Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the surgical outcomes of small-gauge vitrectomy with subretinal injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) for a submacular hemorrhage caused by a ruptured retinal arterial macroaneurysm (RAM).
Methods
Non-comparative, consecutive case-series performed at two ophthalmological institutions. We examined 22 eyes of 22 patients with a submacular hemorrhage associated with a RAM but without a preretinal or sub-internal limiting membrane hemorrhage at the fovea. During 25-gauge vitrectomy, approximately 4000–8000 IU of rt-PA was injected subretinally, followed by the injection of air or 10 % sulfur hexafluoride as a tamponade. The patients maintained an upright position for 1 hour, then turned to a facedown position for 1 to 3 days. The best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and postoperative complications were evaluated.
Results
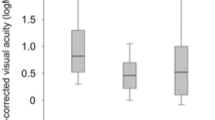
The average interval from the onset of symptoms to surgery was 8.4 ± 7.6 days, and the average size of the subretinal hemorrhage was 3.4 ± 1.0 disc diameters. The submacular hemorrhage was displaced from the foveal area in all eyes after 1 week. The mean baseline BCVA was 1.41 ± 0.41 logMAR units, and it improved to 0.91 ± 0.43 at 1 month and to 0.64 ± 0.45 at the final visit (P = 0.0001, P < 0.0001 respectively). A macular hole was detected intraoperatively in two eyes and postoperatively in two eyes, and both were closed by internal limiting membrane peeling or a second vitrectomy.
Conclusions
Small-gauge vitrectomy with subretinal rt-PA injection and gas tamponade were effective in displacing a submacular hemorrhage associated with a RAM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabb MF, Gagliano DA, Teske MP (1988) Retinal arterial macroaneurysms. Surv Ophthalmol 33:73–96
Tonotsuka T, Imai M, Saito K, Iijima H (2003) Visual prognosis for symptomatic retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Jpn J Ophthalmol 47:498–502
Berrocal MH, Lewis ML, Flynn HW Jr (1996) Variations in the clinical course of submacular hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol 122:486–493
Hochman MA, Seery CM, Zarbin MA (1997) Pathophysiology and management of subretinal hemorrhage. Surv Ophthalmol 42:195–213
Tennant MT, Borrillo JL, Regillo CD (2002) Management of submacular hemorrhage. Ophthalmol Clin North Am 15:445–452
Glatt H, Machemer R (1982) Experimental subretinal hemorrhage in rabbits. Am J Ophthalmol 94:762–773
Toth CA, Morse LS, Hjelmeland LM, Landers MB 3rd (1991) Fibrin directs early retinal damage after experimental subretinal hemorrhage. Arch Ophthalmol 109:723–729
Benner JD, Hay A, Landers MB 3rd, Hjelmeland LM, Morse LS (1994) Fibrinolytic-assisted removal of experimental subretinal hemorrhage within seven days reduces outer retinal degeneration. Ophthalmology 101:672–681
Johnson MW, Olsen KR, Hernandez E (1991) Tissue plasminogen activator treatment of experimental subretinal hemorrhage. Retina 11:250–258
Johnson MW, Olsen KR, Hernandez E (1992) Tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis during surgical evacuation of experimental subretinal hemorrhage. Ophthalmology 99:515–521
Lewis H, Resnick SC, Flannery JG, Straatsma BR (1991) Tissue plasminogen activator treatment of experimental subretinal hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol 111:197–204
Chen CY, Hooper C, Chiu D, Chamberlain M, Karia N, Heriot WJ (2007) Management of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreal injection of tissue plasminogen activator and expansile gas. Retina 27:321–328
Johnson MW (2000) Pneumatic displacement of submacular hemorrhage. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 11:201–206
Hassan AS, Johnson MW, Schneiderman TE, Regillo CD, Tornambe PE, Poliner LS, Blodi BA, Elner SG (1999) Management of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreous tissue plasminogen activator injection and pneumatic displacement. Ophthalmology 106:1900–1906
Hattenbach LO, Klais C, Koch FH, Gümbel HO (2001) Intravitreous injection of tissue plasminogen activator and gas in the treatment of submacular hemorrhage under various conditions. Ophthalmology 108:1485–1492
Hesse L, Schmidt J, Kroll P (1999) Management of acute submacular hemorrhage using recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and gas. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 237:273–277
Haupert CL, McCuen BW 2nd, Jaffe GJ, Steuer ER, Cox TA, Toth CA, Fekrat S, Postel EA (2001) Pars plana vitrectomy, subretinal injection of tissue plasminogen activator, and fluid-gas exchange for displacement of thick submacular hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol 131:208–215
Hillenkamp J, Surguch V, Framme C, Gabel VP, Sachs HG (2010) Management of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreal versus subretinal injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248:5–11
Kapran Z, Ozkaya A, Uyar OM (2013) Hemorrhagic age-related macular degeneration managed with vitrectomy, subretinal injection of tissue plasminogen activator, gas tamponade, and upright positioning. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina 44:471–476
Olivier S, Chow DR, Packo KH, MacCumber MW, Awh CC (2004) Subretinal recombinant tissue plasminogen activator injection and pneumatic displacement of thick submacular hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 111:1201–1208
Saika S, Yamanaka A, Yamanaka A, Minamide A, Kin K, Shirai K, Tanaka S, Kawashima Y, Katoh T, Okada Y, Ohkawa K, Ohnishi Y (1998) Subretinal administration of tissue-type plasminogen activator to speed the drainage of subretinal hemorrhage. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 236:196–201
Treumer F, Roider J, Hillenkamp J (2012) Long-term outcome of subretinal coapplication of rtPA and bevacizumab followed by repeated intravitreal anti-VEGF injections for neovascular AMD with submacular haemorrhage. Br J Ophthalmol 96:708–713
Humayun M, Lewis H, Flynn HW Jr, Sternberg P Jr, Blumenkranz MS (1998) Management of submacular hemorrhage associated with retinal arterial macroaneurysms. Am J Ophthalmol 126:358–361
Kamei M, Tano Y, Maeno T, Ikuno Y, Mitsuda H, Yuasa T (1996) Surgical removal of submacular hemorrhage using tissue plasminogen activator and perfluorocarbon liquid. Am J Ophthalmol 121:267–275
Peyman GA, Nelson NC Jr, Alturki W, Blinder KJ, Paris CL, Desai UR, Harper CA 3rd (1991) Tissue plasminogen activating factor assisted removal of subretinal hemorrhage. Ophthalmic Surg 22:575–582
Sonmez K, Ozturk F, Ozcan PY (2012) Treatment of multilevel macular hemorrhage secondary to retinal arterial macroaneurysm with submacular tissue plasminogen activator. Eur J Ophthalmol 22:1026–1031
van Zeeburg EJ, Cereda MG, van Meurs JC (2013) Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator, vitrectomy, and gas for recent submacular hemorrhage displacement due to retinal macroaneurysm. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251:733–740
Wu TT, Sheu SJ (2005) Intravitreal tissue plasminogen activator and pneumatic displacement of submacular hemorrhage secondary to retinal artery macroaneurysm. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 21:62–67
Zhao P, Hayashi H, Oshima K, Nakagawa N, Ohsato M (2000) Vitrectomy for macular hemorrhage associated with retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Ophthalmology 107:613–617
Jonas JB, Schmidbauer M (2010) Intravitreal bevacizumab for retinal macroaneurysm. Acta Ophthalmol 88:e284
Pichi F, Morara M, Torrazza C, Manzi G, Alkabes M, Balducci N, Vitale L, Lembo A, Ciardella AP, Nucci P (2013) Intravitreal bevacizumab for macular complications from retinal arterial macroaneurysms. Am J Ophthalmol 155:287–294
Ciardella AP, Barile G, Schiff W, Del Priore L, Langton K, Chang S (2003) Ruptured retinal arterial macroaneurysm associated with a stage IV macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol 135:907–909
Colucciello M, Nachbar JG (2000) Macular hole following ruptured retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Retina 20:94–96
Mitamura Y, Terashima H, Takeuchi S (2002) Macular hole formation following rupture of retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Retina 22:113–115
Tashimo A, Mitamura Y, Ohtsuka K, Okushiba U, Imaizumi H, Takeda M (2003) Macular hole formation following ruptured retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Am J Ophthalmol 135:487–492
Shultz RW, Bakri SJ (2011) Treatment for submacular hemorrhage associated with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Semin Ophthalmol 26:361–371
Acknowledgments
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony, or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge, or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. Contributions of authors: Involved in data collection (MI, FS, YS, YM, SK). Involved in management, analysis, interpretation, and preparation of the data (MI, FS, YS). Involved in interpretation, and preparation of the manuscript (MI, FS, AH). The study and data accumulation were carried out with approval from the Institutional Review Board of the Kagawa University Faculty of Medicine, the Okayama University Medical School, and the Kyorin University School of Medicine, and conformed to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent for the research was obtained from all patients. Scientific writing assistance was provided by Professor Duco I. Hamasaki, PhD of Hamasaki Scientific Editing (Miami, FL, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, M., Shiraga, F., Shirakata, Y. et al. Subretinal injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for submacular hemorrhage associated with ruptured retinal arterial macroaneurysm. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 253, 1663–1669 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2861-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2861-6