos J, Moreno RD, Wessel GM, Chan EK, Schatten G (2001) Membrane trafficking machinery components associated with the mammalian acrosome during spermiogenesis. Exp Cell Res 267:45–60
Ramalho-Santos J, Schatten G, Moreno RD (2002) Control of membrane fusion during spermiogenesis and the acrosome reaction. Biol Reprod 67:1043–1051
Rorandelli R, Paoli F, Cannicci S, Mercati D, Giusti F (2008) Characteristics and fate of the spermatozoa of Inachus phalangium (Decapoda, Majidae): description of novel sperm structures and evidence for an additional mechanism of sperm competition in Brachyura. J Morphol 269:259–271
Ross JL, Ali MY, Warshaw DM (2008) Cargo transport: molecular motors navigate a complex cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:41–47
Roux A, Cuvelier D, Bassereau P, Goud B (2008) Intracellular transport: from physics to biology. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1123:119–125
Smita M, George JM, Girija R, Akbarsha MA, Oommen OV (2004) Spermiogenesis in caecilians Ichthyophis tricolor and Uraeotyphlus cf. narayani (Amphibia: Gymnophiona): analysis by light and transmission electron microscopy. J Morphol 262:484–499
Sperry AO, Zhao LP (1996) Kinesin-related proteins in the mammalian testes: candidate motors for meiosis and morphogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 7:289–305
Toshimori K (1998) Maturation of mammalian spermatozoa: modifications of the acrosome and plasma membrane leading to fertilization. Cell Tissue Res 293:177–187
Vaid KS, Guttman JA, Singaraja RR, Vogl AW (2007) A kinesin is present at unique Sertoli/spermatid adherens junctions in rat and mouse testes. Biol Reprod 77:1037–1048
Van Horck FP, Holt CE (2008) A cytoskeletal platform for local translation in axons. Sci Signal 1:pe11
Wang R, Sperry AO (2008) Identification of a novel leucine-rich repeat protein and candidate PP1 regulatory subunit expressed in developing spermatids. BMC Cell Biol 9:9
Yang WX, Sperry AO (2003) C-terminal kinesin motor KIFC1 participates in acrosome biogenesis and vesicle transport. Biol Reprod 69:1719–1729
Yang WX, Jefferson H, Sperry AO (2006) The molecular motor KIFC1 associates with a complex containing nucleoporin NUP62 that is regulated during development and by the small GTPase RAN. Biol Reprod 74:684–690
Yoshinaga K, Toshimori K (2003) Organization and modifications of sperm acrosomal molecules during spermatogenesis and epididymal maturation. Microsc Res Tech 61:39–45
Yoshinaga K, Tanii I, Oh-oka T, Toshimori K (2001) Changes in distribution and molecular weight of the acrosomal protein acrin2 (MC41) during guinea pig spermiogenesis and epididymal maturation. Cell Tissue Res 303:253–261
Zama U, Lino-Neto J, Dolder H (2004) Structure and ultrastructure of spermatozoa in Meliponini (stingless bees) (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Tissue Cell 36:29–41
Zhang Y, Sperry AO (2004) Comparative analysis of two C-terminal kinesin motor proteins: KIFC1 and KIFC5A. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 58:213–230
Zhang Y, Oko R, Hoorn FA van der (2004) Rat kinesin light chain 3 associates with spermatid mitochondria. Dev Biol 275:23–33
Zou Y, Millette CF, Sperry AO (2002) KRP3A and KRP3B: candidate motors in spermatid maturation in the seminiferous epithelium. Biol Reprod 66:843–855
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Hans-Uwe Dahms and Prof. Junda Lin (Florida Institute of Technology, USA) for their critical reading and English improvement of this paper and to members of the Sperm Laboratory for many helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the following projects: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30671606 and 40776079) and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program; grant no. 2007CB948104).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, K., Hou, L., Zhu, JQ. et al. KIFC1 participates in acrosomal biogenesis, with discussion of its importance for the perforatorium in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis . Cell Tissue Res 337, 113–123 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0800-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0800-3