Abstract
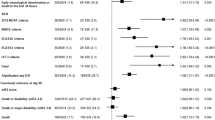
The question of whether i.v. rt-PA is beneficial in patients with ischaemic stroke and atrial fibrillation (AF) remains unresolved. Our objective was to evaluate the outcome of patients with AF who received i.v. rt-PA for stroke in the registries of Lille (France) and Belgrade (Serbia). End-points were poor outcome [modified Rankin Scale (mRS) 3–6], and symptomatic haemorrhagic transformation (sHT) according to ECASS3. Of 734 consecutive patients, 155 (21.2 %) had AF. The unadjusted comparison found patients with AF to be 12 years older, more likely to be women, to have hypertension, and baseline INR > 1.2, and less likely to be smokers. They had higher baseline NIHSS scores, diastolic blood pressure, and serum glucose concentrations, and lower platelet counts. They did not differ for sHT (5.8 vs. 5.5 %; p = 0.893), but they more frequently had poor outcomes (52.3 vs. 35.2 %; p < 0.001) and death (21.9 vs. 9.0 %; p < 0.001). The only independent predictor of sHT was baseline NIHSS (adjOR 1.05 per 1 point increase; 95 % CI 1.01–1.10). Independent variables associated with poor outcome were age (adjOR 1.04 for 1 year increase; 95 % CI 1.03–1.06), baseline NIHSS (adjOR 1.17 per 1 point increase; 95 % CI 1.13–1.21), and sHT (adjOR 47.6; 95 % CI 10.2–250) but not AF. In patients treated with i.v. rt-PA for cerebral ischaemia, those with AF have worse outcomes because they are older and have more severe strokes at admission. This result suggests that we should focus on prevention and research of more aggressive strategies at the acute stage.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lees KR, Bluhmki E, von Kummer R, Brott TG, Toni D, Grotta JC, Albers GW, Kaste M, Marler JR, Hamilton SA, Tilley BC, Davis SM, Donnan GA, Hacke W, Allen K, Mau J, Meier D, del Zoppo G, De Silva DA, Butcher KS, Parsons MW, Barber PA, Levi C, Bladin C, Byrnes G (2010) Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in stroke: an updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS, and EPITHET trials. Lancet 375(9727):1695–1703
Sandercock P, Wardlaw JM, Lindley RI, Dennis M, Cohen G, Murray G, Innes K, Venables G, Czlonkowska A, Kobayashi A, Ricci S, Murray V, Berge E, Slot KB, Hankey GJ, Correia M, Peeters A, Matz K, Lyrer P, Gubitz G, Phillips SJ, Arauz A (2012) The benefits and harms of intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator within 6 h of acute ischaemic stroke [the third international stroke trial (IST-3)]: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 379(9834):2352–2363
Wardlaw JM, Murray V, Berge E, del Zoppo G, Sandercock P, Lindley RL, Cohen G (2012) Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischaemic stroke: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 379(9834):2364–2372
Kimura K, Minematsu K, Yamaguchi T (2005) Atrial fibrillation as a predictive factor for severe stroke and early death in 15,831 patients with acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(5):679–683
Jaillard A, Cornu C, Durieux A, Moulin T, Boutitie F, Lees KR, Hommel M (1999) Hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. The MAST-E study. MAST-E Group. Stroke 30(7):1326–1332
Lee JH, Park KY, Shin JH, Cha JK, Kim HY, Kwon JH, Oh HG, Lee KB, Kim DE, Ha SW, Cho KH, Sohn SI, Oh MS, Yu KH, Lee BC, Kwon SU (2010) Symptomatic hemorrhagic transformation and its predictors in acute ischemic stroke with atrial fibrillation. Eur Neurol 64(4):193–200
Lin HJ, Wolf PA, Kelly-Hayes M, Beiser AS, Kase CS, Benjamin EJ, D’Agostino RB (1996) Stroke severity in atrial fibrillation. The Framingham Study. Stroke 27(10):1760–1764
Larrue V, von Kummer RR, Muller A, Bluhmki E (2001) Risk factors for severe hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: a secondary analysis of the European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study (ECASS II). Stroke 32(2):438–441
Kimura K, Iguchi Y, Yamashita S, Shibazaki K, Kobayashi K, Inoue T (2008) Atrial fibrillation as an independent predictor for no early recanalization after IV-t-PA in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci 267(1–2):57–61
Murao K, Bodenant M, Cordonnier C, Bombois S, Henon H, Pasquier F, Bordet R, Leys D (2013) Does pre-existing cognitive impairment no-dementia influence the outcome of patients treated by intravenous thrombolysis for cerebral ischaemia? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2013-305281
Leys D, Cordonnier C (2012) rt-PA for ischaemic stroke: what will the next question be? Lancet 379(9834):2320–2321
Bluhmki E, Chamorro A, Davalos A, Machnig T, Sauce C, Wahlgren N, Wardlaw J, Hacke W (2009) Stroke treatment with alteplase given 3.0–4.5 h after onset of acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS III): additional outcomes and subgroup analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 8(12):1095–1102
The NINDS t-PA Stroke Study Group (1997) Generalized efficacy of t-PA for acute stroke. Subgroup analysis of the NINDS t-PA Stroke Trial. Stroke 28(11):2119–2125
Frank B, Fulton R, Weimar C, Shuaib A, Lees KR (2012) Impact of atrial fibrillation on outcome in thrombolyzed patients with stroke: evidence from the Virtual International Stroke Trials Archive (VISTA). Stroke 43(7):1872–1877
Zhang JB, Ding ZY, Yang Y, Sun W, Hai F, Sui XN, Li XY, Wang HZ, Wang XT, Zheng JL (2010) Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischemic stroke patients with atrial fibrillation. Neurol Res 32(4):353–358
Sung SF, Chen YW, Tseng MC, Ong CT, Lin HJ (2012) Atrial fibrillation predicts good functional outcome following intravenous tissue plasminogen activator in patients with severe stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(7):892–895
Seet RC, Zhang Y, Wijdicks EF, Rabinstein AA (2011) Relationship between chronic atrial fibrillation and worse outcomes in stroke patients after intravenous thrombolysis. Arch Neurol 68(11):1454–1458
Kimura K, Iguchi Y, Shibazaki K, Iwanaga T, Yamashita S, Aoki J (2009) IV t-PA therapy in acute stroke patients with atrial fibrillation. J Neurol Sci 276(1–2):6–8
Tu HT, Campbell BC, Christensen S, Collins M, De Silva DA, Butcher KS, Parsons MW, Desmond PM, Barber PA, Levi CR, Bladin CF, Donnan GA, Davis SM (2010) Pathophysiological determinants of worse stroke outcome in atrial fibrillation. Cerebrovasc Dis 30(4):389–395
Sanak D, Herzig R, Kral M, Bartkova A, Zapletalova J, Hutyra M, Skoloudik D, Vlachova I, Veverka T, Horak D, Kanovsky P (2010) Is atrial fibrillation associated with poor outcome after thrombolysis? J Neurol 257(6):999–1003
Saposnik G, Gladstone D, Raptis R, Zhou L, Hart RG (2013) Atrial fibrillation in ischemic stroke: predicting response to thrombolysis and clinical outcomes. Stroke 44(1):99–104
Jovanovic DR, Beslac-Bumbasirevic L, Budimkic M, Pekmezovic T, Zivkovic M, Kostic VS (2009) Do women benefit more from systemic thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke? A Serbian experience with thrombolysis in ischemic stroke (SETIS) study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111(9):729–732
Bodenant M, Leys D, Debette S, Cordonnier C, Dumont F, Henon H, Girot M, Lucas C, Devos D, Defebvre L, Deplanque D, Leclerc X, Bordet R (2010) Intravenous thrombolysis for acute cerebral ischaemia: comparison of outcomes between patients treated at working versus nonworking hours. Cerebrovasc Dis 30(2):148–156
Cordonnier C, Girot M, Dorp E, Rimetz P, Bouillaguet S, Henon H, Lucas C, Godefroy O, Leys D (2000) Stroke units from scientific evidence to practice: the experience of the Lille stroke unit. Cerebrovasc Dis 10(Suppl 4):17–20
Leys D, The members of the Lille stroke program (1997) Misdiagnoses in 1250 consecutive patients admitted in an acute stroke unit. Cerebrovasc Dis 7:284–288
Bogosavljevic V, Bodenant M, Beslac-Bumbasirevic L, Cordonnier C, Jovanovic DR, Budimkic M, Leys D (2011) Intravenous thrombolysis for acute cerebral ischemia in Belgrade, Serbia: comparison with Lille, France. Eur Neurol 66(1):30–36
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group (1995) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. New Engl J Med 333:1581–1587
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24(1):35–41
van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19(5):604–607
Bendel R, Afifi A (1977) Comparison of stopping rules in forward regression. J Am Stat Ass 72:46–53
Glantz S, Slinker B (1990) Primer of applied regression and analysis of variance. McGraw Hill, New York
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A, Ford GA, Grond M, Hacke W, Hennerici MG, Kaste M, Kuelkens S, Larrue V, Lees KR, Roine RO, Soinne L, Toni D, Vanhooren G (2007) Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study (SITS-MOST): an observational study. Lancet 369(9558):275–282
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A, Hacke W, Millan M, Muir K, Roine RO, Toni D, Lees KR (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3–4.5 h after acute ischaemic stroke (SITS-ISTR): an observational study. Lancet 372(9646):1303–1309
Hill MD, Buchan AM (2005) Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: results of the Canadian Alteplase for Stroke Effectiveness Study (CASES). CMAJ 172(10):1307–1312
Koga M, Shiokawa Y, Nakagawara J, Furui E, Kimura K, Yamagami H, Okada Y, Hasegawa Y, Kario K, Okuda S, Endo K, Miyagi T, Osaki M, Minematsu K, Toyoda K (2012) Low-dose intravenous recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator therapy for patients with stroke outside European indications: stroke acute management with urgent risk-factor assessment and improvement (SAMURAI) rtPA Registry. Stroke 43:253–255
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Davalos A, Guidetti D, Larrue V, Lees KR, Medeghri Z, Machnig T, Schneider D, von Kummer R, Wahlgren N, Toni D (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 359(13):1317–1329
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, Toni D, Lesaffre E, von Kummer R, Boysen G, Bluhmki E, Hoxter G, Mahagne MH et al (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274(13):1017–1025
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, Larrue V, Bluhmki E, Davis S, Donnan G, Schneider D, Diez-Tejedor E, Trouillas P (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet 352(9136):1245–1251
Meretoja A, Putaala J, Tatlisumak T, Atula S, Artto V, Curtze S, Happola O, Lindsberg PJ, Mustanoja S, Piironen K, Pitkaniemi J, Rantanen K, Sairanen T, Salonen O, Silvennoinen H, Soinne L, Strbian D, Tiainen M, Kaste M (2010) Off-label thrombolysis is not associated with poor outcome in patients with stroke. Stroke 41(7):1450–1458
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to those who contributed to the collection of data and follow-up of the patients: Ivana Berisavac, Anne-Marie Bordet, Stéphanie Debette, Dominique Deplanque, Frédéric Dumont, Marko Ercegovac, Marie Girot, Hilde Hénon, Catherine Lefebvre, Christian Lucas, Costanza Rossi, Olivera Savic, Predrag Stanarcevic, Maja Stefanovic-Budimkic.
Conflicts of interest
Charlotte Cordonnier and Didier Leys have been investigators for the ECASS3 trial. The other authors declare no disclosure in relation with this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padjen, V., Bodenant, M., Jovanovic, D.R. et al. Outcome of patients with atrial fibrillation after intravenous thrombolysis for cerebral ischaemia. J Neurol 260, 3049–3054 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7119-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7119-4