Abstract
Purpose
The activity of the application of single-session ultrasonography (US)-guided percutaneous radio frequency ablation (RFA) in benign thyroid nodules was investigated in this prospective clinical study.
Methods
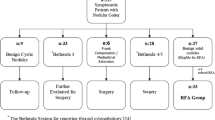
RFA treatment was applied to 100 nodules in 100 patients (78 women, 22 men; average age 44.5 years old; age range 18–71) who had euthyroid condition, nodule size larger than 1 cm in the ultrasonography, proven to be benign by fine needle aspiration cytology. The nodules were separated into three groups according to the content: solid, cystic and mixed. In first 73 cases, the process performed under local anesthesia and the other 27 cases were performed under general anesthesia. RFA process was standardized to 70 W in all of the patients, and a moving shot technique was used. The results acquired in the third and sixth months of the controls were evaluated, and the volume of the nodules was screened.
Results
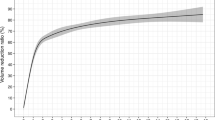
No differences between the thyroid function tests performed before and after RFA were detected (p > 0.05). The mean volume of the nodules before the process, in the third month after the process, and in the sixth month were 16.8, 4.8, and 2.6 ml, respectively (p < 0.001). The decrease in cystic nodules was greater than solid and mixed structures. Temporary hoarseness occurred in one case and skin edema was detected in a patient at the isthmus.
Conclusions
RFA is an option for treatment, with minimal invasiveness and a low complication rate, and it is effective primarily in cases with benign nodules and nodular goiter. In cases with good compliance, the likelihood of success is greater. General anesthesia can be a good option for anxious cases to gather better results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dillmann WH (1996) The Thyroid. In: Bennett JC, Plum F (eds) Cecil Textbook of Medicine. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1227–1245
Tan GH, Gharib H (1997) Thyroid incidentalomas: management approaches to nonpalpable nodules discovered incidentally on thyroid imaging. Ann Intern Med 126:226–231
Lima N, Knobel M, Cavaliere H, Sztejnsznajd C, Tomimori E, Medeiros- Neto G (1997) Levothyroxine suppressive therapy is partially effective in treating patients with benign, solid thyroid nodules and multinodular goiters. Thyroid 7:691–697
Tsai CC, Pei D, Hung YJ et al (2006) The effect of thyroxine-suppressive therapy in patients with solitary nontoxic thyroid nodules a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Clin Pract 60:23–26
Livraghi T, Paracchi A, Ferrari CP et al (1990) Treatment of autonomous thyroid nodules with percutaneous ethanol injection: preliminary results. Work in progress. Radiology 175:827–829
Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL et al (2014) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria—a 10-year update. J Vasc Interv Radiol 25:1691–1705.e1694
Zingrillo M, Torlontano M, Chiarella RM et al (1999) Percutaneous ethanol injection may be a definitive treatment for symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules not treatable by surgery: five-year follow-up study. Thyroid 9:763–767
Del Prete S, Caraglia M, Russo D et al (2002) Percutaneous ethanol injection efficacy in the treatment of large symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules: ten-year follow-up of a large series. Thyroid 12:815–821
Bennedbæk FN, Hegedus L (2003) Treatment of recurrent thyroid cysts with ethanol: a randomized double-blinded controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5773–5777
Kim JH, Lee HK, Lee JH, Ahn IM, Choi CG (2003) Efficacy of sonographically guided percutaneous ethanol injection for treatment of thyroid cyst versus solid thyroid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1723–1726
Ozdemir H, Ilgit ET, Yucel C et al (1996) Treatment of autonomous thyroid nodules: safety and efficacy of sonographically guided percutaneous injection of ethanol. AJR Am J Roentgenol 163:929–932
Del Pretes S, Russo D, Caraglia M, Giuberti G, Marra M, Vitale G et al (2001) Percutaneous ethanol injection of autonomous thyroid nodules with a volume larger than 40 ml: three years of follow-up. Clin Radiol 56:859–901
Dossing H, Bennedbæk FN, Karstrup S, Hegedu’s L (2002) Benign solitary cold thyroid nodules: US-guided interstitial laser photo coagulation – initial experience. Radiology 225:53–57
Dossing H, Bennedbæk FN, Hegedu’s L (2003) Ultrasound guided interstitial laser photocoagulation of an autonomous thyroid nodule: the introduction of a novel alternative. Thyroid 13:885–888
Pacella CM, Bizzarri G, Spiezia S et al (2004) Thyroid tissue: US-guided percutaneous laser thermal ablation. Radiology 232:272–280
Spiezia S, Vitale G, Di Somma C et al (2003) Ultrasound-guided laser thermal ablation in the treatment of autonomous hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules and compressive nontoxic nodular goiter. Thyroid 13:941–947
Dossing H, Bennedbaek FN, Bonnema SJ, Grupe P, Hegedüs L (2007) Randomized prospective study comparing a single radioiodine dose and asingle laser therapy session in autonomously functioning thyroid nodules. Eur J Endocrinol 157:95–100
Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Halpern EF, Gazelle GS (2000) Variables affecting proper system grounding for radiofrequency ablation in an animal model. J Vasc Interv Radiol 11:1069–1075
Gazelle GS, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Livraghi T (2001) Tumor ablation with radio-frequency energy. Radiology 217:633–646
McGahan JP, Browning PD, Brock JM, Tesluk H (1990) Hepatic ablation using radiofrequency electrocautery. Investig Radiol 210:127–138
Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F et al (1998) Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. Am J Roentgenol 170:1015–1022
Dupuy D, Monchik J, Decrea C, Pisharodi L (2001) Radiofrequency ablation of regional recurrence from well-differentiated thyroidmalignancy. Surgery 130:971–977
Jeong WK, Baek JH, Rhim H et al (2008) Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-upin 236 patients. Eur Radiol 18:1244–1250
Deandrea M, Limone P, Basso E et al (2008) US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation for the treatment of solid benign hyperfunctioning or compressive thyroid nodules. Ultrasound Med Biol 34:784–791
Spiezia S, Garberoglio R, Milone F et al (2009) Thyroid nodules and related symptoms are stably controlled two years after radiofrequency thermal ablation. Thyroid 19:10
Hegedu’s L, Bonnema SJ, Bennedbæk FN (2003) Management of simple nodular goiter: current status and future perspectives. Endocr Rev 24:102–132
Crile G Jr (1996) Treatment of thyroid cysts by aspiration. Surgery 59:210–212
Miller JM, Zafar SU, Karo JJ (1974) The cystic thyroid nodule. Radiology 110:257–261
Lee SJ, Ahn IM (2005) Effectiveness of percutaneous ethanol injection therapy in benign nodular and cystic thyroid diseases: long-term follow-up experience. Endocr J 52:455–462
Dossing H, Bennedbæk FN, Hegedüs L (2006) Effect of ultrasound-guided interstitial laser photocoagulation on benign solitary solid cold thyroid nodules: one versus three treatments. Thyroid 16:763–768
Na DG, Lee JH, Jung SL et al (2012) Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers: consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol 13:117–125
Baek JH, Ha EJ, Choi YJ, Sung JY, Kim JK, Shong YK (2015) Radiofrequency versus ethanol ablation for treating predominantly cystic thyroid nodules: a randomized clinical trial. Korean J Radiol 16:1332–1340
Sung JY, Baek JH, Kim KS et al (2013) Single-session treatment of benign cystic thyroid nodules with ethanol versus radiofrequency ablation: a prospective randomized study. Radiology 269:293–300
Amin Z, Donald JJ, Masters A et al (1993) Hepatic metastases: interstitial laser photocoagulation with real-time US monitoring and dynamic CT evaluation of treatment. Radiology 187:339–347
Pacella CM, Bizzarri G, Guglielmi R et al (2000) Thyroid tissue: US-guided percutaneous interstitial laser ablation—a feasibility study. Radiology 217:673–677
Kanauchi H, Mimura Y, Kaminishi M (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of the thyroid guided by ultrasonography. Eur J Surg 167:305–307
Fuller CW, Nguyen SA, Lohia S, Gillespie MB (2014) Radiofrequency ablation for treatment of benign thyroid nodules: systematic review. Laryngoscope 124(1):346–353
Kim YS, Rhim H, Tae K, Park DW, Kim ST (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of benign cold thyroid nodules: initial clinical experience. Thyroid 16:361–367
Deandrea M, Sung JY, Limone P et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation versus observation for nonfunctioning benign thyroid nodules: a randomized controlled international collaborative trial. Thyroid 25(8):890–896
Sung JY, Baek JH, Jung SL et al (2015) Radiofrequency ablation for autonomously functioning thyroid nodules: a multicenter study. Thyroid 25:112–117
Baek JH, Lee JH, Sung JY et al (2012) Complications encountered in the treatment of benign thyroid nodules with US-guided radiofrequency ablation: a multicenter study. Radiology 262:335–342
Garberoglio R, Aliberti C, Appetecchia M et al (2015) Radiofrequency ablation for thyroid nodules: which indications? the first Italian opinion statement. J Ultrasound 18:423–430
Bernardi S, Lanzilotti V, Papa G et al (2015) Full-thickness skin burn caused by radiofrequency ablation of a benign thyroid nodule., Thyroid, [Epub ahead of print]
Authors’ contribution
-
Study conception and design: Erhan Aysan and Ufuk Oguz Idiz
-
Acquisition of data: Huseyin Akbulut and Leyla Elmas
-
Analysis and interpretation of data: Erhan Aysan, Ufuk Oguz Idiz, Leyla Elmas, and Huseyin Akbulut
-
Drafting of manuscript: Ufuk Oguz Idiz and Huseyin Akbulut
-
Critical revision of manuscript: Erhan Aysan
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Erhan Aysan declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Author Ufuk Oguz Idiz declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Author Huseyin Akbulut declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Author Leyla Elmas declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aysan, E., Idiz, U.O., Akbulut, H. et al. Single-session radiofrequency ablation on benign thyroid nodules: a prospective single center study. Langenbecks Arch Surg 401, 357–363 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1408-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1408-1