Abstract
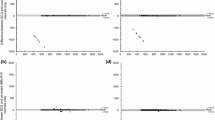
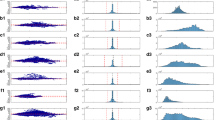
This study was designed to examine the RR interval signal qualities of a Holter device and a heart rate chest belt monitor at rest and during exercise. Ten healthy individuals completed five low- to high-intensity activities while simultaneously using the medilog® AR12plus Holter monitor and the Polar H10 heart rate monitor. The RR interval signal quality was based on the quantification of the missing RR intervals and RR interval detection errors. Therefore, both measurement systems were compared against visual inspection of the raw electrocardiography signal. The missing and wrong R-wave peak detections were counted manually for both measurement systems. RR interval signal quality was defined as the relative number of correctly detected RR intervals. Overall, RR interval signal qualities of 94.6% and 99.6% were demonstrated for the medilog® AR12plus and the Polar H10. During the high-intensity activities, the RR interval signal quality of the medilog® AR12plus dropped to 89.8%, whereas the Polar H10 maintained a signal quality of 99.4%. The correlation between both systems was high (r = 0.997, p > 0.001). The excellent RR interval signal quality during low- to moderate-intensity activities in the medilog® AR12plus and during low- to high-intensity activities in the Polar H10 demonstrates both measurement systems’ validity for the detection of RR intervals throughout a wide range of activities. A simple chest strap such as the Polar H10 might be recommended as the gold standard for RR interval assessments if intense activities with strong body movements are investigated.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiography
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- LoA:
-
Limits of agreement
- PPG:
-
Photoplethysmography
References
Barbosa MP, da Silva NT, de Azevedo FM, Pastre CM, Vanderlei LC (2016) Comparison of Polar(R) RS800G3 heart rate monitor with Polar(R) S810i and electrocardiogram to obtain the series of RR intervals and analysis of heart rate variability at rest. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 36(2):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12203
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Borg G (1970) Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scand J Rehabil Med 2(2):92–98
Caminal P, Sola F, Gomis P, Guasch E, Perera A, Soriano N, Mont L (2018) Validity of the Polar V800 monitor for measuring heart rate variability in mountain running route conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol 118(3):669–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3808-0
Cassirame J, Vanhaesebrouck R, Chevrolat S, Mourot L (2017) Accuracy of the Garmin 920 XT HRM to perform HRV analysis. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 40(4):831–839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-017-0593-8
Cheatham SW, Kolber MJ, Ernst MP (2015) Concurrent validity of resting pulse-rate measurements: a comparison of 2 smartphone applications, the polar H7 belt monitor, and a pulse oximeter with bluetooth. J Sport Rehabil 24(2):171–178
Costa RBMPd, Mícolis AF, Marcelo PC, Marques VLC (2016) Comparison of Polar® RS800G3™ heart rate monitor with Polar® S810i™ and electrocardiogram to obtain the series of RR intervals and analysis of heart rate variability at rest. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 36(2):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpf.12203
Gamelin FX, Berthoin S, Bosquet L (2006) Validity of the polar S810 heart rate monitor to measure R–R intervals at rest. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38(5):887–893. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000218135.79476.9c
Giles D, Draper N, Neil W (2016) Validity of the Polar V800 heart rate monitor to measure RR intervals at rest. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(3):563–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3303-9
Hedelin R, Wiklund U, Bjerle P, Henriksson-Larsen K (2000) Cardiac autonomic imbalance in an overtrained athlete. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(9):1531–1533
Horton JF, Stergiou P, Fung TS, Katz L (2017) Comparison of polar M600 optical heart rate and ECG heart rate during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 49(12):2600–2607. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001388
Kingsley M, Lewis MJ, Marson RE (2005) Comparison of Polar 810 s and an ambulatory ECG system for RR interval measurement during progressive exercise. Int J Sports Med 26(1):39–44. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-817878
Malliani A, Lombardi F, Pagani M (1994) Power spectrum analysis of heart rate variability: a tool to explore neural regulatory mechanisms. Br Heart J 71(1):1–2
Mourot L, Bouhaddi M, Perrey S, Cappelle S, Henriet MT, Wolf JP, Rouillon JD, Regnard J (2004) Decrease in heart rate variability with overtraining: assessment by the Poincare plot analysis. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 24(1):10–18
Nunan D, Jakovljevic DG, Donovan G, Hodges LD, Sandercock GR, Brodie DA (2008) Levels of agreement for RR intervals and short-term heart rate variability obtained from the Polar S810 and an alternative system. Eur J Appl Physiol 103(5):529–537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0742-6
Nunan D, Donovan G, Jakovljevic DG, Hodges LD, Sandercock GR, Brodie DA (2009) Validity and reliability of short-term heart-rate variability from the Polar S810. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(1):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e318184a4b1
Parrado E, Garcia MA, Ramos J, Cervantes JC, Rodas G, Capdevila L (2010) Comparison of omega wave system and polar S810i to detect R–R intervals at rest. Int J Sports Med 31(5):336–341. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1248319
Plews DJ, Scott B, Altini M, Wood M, Kilding AE, Laursen PB (2017) Comparison of heart-rate-variability recording with smartphone photoplethysmography, polar H7 chest strap, and electrocardiography. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 12(10):1324–1328. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijspp.2016-0668
Rompelman O, Kampen WHAV, Backer E, Offerhaus RE (1980) Heart rate variability in relation to psychological factors. Ergonomics 23(12):1101–1115. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140138008924817
Ruha A, Sallinen S, Nissilä S (1997) A real-time microprocessor QRS detector system with a 1-ms timing accuracy for the measurement of ambulatory HRV. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 44(3):159–167
Singh N, Moneghetti K, Christle JW, Hadley D, Plews D, Froelicher V (2018) Heart rate variability: an old metric with new meaning in the era of using mHealth technologies for health and exercise training guidance. Part one: physiology and methods. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 7(3):193–198. https://doi.org/10.15420/aer.2018.27.2
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996) Heart Rate Variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 93(5):1043–1065
Tulppo MP, Makikallio TH, Seppanen T, Laukkanen RT, Huikuri HV (1998) Vagal modulation of heart rate during exercise: effects of age and physical fitness. Am J Physiol 274(2 Pt 2):H424–H429
Weippert M, Kumar M, Kreuzfeld S, Arndt D, Rieger A, Stoll R (2010) Comparison of three mobile devices for measuring R–R intervals and heart rate variability: polar S810i, Suunto t6 and an ambulatory ECG system. Eur J Appl Physiol 109(4):779–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1415-9
Funding
Polar Electro Oy (Finland) funded in part the experiment described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RGA and TW conceived and designed the research. RGA and TS conducted the experiments. RGA analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the cantonal ethics committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Communicated by Mark Olfert.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilgen-Ammann, R., Schweizer, T. & Wyss, T. RR interval signal quality of a heart rate monitor and an ECG Holter at rest and during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 119, 1525–1532 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04142-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04142-5