Abstract
Background
Randomized controlled clinical trials (RCT) have demonstrated varied efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists for cardiovascular outcomes. We sought to evaluate the efficacy and safety of GLP-1R agonists among patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) for stroke prevention.
Methods
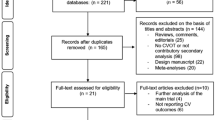
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs reporting the following outcomes among patients with Type 2 DM treated with GLP-1R agonists (vs. placebo): nonfatal or fatal strokes, all-cause or cardiovascular mortality, myocardial infarction (MI) and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). The protocol of our systematic review and meta-analysis was registered to the PROSPERO database. We pooled odds ratios (OR) using random-effect models, and assessed the heterogeneity using Cochran Q and I2 statistics.
Results
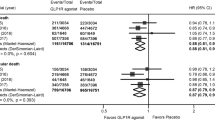
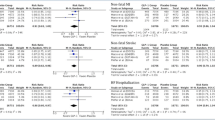
We identified 8 RCTs, comprising 56,251 patients. In comparison to placebo, GLP-1R agonists reduced nonfatal strokes (OR 0.84; 95% CI 0.76–0.94, p = 0.002; I2 = 0%) and all strokes (OR 0.84; 95% CI 0.75–0.93, p = 0.001; I2 = 0%) by 16%. Overall, GLP-1R agonists reduced MACE by 13% (OR 0.87; 95% CI 0.81–0.94, p = 0.0003; I2 = 42%), cardiovascular mortality by 12% (OR 0.88; 95% CI 0.81–0.95; p = 0.002; I2 = 0%) and all-cause mortality by 12% (OR 0.88; 95% CI 0.82–0.95, p = 0.0007; I2 = 15%). Additional analyses demonstrated that GLP-1R agonists reduced the risk of incident MACE (OR 0.86; 95% CI 0.80–0.92; p < 0.0001; I2 = 0%) among patients with prior history of MI or nonfatal strokes.
Conclusions
Among patients with type 2 DM, GLP-1R agonists are beneficial for primary stroke, MACE, and cardiovascular mortality prevention. Further RCTs are needed to evaluate their role for secondary stroke prevention.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, Probstfield J, Riesmeyer JS, Riddle MC, Ryden L, Xavier D, Atisso CM, Dyal L, Hall S, Rao-Melacini P, Wong G, Avezum A, Basile J, Chung N, Conget I, Cushman WC, Franek E, Hancu N, Hanefeld M, Holt S, Jansky P, Keltai M, Lanas F, Leiter LA, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Cardona Munoz EG, Pirags V, Pogosova N, Raubenheimer PJ, Shaw JE, Sheu WH, Temelkova-Kurktschiev T (2019) Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 394(10193):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)31149-3
Baker L, Juneja R, Bruno A (2011) Management of hyperglycemia in acute ischemic stroke. Curr Treat Options Neurol 13(6):616–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-011-0143-8
Tsivgoulis G, Katsanos AH, Mavridis D, Lambadiari V, Roffe C, Macleod MJ, Sevcik P, Cappellari M, Nevsimalova M, Toni D, Ahmed N (2019) Association of baseline hyperglycemia with outcomes of patients with and without diabetes with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis: a propensity score-matched analysis from the SITS-ISTR registry. Diabetes 68(9):1861–1869. https://doi.org/10.2337/db19-0440
Lu GD, Ren ZQ, Zhang JX, Zu QQ, Shi HB (2018) Effects of diabetes mellitus and admission glucose in patients receiving mechanical thrombectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurocrit Care 29(3):426–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-018-0562-4
Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products in the treatment or prevention of diabetes mellitus (2012) In: Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, London, European Medicines Society
Kristensen SL, Rorth R, Jhund PS, Docherty KF, Sattar N, Preiss D, Kober L, Petrie MC, McMurray JJV (2019) Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 7(10):776–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(19)30249-9
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol 62(10):e1–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006
Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Cochrane Statistical Methods Group (2019) Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (eds) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley, Chichester, pp 241–284
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 343:d5928. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928
Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, Dickstein K, Gerstein HC, Kober LV, Lawson FC, Ping L, Wei X, Lewis EF, Maggioni AP, McMurray JJ, Probstfield JL, Riddle MC, Solomon SD, Tardif JC (2015) Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med 373(23):2247–2257. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1509225
Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, Thompson VP, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, Chan JC, Choi J, Gustavson SM, Iqbal N, Maggioni AP, Marso SP, Ohman P, Pagidipati NJ, Poulter N, Ramachandran A, Zinman B, Hernandez AF (2017) Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 377(13):1228–1239. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1612917
Hernandez AF, Green JB, Janmohamed S, D'Agostino RB Sr, Granger CB, Jones NP, Leiter LA, Rosenberg AE, Sigmon KN, Somerville MC, Thorpe KM, McMurray JJV, Del Prato S (2018) Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London, England) 392(10157):1519–1529. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32261-x
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, Nissen SE, Pocock S, Poulter NR, Ravn LS, Steinberg WM, Stockner M, Zinman B, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB (2016) Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 375(4):311–322. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1603827
Husain M, Birkenfeld AL, Donsmark M, Dungan K, Eliaschewitz FG, Franco DR, Jeppesen OK, Lingvay I, Mosenzon O, Pedersen SD, Tack CJ, Thomsen M, Vilsboll T, Warren ML, Bain SC (2019) Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 381(9):841–851. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1901118
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, Lingvay I, Rosenstock J, Seufert J, Warren ML, Woo V, Hansen O, Holst AG, Pettersson J, Vilsboll T (2016) Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 375(19):1834–1844. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1607141
Sharma A, Ambrosy AP, DeVore AD, Margulies KB, McNulty SE, Mentz RJ, Hernandez AF, Michael Felker G, Cooper LB, Lala A, Vader J, Groake JD, Borlaug BA, Velazquez EJ (2018) Liraglutide and weight loss among patients with advanced heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction: insights from the FIGHT trial. ESC Heart Fail 5(6):1035–1043. https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.12334
Sposito AC, Berwanger O, de Carvalho LSF, Saraiva JFK (2018) GLP-1RAs in type 2 diabetes: mechanisms that underlie cardiovascular effects and overview of cardiovascular outcome data. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17(1):157. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0800-2
Barkas F, Elisaf M, Milionis H (2019) Protection against stroke with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol 26(4):559–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13905
Funding
The study received no specific grant or funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KM: study concept and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. AHK: acquisition of data & critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. VL: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. NG: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. LP: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. MK: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. CK: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. AVA: critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. GT: study concept and design, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors report no disclosures.
Ethical standard
The manuscript provides aggregate data that is publically available from published studies. It does not contain individual patient data, and therefore approval from the ethics committee or patient consent was not required.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malhotra, K., Katsanos, A.H., Lambadiari, V. et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetes for stroke prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol 267, 2117–2122 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09813-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09813-4