Abstract
Background
The aim of the present study was to compare the measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP) through a therapeutic soft contact lens with the “native” measurement. We additionally investigate whether a rebound tonometer (RT) or non-contact tonometer (NCT) is more suitable to measure IOP through a bandage contact lens.
Methods
The IOP was determined using each of the two methods, three times successively with (lens measurement) and without (native measurement) a soft contact lens. The Icare tonometer (Icare® TA01i, Icare Finland Oy, 23 subjects) and the Airpuff tonometer (Nidek NT 53OP, Nidek CO., LTD, Hiroishi Gamagori, Aichi, Japan, 16 subjects) were used. We compared the mean values (validity parameter) and standard deviation (precision parameter) of the three individual measurements in each case using the paired t-test. In addition, we conducted a power analysis to estimate the maximum error in the measurement caused by the contact lens (power level set to 0.8).
Results
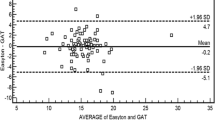
With the Airpuff tonometer we detected no statistically significant between the lens and the native measurement (15.6 ± 2.6 vs. 15.3 ± 2.6 mmHg; p = 0.42). The power analysis revealed that the maximum error caused by the contact lens was 1.2 mmHg. The Icare tonometry, however, trended toward higher values in the contact lens measurements (17.5 ± 4.3 vs. 16.4 ± 3.5 mmHg in the native measurements; p = 0.05). Interestingly, this difference exhibited a statistically significant correlation with the corneal thickness (0.03 mmHg per μm corneal thickness; p = 0.04).
Conclusion
The use of NCT and RT for IOP measurement over a soft contact lens is feasible. The accuracy appears to be sufficient for the most common clinical applications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Jimenez-Santos M, Saenz-Frances F, Matilla-Rodero M, Mendez-Hernandez C, Herrero-Vanrell R, Garcia-Feijoo J (2011) Performance of the rebound, noncontact and goldmann applanation tonometers in routine clinical practice. Acta Ophthalmol 89:676–680
Jablonski KS, Rosentreter A, Gaki S, Lappas A, Dietlein TS (2012) Clinical Use of a New Position-independent Rebound Tonometer. J. Glaucoma. PMID: 23172572
Abraham LM, Epasinghe NCR, Selva D, Casson R (2008) Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann applanation tonometer by experienced and inexperienced tonometrists. Eye (Lond) 22:503–506
Marini M, Da Pozzo S, Accardo A, Canziani T (2011) Comparing applanation tonometry and rebound tonometry in glaucomatous and ocular hypertensive eyes. Eur J Ophthalmol 21:258–263
Gandhi NG, Prakalapakorn SG, El-Dairi MA, Jones SK, Freedman SF (2012) Icare ONE rebound versus Goldmann applanation tonometry in children with known or suspected glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 154:843–849.e1
Halkiadakis I, Stratos A, Stergiopoulos G, Patsea E, Skouriotis S, Mitropoulos P, Papaconstantinou D, Georgopoulos G (2012) Evaluation of the Icare-ONE rebound tonometer as a self-measuring intraocular pressure device in normal subjects. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250:1207–1211
Flemmons MS, Hsiao Y-C, Dzau J, Asrani S, Jones S, Freedman SF (2011) Home tonometry for management of pediatric glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 152:470–478.e2
Blackmore SJ (2010) The use of contact lenses in the treatment of persistent epithelial defects. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 33:239–244
Sugimoto-Takeuchi R, Yamamoto R, Kuwayama Y, Kinoshita S (1991) Effect of intraocular pressure measurement through therapeutic soft contact lenses by noncontact tonometer. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 95:869–872
Firat PG, Cankaya C, Doganay S, Cavdar M, Duman S, Ozsoy E, Koc B (2012) The influence of soft contact lenses on the intraocular pressure measurement. Eye (Lond) 26:278–282
Liu Y-C, Huang J-Y, Wang I-J, Hu F-R, Hou Y-C (2011) Intraocular pressure measurement with the noncontact tonometer through soft contact lenses. J Glaucoma 20:179–182
Patel S, Illahi W (2004) Non-contact tonometry over soft contact lenses: effect of contact lens power on the measurement of intra-ocular pressure. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 27:33–37
Patel S, Stevenson G (2009) Influence of lens material and intra-ocular pressure on the outcome of non-contact tonometry over soft contact lenses. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 32:68–72
Zeri F, Calcatelli P, Donini B, Lupelli L, Zarrilli L, Swann PG (2011) The effect of hydrogel and silicone hydrogel contact lenses on the measurement of intraocular pressure with rebound tonometry. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 34:260–265
Khan JA, Graham CE (1991) Effect of contact lens removal or displacement on intraocular pressure. Arch Ophthalmol 109:825–828
Rüfer F (2011) Sources of error in Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmologe 108:546–552
Neuburger M, Maier P, Böhringer D, Reinhard T, FJordan J (2012) The Impact of Corneal Edema on Intraocular Pressure Measurements Using Goldmann Applanation Tonometry, Tono-Pen XL, iCare, and ORA: An In Vitro Model. J glaucoma. PMID 22366704
Conflict of Interest
The authors do not have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context of the subject of this presentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anton, A., Neuburger, M., Böhringer, D. et al. Comparative measurement of intraocular pressure by Icare tonometry and Airpuff tonometry in healthy subjects and patients wearing therapeutic soft contact lenses. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251, 1791–1795 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2329-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2329-0